![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium)
|
1. epithelium
2. Mesothelia lining ventral body cavities; endothelia lining heart and blood vessels; portions of kidney tubules (thin sections of nephron loops); inner lining of cornea; alveoli of lungs. 3. Reduces friction; controls vessel permeability; performs absorption and secretion. |
|
|
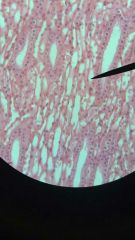
simple cubodial epithelium
|
1. Epithelium
2. Glands, ducts, portions of the kidney tubules, thyroid gland. 3.Limited protection, secretion, absorption. |
|
|
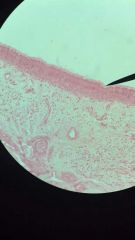
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
|
1. Epithelium
2. Lining of the nasal cavity, trachea and bronchi, portion of male reproductive tract. 3. Protection, secretion. |
same view just less magnification
|
|
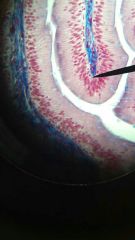
Simple Columnar Epithelium (amphibian)
|
1. Epithelium
2. Lining of the stomach, intestine, gallbladder, uterine tubes, and collecting ducts of kidneys. 3. Protection, secretion, absorption |
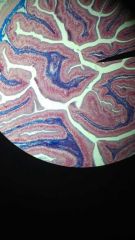
same pic just less magnified
|
|
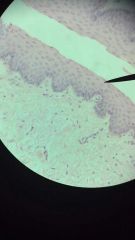
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
|
1. Epithelium
2. Surface of skin; lining of mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum, anus, and vagina. 3. Provides physical protection from abrasion, pathogens, and Chemical attack. |
|
|
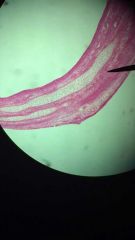
Hyaline Cartilage
|
1. Connective, (Supporting connective tissue)
2. Between tips of ribs and bones of sternum; covering bone surfaces at synovial joints; supporting larynx (voice box), trachea and bronchi; forming part of nasal septum. 3. Provides stiff but somewhat flexible support; reduces friction between bony surfaces. |
different slide, different specimen
|
|
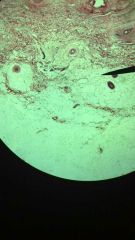
human elastic tissue
|
1. Connective (Dense Regular Connective Tissue)
2. Between vertebrae of the spinal column (ligamentum flavum and ligamentum nuchae); ligaments supporting penis; ligaments supporting traditional epithelia; in blood vessel walls. 3. Stabilizes position of vertebrae and penis; cushions shocks; permits expansion and contraction of organs. |
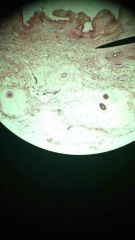
same slide
|
|

aorta elastic tissue
|
1. Connective (Dense Regular Connective Tissue)
2. Between vertebrae of the spinal column (ligamentum flavum and ligamentum nuchae); ligaments supporting penis; ligaments supporting traditional epithelia; in blood vessel walls. 3. Stabilizes position of vertebrae and penis; cushions shocks; permits expansion and contraction of organs. |
|
|
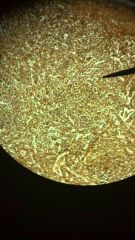
Human Reticular Tissue
|
1. Loose connective tissue
2. Liver, kidney, spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow. 3. Provides supporting framework. |

same slide, different view
|
|
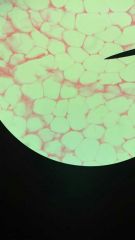
Adipose tissue
|
1. Loose Connective Tissue
2. Deep to the skin, especially at sides, buttocks, breasts; padding around eyes and kidneys. 3. Provides padding and cushions shocks; insulates; stores energy. |
