![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
oxytocin gene knock out mice |
can't remember with which females they've interacted |
|
|
Fox B knock out mice |
don't coll their pups to warm them |
|
|
social amnesia |
due to loss of oxytocin gene. when they forget who they have interacted with previously |
|
|
oxytocinergic neurons have cell bodies in the _____ that project to the _______ to ________ |
hypothalamus, pituitary, release oxytocin into blood |
|
|
nucleus accumbens |
reward seeking behavior. oxytocin is also released here |
|
|
inland snakes eat |
fish and frogs |
|
|
coastal snakes eat |
banana slugs |
|
|
how was the question "will inland snakes eat slugs if they are presented" tested |
tested by taking pregnant females from coastal and inland snakes and raised them in identical conditions and isolated them from a lot of cues. Then they gave them freshly cut slugs everyday. inland snakes did not see the thawed slugs as food. They also let baby snakes dip their tongue in tadpole solution and a slug solution. coastal snakes viewed the slug solution as food, but inland didn't. Suggests that this is from genes, and not learned |
|
|
artificial selection example |
size of nest from house mice |
|
|
house mice nest size experiment |
artifically selected a high, control, and low line of nest builders. bred for 15 generations and found that if high nest builders were bred together with the other highest nest builder, then their childrens nest got continually bigger and the opposite was found for low nest builders |
|
|
polyphenism |
poly- many, phen- phenotype polyphenism- many behaviors |
|
|
developmental homeostasis |
throughout development, we tend to seek the average for certain traits in our features. Harlow experiment is an example because it showed that the monkeys wanted a basal level of socialization in order to develop normally. |
|
|
Australian Brush Turkey |
don't need any interactions with parents or other animals in the species. Males scrape together a huge mound for a nest so the female can lay eggs in it. bigger nest attracts females better. Mound keeps eggs warm. Father isn't around when chicks hatch. Recognize same species because they all make the same pecking motion. |
|
|
How are cowbirds a brood parasite |
lays eggs in other birds nests and push out other eggs. Yells a lot which shows pink rhomboid which makes the mother make a releasing mechanism to feed it. It is a lot bigger so it can get more food from the mother. Don't have strong imprinting mechanisms, but recognizes precopulatory pose from males so can recognize it's own species |
|
|
reproductive advantages of developmental homeostasis are particularly great in species that choose mates based on _______ like the ______. Why is this |
symmetry, barn swallow. this is because stress or nutritional deficiencies lead to less symmetry in adulthood then the others. |
|
|
barn swallow |
female barn swallows prefer males with very long symmetrical outer tail feathers. |
|
|
brush legged wolf spiders |
rely on symmetry and size of legs to attract females. Preform a mating dance to attract females where they wave around their legs to show how symmetrical and large they are |
|
|
highly canalyzed phenotype |
there are less variation between members of the species (bell curve) |
|
|
tiger salamanders |
if food is lacking, some will become canibalistic and others will remain in the larval stage. Example of food-induced polyphenism |
|
|
male cichlids |
example of socially induced polyphenism. males can either become really colorful if they are dominant, but if they are subordinant, they will remain plane |
|
|
aphids "soldier caste" |
example of predator induced polyphenism. if there are a lot of predators, this can change their phenotypes. Some aphids become soldier caste where they develop strong arms to become a guard |
|
|
if a cichlid is given more Gonadotropin-releasing hormone, what will happen |
more sex steroids will be released which leads to more aggression, maturation of gonads, and more color and black "eyebar" appearance. |
|
|
subordinant male cichlids show an increase in ______ during __________ |
egr-1. During the transmission to dominant and then later on it will decline. Shows neuroplasticity happening |
|
|
male thynnine wasps |
Females release sex pheromones to attract males. Orchids have evolved to serve as a female decoy where they look like the female and emit odors that mimic wasp sex pheromones. This males males go to them to copulate. This enhances orchid pollination. Wasps know this, so they have learned not to go near the plant. This shows spatial learning in the wasps |
|
|
What was the experiment to evaluate spatial learning in male thynnine wasps |
they had an orchid and measured the number of visits by the wasp to the plant over time. Found that the wasp was able to learn not to got there. Then they added a female, but the wasp still wouldn't go there because it had learned that when there was something that looked like a female and the scent on that particular orchid, that it was nothing |
|
|
learning abilities among members of the crow family experiment |
