![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

|
Sarcomeres |
|
|
|
True or false? the attachment of myosin to the binding sites on the actin molecule. |
FALSE |
|
|
|
What is attached to M lines in a sarcomere? |
Myosin tails |
|
|
|
What changes shape during contractions of a sarcomere? |
Myosin heads |
|
|

|
d) |
|
|

|
e) |
|
|

|
c) |
|
|
|
All animals are capable of movement. True or False? |
True |
|
|

|
Homeostasis!!!! |
|
|

|
Blood |
|
|
|
The similar fusiform body shape of diverse animals, such as sharks, penguins, and aquatic mammals has evolved because... |
This is the body shape that makes it possible for aquatic animals to swim rapidly. |
It's not because of a common ancestor. |
|
|
Some animals suppress their immune functions during times of reproduction. |
It is not d or e |
|

|
C |
|
|
|
B) Positive feedback's responses are in the same direction as the initiating stimulus rather than opposite to it. |
|
|
|
Define the term: fertilization |
The joining of haploid gametes to form a diploid zygote. |
|
|
|
The cavity inside the blastula is called the... gastrula, blastomere, or blastocoel? |
BLASTOCOEL!!!!!!! |
|
|
|
The formation of the fertilization envelope and the slow block to polyspermy are dependant on the (entrance?/departure?) of *** ions (into?/from?) The egg. |
...on the ENTRANCE of CALCIUM ions INTO the egg. |
|
|
|
Heterotrophic? |
Obtains energy and nutrients from other organismes. |
|
|
|
How does function influence structure? |
EVILUTION!!! it aint functioning? That structure's not fit! Only the fittest survive!!!!! 🐩🐈🐏🐀🐥🐄🐸🐸 |
|
|
|
Acrosome! WHAT DOES THIS MEAN?? |
Magic tidbits in the head the sperm (hydrolytic enzymes) that are released and eat a hole in the jelly coat of the egg (acrosomal reaction) and protiens that bind to receptors under that jelly coat. (Acrosomal process) 😜 |
|
|
|
What the heck is POLYSPERMY? IS THAT EVEN A WORD!?? (It is) |
When sperm and egg plasmas fuse good ol slow block to POLYSPERMY stop other sperms from fertalizing the egg. 😲 |
|
|
|
Perivitelline space is what? |
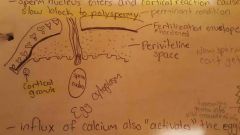
The space between FERTILIZARION ENVELOPE and the egg. Too lazy to explain further observe doodle |
|
|
|
If you injected an unfertilized egg with calcium what would happen? |
The egg would activate but there is no sperm so no embryo 🚫👪no baby❎ no further development. yall just got that eggs hopes up |
|
|
|
Zygote becomes Blastula! How? What makes a Blastula different? Which is bigger? |
CLEAVAGE!!!! 🍑🍑🍑 Single cell becomes multi cellular and is the exact same size! 😲 |
|
|
|
💣🎆BLASTOCOEL!!! WHERE IS THAT??? |
The hollow cavity in the BLASTULA filled with fluid 💧🌊 |
|
|
|
ANIMAL POLE VS VEGETAL POLE 🐙🐘🐣💈 VS 🌽🌽🌾💈 |
Vegetal pole has more yoke 🍳 to feed the embryo and has bigger cells. Animal pole has less yoke and smaller cells |
|
|
|
Differential gene expression? ☺😑😬😉😎😘 |
All these cells in early development have the same genome so why would they do different things and look different? Well this fancy gene expression thingy means that cells in different locations are exposed to different signals so that determines there structure and behaviour. Like if you had a set of identical twins and one was raised by the Kardshians and the other by Duggars would they be the would they grow up to lead the same lives??? Be the smae person??? Probs no... |
|
|
|
Morphogenesis is word that means??? 😨 |
The rearrangement of cells or sheets of cells in the embryo! Ex: gastrulation (formation of germ layers), organogeniesis (formation of organs) |
|
|
|
What happens to the poles (animal/vegetal) during gastrulation? |
Vegetal hemisphere is pushed inward and will become the future endoderm. And the animal hemisphere stretches over the whole surface of the cell and will become the future ectoderm. |
|
|
|
During GASTRULATION the blastuocoel collapses. What is formed in its place? |
The ARCHENTERON 😈 (arch nemesis of the poor defeated blastocoel) is a new cavity that is formed that will eventually become the digestive track. 🍕🍝🍌 |
|
|
|
Apoptosis is when... |
😱🔫 programed cell death. The cells commit honorable suicide for the success of there kingdom. Let us take a moment to remeber the brave cells who dutifly died to bring us where we are today 😢. May the webbing between my fingers rest in peace. |
|
|
|
What the fudge is neurulation??? |
