![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
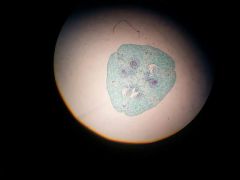
|
Lilium ovary |
|

|
Structure of angiosperm |
|
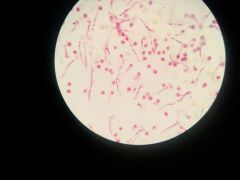
|
Pollon tubes |
|

|
Fruit nuts |
|

|
Berry |
|

|
Berry: fleshy pericarp |
|

|
Pepo: berry with hard thick rind |
|

|
Dragonfruit |
|

|
Coalesced berry |
|

|
Maple |
|

|
Valley oak with Samaria (one seeded, winged) |
|

|
Poaceae: monocots |
|

|
Asteraceae: dicots |
|
|
What are in poaceae? |
Grass |
|
|
What are in asteraceae plant family? |
Daisies, sunflowers, asters |
|

|
Hesperidium: berries with leathery rind |
|

|
Jujube |
|

|
Dried fruits become dry when mature |
|
|
All angiosperms are under what phylum? |
Anthophyta |
|
|
The haploid male microgametophyte is formed where? |
The anthers |
|
|
The haploid female megagametophyte is formed where? |
The pistil |
|
|
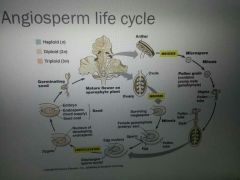
Double fertilization |
One of the sperm nuclei fertilizes the egg to form a zygote. The second sperm nucleus fuses with the embryo sac which creates a 3n nucleus and eventually gives rise to the endowed (nutritious tissue in ovule) |
|
|
What happens after double fertilization? |
1) zygote develops into tint sporophyte embryo 2) rest of the ovule develops into a seed 3) surrounding ovary and tissues develop into fruit |
|
|
Male and female reproductive parts evolved from what? |
Sporophylles (spore bearing leaves) |
|
|
Pedicle |
The stalk that attaches the flower to the stem |
|
|
Receptacle |
The large region at the tip of the pedicle where the flower arises |
|
|
Inflorescence |
Cluster of pedicles |
|
|
Septals |
The part that enclose and protect flower buds |
|
|
Calyx |
All septals of a flower collectively |
|
|
Petals |
Visual attractants for pollinators |
|
|
Corolla |
All petals of a flower collectively |
|
|
Stamens |
Malet reproductice organs (anthers and filaments) |
|
|
Filament |
Stalk like structure of the stamen |
|
|
Anther |
Contain pollen sacs of stamen |
|
|
Carpel |
Female reproductive organ (style, stigma, ovary) |
|
|
Stigma |
Receives pollen |
|
|
Style |
Where pollen grains produce a pollen tube that extends down to the ovary |
|
|
Monocot |
Number of petals, septals, and stamina occur in threes or multiples of threes |
|
|
Dicot |
The floral parts occur in fours or fives |
|
|
Perfect flower |
A flower with both stamens and pistol but calyx and corollary may be absent (only presence of both sexes) |
|
|
Imperfect flower |
A flower that lacks either stamens or pistil |
|
|
Stamintate flower |
An imperfect flower that has only stamens |
|
|
Pistillate flower |
An imperfect flower thats has pistils only |
|
|
Complete flower |
A flower that possesses septals, petals, stamens, and pistil |
|
|
Incomplete flower |
A flower that lacks one or more of the four organs types (septals, petals, stamens, pistil) |
|
|
Dioescious |
The sexes are separate |
|
|
Monoecious |
Both sexes are on the same plant |
|
|
What two terms deceive floral symmetry? |
Radial symmetry and bilateral symmetry |
|
|
Hypogynous flower |
The ovary is superior |
|
|
Epigynous flower |
The ovary is inferious |
|
|
What are in the plant family poaceae? |
Grasses (wheat, oats, rye, barley, rice) |
|
|
Asteraceae |
1) dicot 2) inflorescnese of many mini flowers that form a floral head 3) disk flowers or ray flowers |
|
|
Poaceae |
1) monocots 2) inflorescence 3) wind pollinated |
|
|
What produces the pollen tube? |
The vegetative cell of the pollen grain |
|
|
Fruit |
Mature ovary or ovaries of an angiosperm |
|
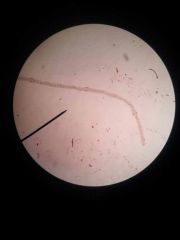
|
Zea leaf monocot (parallel venation) |
|
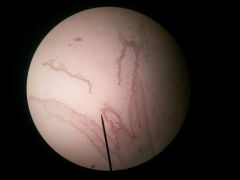
|
Coleus stem tip |
|
|
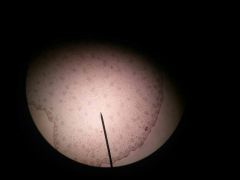
Zea stem monocot |
|
|
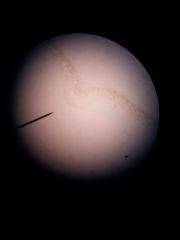
Ligustrum leaf dicot (pinnate) |
|
|
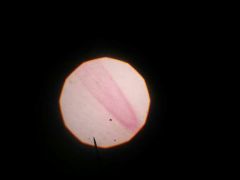
Onion root tip |
|
|
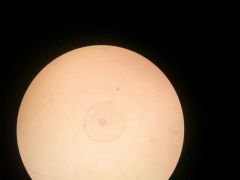
Ranunculus mature root |
|
|
Syringa leaf dicot |
|
|
Coleus stem |
|
|
Ginger with Rhizome stem to specialize in storage and vegetative reproduction |
|