different types of birds were trained to remember a location of a circle on a screen. the amount of time they retained this information was tested (retention interval). found that clark's nutcrackers by far remembered the circle the best. In non spatial tasks, however, the clark's nutcracker falls about in the middle of the pack. |
|
|
spatial learning differences in meadow vole and prairie vole experiment |
polygynous male meadow voles roam a huge area, whereas monogamous prairie voles have small area. Looked at sex differences between the two in a maze and found that in meadow voles, males out preformed females and made less errors in the maze because they roamed more, but in prairie voles, they were about the same because males and females roamed about the same. |
|
|
sex differences in hippocampal volume example |
female cowbirds have a larger hippocampus than males. This isn't shared with blackbird or grackle so is something with that species. suggests that females have more difficult task to remember where to find nests to lay eggs. |
|
|
operant conditioning |
type of instrumental learning (by skinner) in which animals can make choices in a box and then are rewarded or punished |
|
|
associative learning is limited by |
the natural environmetnal conditions in which an animal has evolved. If you are doing a taste aversion with a mouse and give them a foot shock, they won't learn it because there isn't anything in their natural environment that would teach them that |
|
|
why can't vampire bats form learned taste aversions compared to other kinds of bats |
because bats go after blood from alive animals, which means that it probably isn't going to have toxins. In experiments where the bat is injected with either saline, a toxin, or a delayed toxin, insectivorous bats learned quickly, but vampire bats did not |
|
|
cane toad history |
introduced to australia where they didn't have any natural predators and thrived. Released bufotoxin which is a type of catecholamine that leads to increased heart rate, salivation, hallucination, paralysis, and death. This lead to the endangerment of the Quoll. |
|
|
grasping behavior |
a type of complex response to a simple stimuli generated by the nervous system where male toads will mount anything with the shape of a female (like a toe of a boot) |
|
|
centris pallida |
a type of bee that does the same type of grasping behavior that the toad does to a simple stimuli (roundedness which is shape of female) |
|
|
fixed behavior |
occur in response to a simple stimuli. Produce predictable responses and allow optimal behaviors with limited experience |
|
|
fixed behavior bull gull chicks |
begging behavior. pecking in response to red dot. This was tested by measuring how much baby gull chicks would peck to either a normal looking head, just the beak, a head without the red dot, or just the red dot. Found out that just the red dot was the releaser that caused the begging behavior. Did another study and found that really what they are paying attention to is contrast in the dot |
|
|
innate releasing mechanism |
the neural network that can detect a simple cue (releaser) and activate an instinct (fixed action potential) |
|
|
what enables bill spots to be big and have high contrast |
dietary carotenoids (antioxidants) found in food. They did a study where they took birds from crude oil places and birds with good nutrition and looked at size of dot. |
|
|
instinct theory |
developed by Niko Tinbergen and Konrad Lorenz. states that simple stimuli activate or release complex behaviors. |
|
|
code breaking |
when species exploit other species fixed action pattern (cowbird) |
|
|
bolas spider deception |
have a little sticky globul at the end of them that it uses as a laso to reel in prey (moth species). The globule releases pheromones to attract male moths depending on which moths are most popular at the moment. |
|
|
wasps and caterpillar deception |
wasps lay eggs in caterpillar bodies by tricking the red ants that guard the caterpillars. the caterpillars trick the ants to take care of them by making the same noise as the queen and releasing queen ant pheromones. When wasps fly in, it releases it's own pheromones which cause the ants to be disregulated. This lets the wasps insert eggs into the caterpillar to give the eggs a source of nutrition while developing. |
|
|
Where are A1 and A2 located in the moth |
in the thorax |
|
|
A1 and A2 |
sensory neurons that interact with interneurons to convey information to motor neurons. These cause excitation of muscles which lead to the wing. Mechanical stimulation causes action potentials, and the interneurons that cross over the body. |
|
|
Which audio center is most sensitive |
A1. A low intensity sound doesn't lead to action potentials in Aw, but does for A1. it increases it's firing with increased intensities. |
|
|
When does A2 fire |
only among high intensity sounds. Adds complexity to MCc phonoresponse |
|
|
A1 receptors are very sensitive to _____ but not as sensitive to _____ |
pulses, constant sound (it habituates) |
|
|
terminal buzz |
sound the bat makes to determine exactly where the moth is |
|
|
what are the three hypothesis for ultrasonic clicks from the moth |
1. disrupts the bats first attack, then may learn to ignore the ultrasonic click, i.e. causes startle response (nope) 2. bats will hear the click, and this will serve as a taste indicator that moth is poisonous (nope) 3. Clicks jam the bat's radar with beams of high frequency sond that interfere with echo- location |