It is an example of organogenesis. Dorsal mesoderm forms the NOTOCHORD, ectoderm forms the NEURAL PLATE, which then becomes the NEURAL TUBE, which becomes the brain and spinal cord. |
|
|
|
What are neural crest cells?? |
Cells that develop between the ectoderm and the neural tube to separate them. |
|
|
|
Convergent extensions??? |
OOO OOO ➡ OOOOOOOO OOO Group of cells narrowing and elongating into a line(ish) shape |
|
|
|
Whats the major difference between endocrine and nervous signaling? |
Endo is chemical and nervous is electrical |
|
|
|
What is a glial cell??? |
The little cells surounding (and interwind with) neurons. They beforme housekeeping duties for the neurons such as nurishing them. |
|
|
|
What are the parts of a neuron?? |
Cell body that contain the nucleus, dendrites that come off the main cell body that receive electrical signals that pass throught the cell body, axon hillock then through the axon to pass on the signal to thr next neuron in the chain. |
|
|
|
Where are the synaptic terminals? What is the synapse? |
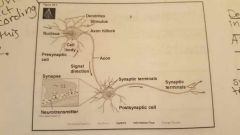
|
|
|
|
Ganglia what is it? |
Mass of cellular neurons in place of brains in some nervouse systems. Example of organisms with this kind of system would be a sea star or a leech * brainy animals have ganglia too as part of their peripheral nervouse system (PNS) which also includes cranial nerves and spinal nerves. |
|
|
|
Cephalization? |
The concentration of nervous tissues at the anterior end of body, forming head and brain. |
|
|
|
What is the central nervous system (CNS)? |
Brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
What are the three stages of information processing in the nervous system? |
Sensory input (from a sensor), integration, (performed by an effector) motor output |
|
|
|
What is a reflex reaction? |
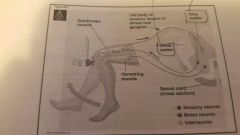
💃actions without requiring integration at the level of the brain. (Only travels to the spinal cord) |
|
|
|
How do endocrine cells get the message out? |
They secrete hormones into the blood steam affecting target cells to regulate physiology and behaviour |
|
|
|
What is the hypothalamus? 👾 |
Region of brain that consists of neural tissues. The master regulator of the endocrine system. Acts primarily through the pituitary glands. |
|
|
|
Fight or flight? Whats happening? |
Hypothalmus send signal to the Adrenal Gland and the adrenal mendella secretes EPINEPHERINE AND NOREPINEPHRINE. These hormones increase breathing and metabolic rate and decrease blood flow to non essential organs (like digestion not important in an imergency) |
|
|
|
Explain hydrophobic and hydrophilic in the context of hormones in the blood stream. |
Philic: water lovers, cant pass through membranes, connects to signal receptors on the membrane of target cell. Phobic: water hater, passes through membranes (lipid-soluble), connects to signal receptors in the target cell past the membrane. |
|
|
|
ANTAGONISTIC hormones?? |
Hormones whose actions oppose each other. Used together to keep homeostasis by the endocrine sysytem. |
|
|
|
Whats up with glucose and insulin? |
They are antagonistic hormones. We get glucose from food. If we get to much the pancrease releases insulin into the blood stream if they're isn't enough glucose the pancrease releases glucagon into the blood which the liver uses to make glucose to release in the blood. |
|
|
|
What is a Metabolic rate? What basal metabolic rate? |
Amount of energy per unit time. And basal metabolic rate (BMR) is how much energy is needed for homeostasis at rest. The BIGGER the animal the BIGGER the BMR. *it is the opposite for BMR per unit body mass |
|
|
|
Biosynthesis? ??? |
Multiple step process in which food bits are converted to more usable products in a living organism. |
|
|
|
Which cell gives off which chef cell or the parietal cell give pelsinogen and HCl |
Cheif gives pep Parietal gives HCl |
|
|
|
Salivary amalase is important for digesting.... pepsin os important for digesting.... |
Carbohydrates, proteins |
|
|
|
Who has the bigger cecum??? Herbivores or carnivores??? |
Herbies!!!! |
|
|
|
What hormones make us hungry or full? |
LEPTIN(longterm appetite) AND INSOLIN (hungry) |
|
|
|
Liver makes bile, gall bladder stores bile, bile released into duodenum to emulsifie fats. Is this a question? |
No just rember it im tired |
|
|
|
What are the 3 main parts of the small intestine?? |
Duodenum, jejunum, ileum |
|