|
Potato with Tuber stem to serve as primary storage organ |
|

|
Bulb |
|

|
Corm with short thick stems to serve as storage function |
|

Leaf structure |
whorled |
|

Leaf structure |
Opposite |
|

|
Stolon stem which serve as vegetative reproduction |
|

Leaf structure |
Alternate |
|

|

|
|

|
Lemon grass monocot parallel |
|

|
Specialized stems |
|

What type of venation |
palmate |
|

|
Doubly compound |
|

What type of venation |
Pinnate |
|

What type of venation |
Pinnate |
|
|
Key characteristics of flowering plants |
1) flower 2) reproductive structures 3) pollination 4) double fertilization |
|
|
Chart |
|
|
Pistil |
1 or more carpels |
|
|
Monocots |
1) one seed leaf 2) parallel leaf veins 3) floral parts in multiples of three 4) usually herbaceous (non-woody) 5) roots are fibrous 6) stem vascualr arrangement is scattered |
|
|
Endicott (dicots) |
1) 2 cotyledons 2) leaf veneration pinnate or palmate 3) reproductive floral parts in fours or fives 4) usually woody 5) one main tap root 6) stem vascualr arrangement is in a ring |
|

|
Chart |
|
|
What are the simple tissues? |
1)Epidermis 2) meristem 3) cambium 4) parenchyma 5) collenchyma 6) sclerenchyma |
|
|
Epidermis |
Thin layer of cells that cover primary tissues. Cutin forms protective layer of cuticle |
|
|
Meristem |
1) Region of active cell division. Found in terminal buds and axillary buds. 2) apical meristems are primary growth (grow up) 3) lateral meristems (Cambrium) are secondary growth (grow horizontal) ¤ cork cambrium are found beneath outer surface and produce cells that become bark ¤ vascualr cambrium has two vascular tissues xylem and phloem |
|
|
Parenchyma |
Thin walled large cells with vacuoles for storage. Become important for young plants but not so much for mature plants |
|
|
Collenchyma |
Thick walled cell for structure support and can still bend petioles (stalk like portion of a leaf that attaches the leaf to the plant) |
|
|
Sclerenchyma |
Similar to collenchyma but provides greater support |
|
|
What are the three general patterns of leaves? |
Alternate, whorled, opposite |
|
|
Xylem |
1 ( Nonliving cells of tracheids and vessel elements which transport water and mineral from the roots to the leaves 2) may contain parenchyma and fibers |
|
|
Phloem |
1)Use living cells of sieve tube elements to transport sugars around 2) may contain companion cells, parenchyma, and fibers |
|
|
What are the complex tissues? |
1) Xylem 2) phloem 3) cortex |
|
|
Cortex |
1) Not a vascualr tissue but acts as filler tissue for structure and support 2) contain combo of parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma |
|

What type of leaf venation |
Palmate: all leaflets emanating from a common point |
|

What type of leaf venation |
Pinnate: leaflets arising along th length of the petiole |
|

What type of leaf |
Simple leaf |
|

What type of leaf |
Compound leaf |
|

What type of leaf |
Doubly compound leaf |
|

|
Monocot root with core of pith surrounded by xylem and phloem |
|
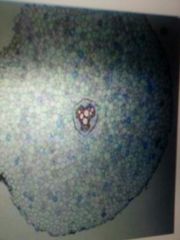
|
Dicot root with xylem and phloem in center |
|

|
Tendril stem which assist to hold plants in place |
|

|
Thorn stem |
|
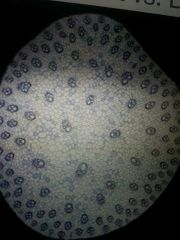
|
Monocot stem |
|
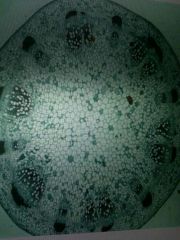
|
Dicot stem |

