![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
228 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hypotension is defined by a MAP < ____mmHg and a systolic BP < ___mmHg.
|
MAP < 65 mmHg
Systolic BP < 80 mmHg |
|
|
How is systolic BP measured?
|
Doppler
|
|
|
How is MAP measured?
|
Direct or indirect
|
|
|
What are some clinical signs of hypotension?
|
Weak peripheral pulses
Pale mm Tachycardia +/- response to surgical stimuli |
|
|
What are some complications associated with hypotension?
|
Decreased renal perfusion, renal ischemia, renal failure
Vasodilative shock, cardiac arrest Equines - post anesthetic myopathy |
|
|
#1 cause of hypotension in young and otherwise healthy veterinary patients:
|
Anesthetics
|
|
|
What is the mechanism associated with hypotension?
|
Decreased preload
Decreased myocardial contractility Decreased PVR |
|
|
The second most common cause of hypotension in young and otherwise healthy veterinary patients:
|
Blood loss during surgery
|
|
|
Name some disease processes that can exacerbate a hypotensive event:
|
Hypovolemia
Shock Cardiomyopathy Valvular disease Hypothyroidism Hypoxemia Addisonian crisis |
|
|
When you first notice that an animal is hypotensive under surgical anesthesia, what do you do?
|
Turn down the vaporizer
Turn up the fluids |
|
|
You have a patient anesthetized and he is hypotensive. He has sustained a lot of blood loss during surgery and neither decreasing the MAC nor increasing fluids is helping. You check a PCV and find that it is below 25. What should you do?
|
Blood transfusion
|
|
|
Name a couple sympathomimetic drugs that can be used to treat hypotension as a second line of defense (after you have tried fluids and decreasing the MAC).
|
Dopamine
Dobutamine Vasopressin Ephedrine |
|
|
When partial pressure of O2 in arterial blood drops below 60 mmHg, this is known as:
|
Hypoxemia
|
|
|
A Pulse-Ox reading below 90% is AKA:
|
Hypoxemia
|
|
|
Hypoxemia leads to ______ and is a frequent cause of mortality in vet patients undergoing anesthesia.
|
Cardiac arrest
|
|
|
What are some causes of hypoxemia?
|
Decreased inspiration O2 concentration
Hypoventilation VQ mismatch Shunt or venous admixture Diffusion barrier The veterinarian |
|
|
What is the #1 cause of anesthetic death?
|
Failure to maintain patent airway leading to hypoxemia
|
|
|
What are some veterinarian mistakes that can lead to hypoxemia and patient death?
|
Unrecognized extubation
Disconnection Aspiration Kinked ET tube Failure to turn off oxygen Closed pop off valve Empty oxygen cylinder OD of anesthetic drugs |
|
|
How do you manage hypoxemia?
|
Check the ET tube
100% oxygen Heart ok? Manual ventilation |
|
|
What is the definition of hypercarbia?
|
When arterial CO2 or end tidal CO2 is > 50 mmHg
|
|
|
When arterial CO2 or end tidal CO2 is > 50 mmHg, this is known as:
|
Hypercarbia
|
|
|
Normal CO2 in the awakened patient:
|
35-45 mmHg
|
|
|
True/false: Anesthetic drugs depress the respiratory drive in a dose dependant fashion.
|
True
|
|
|
True/false: Patients with mild to moderate hypercarbia is usually not a concern unless it is a patient with increased intracranial pressure.
|
True
|
|
|
Increased BP, increased pulse pressure, increased SV, contractility and HR, but a decreased SVR represents which of the three: hypovolemia, hypoxemia, or hypercarbia?
|
Hypercarbia
|
|
|
Clinical signs of hypercarbia:
|
Tachycardia
Hypertension Shallow respiration with increased rate/decreased tidal volume |
|
|
True/false: Hypercarbia and associated shallow breathing results in respiratory alkalosis.
|
False - respiratory acidosis. Remember, its a bit like holding your breath. [H+] will increase on the opposite side of the equation, meaning your pH is dropping
|
|
|
Respiratory acidosis due to hypercarbia results from which - decreased elimination of CO2 or increased production of CO2?
|
Decreased elimination
|
|
|
How do you treat hypercarbia?
|
Control ventilation
Decrease MAC 'Sigh' patients periodically |
|
|
True/false: A cardiac dysarrhythmia is significant only if the hemodynamic status of the patient is affected.
|
True
|
|
|
Are all inhalant anesthetic agents myocardial depressants in a dose dependant fashion?
|
YES
|
|
|
What are our two main anticholinergics?
|
Atropine and glycopyrrolate
|
|
|
How can atropine and glycopyrrolate affect the heart?
|
Sinus tachycardia
2nd degree AV block |
|
|
Acepromazine is what type of drug?
|
Phenothiazine
|
|
|
What affect can Ace have on the heart?
|
Sinus tachycardia
Alpha-1 adrenergic blockade |
|
|
How can opioids affect the heart under anesthesia?
|
Bradycardia
2nd degree AV block |
|
|
Which barbiturate causes bigeminy?
|
Thiopental
|
|
|
This condition describes a state where your heart alternates one "normal" beat with one "premature" beat:
|
Bigeminy
|
|
|
Most common dysarrhythmia seen under anesthesia:
|
Sinus bradycardia
|
|
|
Sinus bradycardia in a large breed dog is when you have <___ bpm.