|
|
tymbal |
produces the clicks in the moth. |
|
|
cricket mating preferences |
island female crickets are less choosy about their mates because their are less mates to choose from. Research shows that island females, compared to mainland females, are way more likely to select a male that is not capable of making any sound (flatwing males) |
|
|
tungara frogs |
female tungara frogs and fringe-lipped bats prefer males who have "chucks" in their mating calls, male frogs adapt to give chuck-less whining calls in areas of high bat predation. |
|
|
where are cricket ears |
on the forelegs. they are ultrasound sensitive sot hey are able to hear bat cries |
|
|
effect of activating the interneurons in the cricket |
leads to bending of the cricket abdomen and which way it depends on pitch of sound. a sound coming from the same side could bend either way depending on frequency. Low frequency causes the cricket to bend towards the source and high frequency means predator (bat) so they bend away from sound. |
|
|
tests to determine if int-1 cells are part of the circuit to guide responses to sound in crickets |
experimentally inactivated int-1 neuron and measured response to 40 kHz (didn't attempt to steer away from stimulus)
Experimentally activate int-1 neurons and measured response (change body orientation by bending abdomen)
decapitated cricket to see if brain is involved and measured response (didn't attempt to steer away)
This tells us that int-1 neurons are critical for regulating ability to hear. |
|
|
escape behavior by sea slugs |
bend by contracting dorsal and ventral muscle |
|
|
S cells |
release glutamate in the sea slug which activates the glutamate receptors on the Trigger Type 1 (Tr1) and the dorsal Ramp Interneuron (DRI). DRI sends excitatory signals to DSI (dorsal swim interneurons). activates dorsal flexion neuron and inhibits ventral flexion neuron and then switches. Activated glutamate receptors admit sodium which can lead to an action potential. |
|
|
male plainfin midshipman fish |
use CPG in muscles that cause singing. causes contraction and relaxtion in sonic muscles which make a drum like sound. Sonic muscle hits the swim bladder isn't where urine is, but is a bladder filled with air that helps to maintain bouyancy |
|
|
photophores |
male plainfin midshipman create light to attract prey |
|
|
sonic motor nuclei |
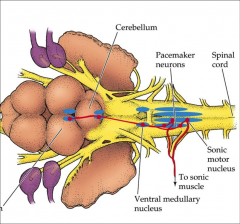
controls the sonic muscles in the plainfin midshipman. Series of activation is the mesencephalon to the cerebellum to the ventral medullary nucleus (which coordinates movement on both sides) to the pacemaker neurons (which set the firing rate for the sonic motor nucleus) |
|
|
what alters neurons during mating season for midshipman fish |
androgens and estrogens. Females is attracted and will lay their eggs which the male will protect. Two different forms of males that vary in size. singing is better in the bigger phenotype (type I) and poor in sneaker phenotype (type II) which sneaks into the puddle of the other phenotype and mate with females there and singing phenotype doesn't mind because they think they are females. Sometimes called sexual parasite |
|
|
stimulus filtering |
selective sensitivity to environmental cues. Female midshipman are only attracted to type I song because of hormones present which intensify auditory sensitivity. they have lower thresholds than noon-reproductive females suggesting they can hear more |
|
|
tympanum |
thin flexible sheet of cuticle over ear of moth |
|
|
electrical synapse |
gap junctions allow ions to move directly between cells (fast/ coupled response).. A1/A2 are electrical synapses |
|
|
which appendage is the most sensitive in star nosed mole |
11 |
|
|
How many appendages does a starnosed mole have and what is on each appendage |
it has 22 and there are eimer's organs on the appendages which are little dots that increase surface area. each eimer's organ has sensory cells that respond to mechanical deformation of skin |
|
|
how quick can a star nosed mole decide if it wants to eat something |
less than 25 ms |
|
|
somatotopically arranged |
there is a tactile map on the cortex that corresponds to areas of the nose |
|
|
somatosensory cortex is responsible for sending out ____ commands |
motor |
|
|
ascending sensory tract |
a relay of 3 neurons which convey touch information. |
|
|
skin acuity |
sensitivity for skin. |
|
|
what is skin acuity based on |
receptor density (brain space devoted to the region) and receptive field size (smaller is more accurate) |
|
|
UV reflection in avian species |
helps to determine sex. this is why male blue throat's feathers are blue and gouldian finch have bright colored necks. |
|
|
UV reflectance in reptiles |
females prefer males with more UV reflectance. UV reflectance is generally a patch inside the mouth that when they open their mouth can be seen. UV light also helps to win fights and is suspected that it helps the reptiles absorb nutrients (why you should always have UV lights when housing reptiles) |
|
|
polarity in monarchs |
they attend to the sunlight's polarity when migrating for the winter |
|
|
what do sea turtles use for their migration |
earth's magnetic field |
|
|
brominating |
