![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Minerals |
minerals are substances found in food that your body needs for growth and health. There are two kinds of minerals: macrominerals and trace minerals. Macrominerals are minerals your body needs in larger amounts. |
|
|
Sodium's Function |
Regulation of osmotic pressure and pH in an animals body fluid |
|
|
Cobalt function |
Structural component of vitamin B12 |
|
|
Iodine function |
Component of thyroid hormone |
|
|
Iron |
Essential constituent of hemoglobin in the blood and myoglobin in muscle tissues |
|
|
Vitamins |
Organic substances required by animal tissuses in very small amounts |
|
|
Vitamin A function |
Helps vision and maintainig the epithelial cells |
|
|
Vitamin D function |
Involved in calcium absorption and bone deposition |
|
|
Vitamin E function |
Metabolic antioxidant |
|
|
Vitamin K function |
Required for normal blood clotting |
|
|
When is the best time to cut legumes or grass to make hay |
When the blooms first begin to appear |
|
|
3 steps to making hay |
Cutting Curing Storing |
|
|
Pasture |
An improved or unimproved plant material on land areas where animals graze |
|
|
Green chop |
Herbage that has been cut and chopped in the field and fed fresh to live stock in confinement |
|
|
Silage |
Chopped plant material that has been fermented |
|
|
Haylage |
Silage that contains less than 50% moisture |
|
|
How to make silage |
Plant materials are ensiled under anaerobic condition. It is then undergoes controlled fermentation thst produces acid which kills off bacteria/mold ect. It is then packed tightly into bunker silos or upright silos to keep its optimal dryness of 30-45% |
|
|
What is the ideal pH of silage |
Atmost 4.2 |
|
|
Corn characteristics |
Corn can ether be ground, cracked or rolled |
|
|
Sorghum or milo |
Small round, relatively hard seeds |
|
|
Batley grain |

Brown seeds |
|
|
Advantage of molasses |
Maximize rumen productivity, reduce dust, aid pellet quality and serve as medium for feeding medication |
|
|
Disadvantages of molasses |
Can create problems with mixing and equipment handling at the feed mill |
|
|
Whats kelp meal made from |
Seaweed |
|
|
Protien quality |
Measure of how much the amino acid content of a protien supplement resembles the amino acid requirements of the animal to be fed |
|
|
Plant source of protien supplements |
Oilseeds Cotton seeds Soybean meal |
|
|
Names of oilseeds |
Canola Linseed Peanut Sunflower Safflower meals |
|
|
Animal protien source |
Blood meal Feather meal Meat meal |
|
|
Non nitrogen protien supplements |
Urea Biuret |
|
|
Distillery and Brewery by-products |
Distillers dried grain Brewers dried grain Corn gluten meal |
|
|
Buffers |
Added to counter act acid generated by ruminal fermentation of grain |
|
|
Antioxidants |
Added to a fourth of feeds to protect polyunsaturated fats from oxidative rancidity |
|
|
Hormones |
(Synthetic steriods) improves feed efficiency and rate gain and manipulates estrous cycle to control animals heat cycle |
|
|
Antibiotics and chemotherapuetic agents |

|
|
|
Direct fed microbials and probiotics |
Microbes that aid in esthablishing a healthy microbiota composition in the animals intestines |
|
|
Yeast and yeast culture |
Stimulatie the growth of specific types of bacteria that utilize lactic acid |
|
|
Enzymes |
Are produced by animals and microbes that inhabit the digestive system |
|
|
Mold inhibitors and mycotoxin binders |
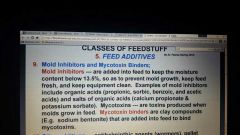
|
|
|
Instrument used to sample grain |
Grain probe |
|
|
Instrument used to sample hay |
Core sampler |
|
|
How to determine ash content |
(Wt of crucible+ash)-wt of crucible ÷ ×100 Wt of sample |
|
|
Parts of a soxgelt apparatus |
Extractor(holds sample) Condenser(cooling and condensing vapor) 250ml flask |
|
|
Equation for crude protien |
Nitrogen content × 6.25 |
|
|
Ether extract equation |
(Wt of flask+extract)-wt of flask ÷ ×100 Wt of sample |
|
|
Nitrogen free extract equation |
100-(%moisture+%CF+%CP+%EE+%Ash) |
|
|
Equipment used to find energy content in feedstuff |
Oxygen bomb calorimeter |
|
|
Calorie |
Heat required to raise temp of 1g of water 1c |
|
|
Gross energy |
Amount of heat produced when feed is completely oxidized |
|
|
Digestible energy |
Amount of energy absorbed after its been consumed and digested |
|
|
Metabolize energy |
Net energy avalible to an animal after the utilization of some energy in the process of digestion and absorption |
|
|
Total digestible nutrients |
Method to estimate engery content of feed |
|
|
Net energy |
Energy available to ingester for metabolic purposes |