|
|
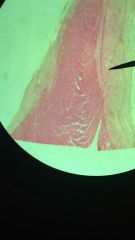
Tendon
|
1. Dense Regular Connective Tissue
2. Between skeletal muscles and skeleton (tendons and aponeuroses); between bones or stabilizing positions of internal organs (ligaments); covering skeletal muscle; deep fasciae. 3. Provides firm attachment; conducts pull of muscles; reduces friction between muscles; stabilizes relative positions of bones. |
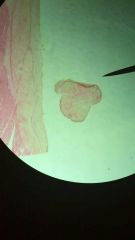
different view of same slide
|
|
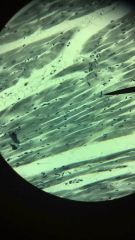
Heart (intercalated disk at pointer)
|
1. Cardiac muscle tissue
2. Heart 3. Circulates blood; maintains (hydrostatic) pressure. |
|
|
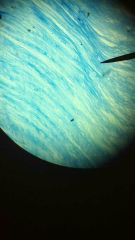
Fibrocartilage
|
1. Supporting Connective Tissue
2. Pads within knee joint, between pubic bones of pelvis, intervertebral discs. 3. Resists compression, prevents bone to bone contact, limits relative movement. |
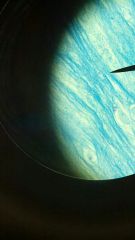
same slide different view
|
|
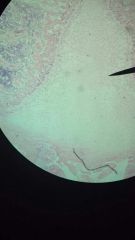
white fibrocartilage (pubic symphysis in middle at pointer)
|
same as for fibrocartilage
|
|
|
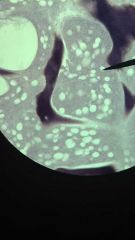
Bone Cancellous Decalcified
|
1. Supporting Connective Tissue
|
|
|
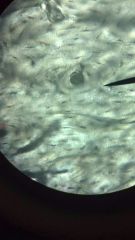
Compact Bone
|
1. Supporting Connective Tissue
2. Found where stresses arrive from a limited range or directions. 3. forms the walls |
|
|
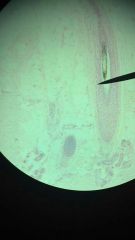
Human Scalp (hair shaft at pointer)
|
idk
|
|
|
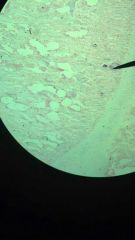
Spongy Bone
|
1. Supporting Connective Tissue
2. in epiphysis and wherever bones are not stressed heavily or where stresses arrive from different directions. 3. reduces weight of skeleton and makes it easier for muscles to move the bones. |
|
|
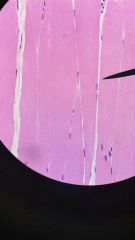
skeletal muscle
|
1. muscle
2. combines with connective tissues and neural tissues in skeletal !muscles 3. moves or stabilizes the position of the skeleton, guards the entrance to the digestive, respiratory, and urinary tract, generates heat and protects internal organs. |
|
|
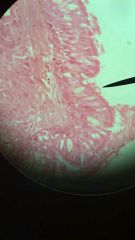
stratified columnar ciliated epithelium
|
1. epithelium
2. Lining of stomach, intestine, gallbladder, uterine tubes, and collecting ducts of kidneys. 3. Protection, secretion, and absorption. |
|
|
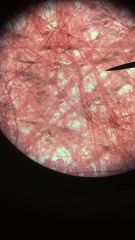
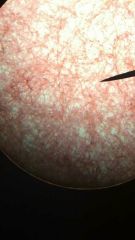
Areolar tissue
|
1. Loose Connective Tissue
2. Within and deep to the dermis of the skin, and covered by the epithelial lining of the digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts; between muscles; around blood vessels, nerves, and joints. 3. Cushions organs; provides support but permits independent movement; phagocytic cells provide defense against pathogens. |
|
|
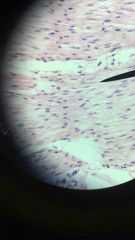
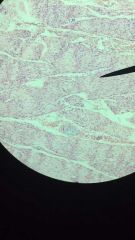
Transitional Epithelium
|
1. Epithelium
2. urinary bladder, renal pelvis, ureters 3. Permits expansion and recoil after stretching. |
|

