![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Breed |
group of animals possessing certain characteristics/traits common to the individuals w/in the group that distinguish them from other groups of animals w/in same species -traits can be genetically transferred -hundreds exist -new breeds being developed |
|
|
how are breeds developed? |
Selection & Mating -choosing animals w/specific characteristics and mating them to produce desired outcomes -ex: feather color, hair color, body conformation/anatomical features |
|
|
why are breeds developed? |
1. original objective -serve specific purpose (meat, milk, transportation, power) 2. improve and standardize animals -animals assume particular form and/or perform certain function 3. human curiosity and pleasure |
|
|
breed differences are genetic differences |
differences occur among and w/in breeds -may originate from a different group of ancestors -humans selected & mated individuals for different purposes -genetic drift over time and geography |
|
|
new breeds |
result from selection of specific trait that was discovered in an existing breed -ex: munchkin cat, mini horses result from crossing existing breeds to capitalize on strengths of each parent breed -santa gertrudis cattle, labradoodle |
|
|
pedigree |
record of an individual's ancestry -includes names and registration numbers of animal and ancestors -may include production or performance data
|
|
|
Registry and Breed Associations |
-established in 1800's for many breeds -started as groups of breeders who cooperated to improve breeds, preserve purity, and promote interests of animal producers -today there's worldwide organizations w/executive branches and thousands of members -compile & issue breeding records -adopt and promote perfection standards -provide rules for admission and registry |
|
|
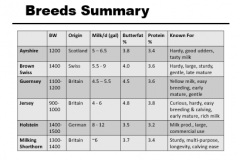
Ayrshire |
-medium sized -first imported into US from County of Ayr in Scotland around 1833 -for use in rocky, hilly areas of New England -efficient grazers -superior udder quality: strongly attached evenly balanced, well-shaped -color: light to deep cherry red, mahogany, brown, or a combo of these w/white, or white alone -strong, robust -show vigor, symmetry, style and balance -mature cows - 1200 lb |
|
|
Ayrshire Picture |

|
|
|
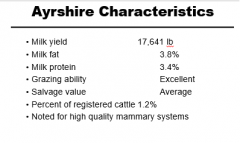
Ayrshire Characteristics |
|
|
|
Brown Swiss |
-one of oldest in world -came to US from Switzerland in 1869 -moved w/settlers & traders across US -color: solid brown varying w/light to dark; nose, tongue and tail are black -strong legs, long life, milking persistency -quickly adapt to dif. environments -mature cows - 1500 lbs |
|
|
Brown Swiss Picture |
|
|
|
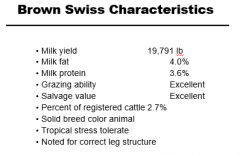
Brown Swiss Charactersitics |
|
|
|
Guernsey |
-developed by Normandy monks on isle of Guernsey; came to US in 1831 -milk = distinct golden brown color -color: shade of fawn w/clear white markings skin has golden yellow pigmentation clear muzzle favored over smoky/black muzzle -mature cow is 1100 lbs |
|
|
Guernsey Picture |
|
|
|
Guernsey Characteristics |

|
|
|
Holstein |
-originated from Netherlands & Northern Germany -second oldest of pure dairy breeds -came to US from Holland in 1621 -black and white, some can be red and white -produce most milk on average -largest breed of dairy cows -mature cows weight 1400-1500 lbs |
|
|
Holstein Picture |

|
|
|
Holstein Characteristics |

|
|
|
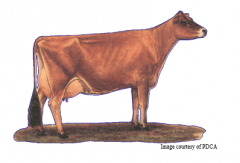
Jersey |
-came to US from Isle of Jersey in English Channel in 1850's -more efficient than some larger-bodied breeds -smallest out of the dairy breeds -produce more lbs of milk per lb of body weight than any other breed -produce milk w/highest butterfat & protein content color: shade of fawn of cream w/black muzzles -mature weight - 1000 lbs |
|
|
Jersey Picture |
|
|
|
Jersey Characteristics |

|
|
|
Milking Shorthorn |
-originated in Northeastern England; came to US in 1783 -served triple purpose - meat, milk, labor -color: either red, red & white, or roan -have deep chest, deep long well-sprung ribs, strong loin, level rump, capacious udder & straight legs -mature weight - 1200 lbs |
|
|
Milking Shorthorn Picture |

|
|
|
Milking Shorthorn Characterstics |

|
|
|
Breeds Summary |
|
|
|
Other Breeds |

|