huddling together in groups which help to keep snakes warm. |
|
|
what drives male ring doves courting behavior |
testosterone |
|
|
what is male ring dove courting behavior |
aggressive chasing, strutting, bowing to the female |
|
|
what drives nest soliciting in male ring doves |
17-beta estradiol (E2) |
|
|
what do female ring doves pay attention to |
nest soliciting activities. Basically ignore the courting behavior. |
|
|
what happens in male ring doves if aromatase is given |
testosterone can't be converted so the males can't do the nest orienting behavior. Therefore, no mating |
|
|
what controls the behavior in preying mantis to strike when prey is within reach |
ganglia, especially in the first thoracic ganglia. |
|
|
what was the result when they cut the link between the first thoracic ganglion and the subesophageal ganglion |
animal couldn't move |
|
|
what were the results when they cut the connection between the protocerebral ganglion and the subesophageal ganglion |
the limbs were walking constantly. this suggests that the subesophageal gnalion is probably constantly excitatory and the rpotocerebrral gnalion is inhibiting it |
|
|
what happens when you decapitate a male preying mantis |
it forms a repetitive circle. this is because the female will decapitate the male if under nutritional stress, but it still needs to finish the job |
|
|
what was the result when they cut the ganglion connection to the rest of the nervous system |
can't strike, but if electrically stimulated restores complete striking motion |
|
|
blowfly |
has sensory cells on feet that help them to find liquids to drink. once the midgut is full, it puts food into the crop. when that is full, it sends signals to the brain to stop eating (recurrent nerve). if you cut this nerve, it eats till it blows. |
|
|
teleogryllus crickets |
notcturnal, males call at night. start chirping about 16 hours apart, unless the sun tells them otherwise. This is an example of internal schedule based on enviromental cues |
|
|
entrained response |
the environment synchonizes the clock |
|
|
free-running cycle |
length of period deviates from the earth's 24 hour cycle |
|
|
what happens when the connection between the eyes and the optic lobes were severed in crickets |
they had a free-running circadian cycle instead meaning it was absent of environmental cues. |
|
|
what happened when they separated optic lobe from the rest of the brain in crickets |
the crickets call anytime (day or night). this suggests that the master clock mechanism resides in the cricket's optic lobes |
|
|
master clock in vertebrates |
suprachiasmatic nucleus |
|
|
syncytium |
neurons in the hypothalamus that are connected through gap junctions so that they fire together as one big cell. |
|
|
suprachiasmatic nucleus leasions in hamsters leads to |
disruption of clock functions making them very whenever instead of just at night. |
|
|
pacemaker cell for circadian rhythm |
suprachiasmatic nucleus |
|
|
naked mole rat |
live in huge colonies with a matriarch. live in dens similar to an ant maze. shows a brief episode of activity and scattered periods of inactivity. aren't exposed to light and don't have a period where they are being predated on more. No pattern was found in circadian rhythm. |
|
|
circannual |
things that occur about a year, every year |
|
|
test to assess circannual behaviors in squirrels |
blinded squirrels and watched them for multiple years without access to outdoor cues. found that when they tracked them throughout the years, they hibernated at about the same time and were active at about the same time. |
|
|
stonechat |
there are rainy seasons in spring that determines their reproductive cycle. when there aren't any outdoor cues, they still show a reproductive cycle but it becomes slightly shifted through the years. looked at testicular width to see how much the hormones were changing through the year. |
|
|
banner-tailed kangaroo rats |
foraging behaviors change over the lunar cycle. This is to avoid nocturnal predators. measured # visits to a feeder. |
|
|
white crowned sparrow |
copes with dramatic seasonal change. detects photoperiod length through their eyes. when put in summer solstace level of light, the testes grow dramatically. when there is more night time than day light (winter) their testes don't grow at all. by putting them in either long or short, or varying days, they found that there is a photosensitivity peak at around 16-20 hours that determine whether the gonads grow or not. |
|
|
crossbills |
feed on conifer seeds which are high year round so it can breed year round. there is still a minimum threshold of photoperiod length for hormonal changes to occur. Eat mostly during winter months. |
|
|
crossbill experiment |
took captive birds and held under natural photoperiods, but food and temp were the same. there was still an ebb and a flow of teste length with the photoperiod. |
|
|
3 basic mechanisms that structure behavior |
neural command centers communicate with one another, clocks schedule activity in neural command centers, hormonal systems respond to physical/ social environments to adjust priorities of competing command centers |
|
|
what determines infanticidal behavior in house mice |
the number of light/ dark cycles, not the 24 hour periods. |

