![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
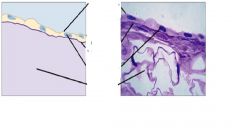
|
Simple squamous epithelial tissue
Lungs |
|
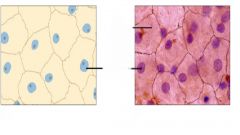
|
Simple squamous epithelial tissue
(superior view) |
|

|
Simple cuboidal epithelial tissue
Kidneys (tubules) |
|
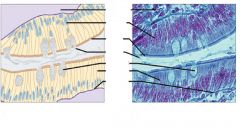
|
Simple columnar epithelial tissue small intestine |
|
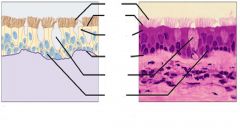
|
Pseudostratified (ciliated) columnarepithelial tissue
trachea lining |
|
|
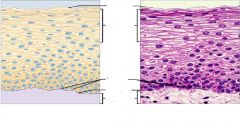
Stratified squamous epithelial tissue mouth lining |
|

|
Stratified cuboidal epithelial tissue salivaryglands, sweat glands |
|
|
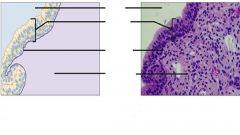
Stratified columnar epithelial tissue malereproductive tract |
|

|
Transitional epithelial tissue empty bladder |
|

|
Transitional epithelial tissue
distended (full) bladder |
|
|
Simple |
one layer |
|
|
Stratified |
more than one layer |
|
|
Pseudostratified
|
False layered |
|
|
Squamous |
flat |
|
|
Cuboidal
|
Cube |
|
|
Columnar |
column (rectangular) |
|
|
Transitional |
ability to change shape |
|
|
IntegumentarySystem |
Forms the external body covering, and protects deeper tissues from injury. Synthesizes vitamin D, and houses cutaneous (pain, pressure, etc.) receptors and sweat and oil glands. |
|
|
SkeletalSystem |
Protects and supports bodyorgans, and provides a frameworkthe muscles use to cause movement.Blood cells are formed within bones.Bones store minerals.
|
|
|
Muscular System |
Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression. Maintains posture, and produces heat. |
|
|
NervousSystem |
As the fast-acting control system of the body, it responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands
|
|
|
Endocrine System |
Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells. |
|
|
CardiovascularSystem |
Blood vessels transport blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes, etc. (The heart pumps blood ) |
|
|
Lymphatic System/Immunity
|
Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood. Disposes of debris in the lymphatic stream. Houses white blood cells (lymphocytes) involved in immunity. The immune response mounts the attack against foreign substances within the body.
|
|
|
RespiratorySystem |
Keeps blood constantlysupplied with oxygen and removes carbondioxide. The gaseous exchangesoccur through the walls of the air sacs of the lungs |
|
|
DigestiveSystem |
Breaks down food intoabsorbable units that enter the bloodfor distribution to body cells.Indigestible foodstuffs are eliminatedas feces. |
|
|
UrinarySystem
|
Eliminates nitrogenouswastes from the body. Regulates water,electrolyte and acid-base balance of the blood.
|