|
60
|
|
|
Sinus bradycardia in a small breed dog is when you have <____ bpm.
|
70
|
|
|
Sinus bradycardia in a cat is when you have <____ bpm.
|
100-120
|
|
|
True/false: A second degree AV block can sometimes be present with sinus bradycardia.
|
True
|
|
|
If palpated pulses are slower but strong and auscultation reveals a slow heart rate with regular rhythm this is AKA:
|
Sinus bradycardia
|
|
|
Describe the ECG of a patient with sinus bradycardia.
|
Normal p-wave for each QRS
Constant P-R interval |
|
|
What are some contributing factors for a sinus bradycardia?
|
Increased PNS activity
Increased vagal tone Decreased SNS output |
|
|
What are some causes of sinus bradycardia?
|
Drugs
Vagal mediated reflexes Hypothermia Hypothyroidism Addison's disease Excessively deep planes of anesthesia |
|
|
If you have a dog with a high vagal tone resulting in sinus bradycardia, what can you treat him with?
|
Anticholinergics (like atropine to increase the HR)
|
|
|
If you suspect that opioids are causing sinus bradycardia, what can you do?
|
Give reversal or anticholinergics
|
|
|
Sinus tachycardia in a large breed dog is when you have more than ____ bpm.
|
160
|
|
|
Sinus tachycardia in a small breed dog is when you have more than ___ bpm.
|
180
|
|
|
Sinus tachycardia in a cat is when you have more than ___ bpm.
|
220
|
|
|
What are some contributing factors to sinus tachycardia?
|
Sympathetic response to surgery
Pain Hypovolemia Shock Hypercarbia Uncontrolled disease process |
|
|
Why are we concerned with sinus tachycardia?
|
Because the rate can become so high that there is inadequate time for ventricular filling (decreased CO and BP)
|
|
|
If your patient is hypovolemic and this is leading to tachycardia, what can you do?
|
Increase fluids
|
|
|
If your patient is hypercarbic and experiencing tachycardia, what can you do?
|
Increase ventilation
|
|
|
True/false: Most supraventricular atrial tachycardias are usually well tolerated under anesthesia.
|
True
|
|
|
What are some supraventricular atrial tachycardias?
|
A-fib
A-flutter A-tach |
|
|
When PVCs originate as electrical impulses generated below the AV node and AV junction, this is AKA:
|
Ventricular dysarrhythmias
|
|
|
During anesthesia, when do you get concerned about PVCs?
|
When you have multifocal complexes or runs with increasing frequency
|
|
|
If VPC's begin to occur in runs, what happens if you do not get them under control?
|
Decreased CO
V-tach, V-fib, death |
|
|
When p-waves are not associated with the QRS complex and the QRS complex is wide and bizarre, this is AKA:
|
Ventricular arrhythmia - PVCs
|
|
|
What are some causes of PVC's?
|
Trauma patients with myocardial bruising
Electrolyte imbalances Acid/base disturbance Hypoxemia Hypothermia Bradycardia |
|
|
If PVC's are getting out of hand, what can you treat them with?
|
Lidocaine
Oxygen and ventilation Analgesics |
|
|
Generally temps less than ____ are considered hypothermic.
|
100.5
|
|
|
When heat loss exceeds heat production, this is AKA:
|
Hypothermia
|
|
|
When is the greatest temperature loss during anesthesia?
|
During the first hour
|
|
|
At what body temp do you no longer see shivering?
|
Below 89.6
|
|
|
At what body temp do you see cardiac arrest?
|
Below 82.4
|
|
|
MAC decreases _____% for every 1 degree C drop in body temp.
|
5-7%
|
|
|
Shivering increases metabolic oxygen by ___%.
|
200-300%
|
|
|
True/false: Some heat loss is to be expected during surgery.
|
True
|
|
|
What three things lead to recovery excitement?
|
Dysphoria
Pain Disorientation |
|
|
What causes disorientation and thus recovery excitement?
|
Too rapid emergence from anesthesia
|
|
|
What causes dysphoria and thus recovery excitement?
|
Too many opioids
|
|
|
Can insufficient pain management cause recovery excitement?
|
YES
|
|
|
What are some benefits of pre-emptive pain management?
|
Decrease MAC of inhalant
Quicker recoveries Lower overall pain scores Patient safety |
|
|
What are the four main steps in pain processing?
|
Transduction
Transmission Modulation Perception |
|
|
You can inhibit peripheral sensitization of nocireceptors with which classes of drugs?
|
NSAIDS
Opioids Local anesthetics |
|
|
You can inhibit impulse conduction associated with pain with which classes of drugs?
|
Local anesthetics
Alpha-2 agonists |
|
|
You can inhibit central sensitization associated with pain with which classes of drugs?
|
Local anesthetics
Opioids Alpha-2 agonists Tricyclic antidepressants Cholinesterase inhibitors NMDA antagonists NSAIDS |
|
|
What are some drugs that can inhibit the perception of pain?
|
Anesthetics
Opioids Alpha-2 agonists Benzodiazapines |
|
|
Why is a multimodal approach to pain management so much better?
|
Less dysfunction
Faster recovery More complete |
|
|
Topical local anesthetics are used for:
|
Desensitization of skin surfaces
|
|
|
Local anesthetics used for infiltration and field blocks are good for:
|
Local tissue desensitization
|
|
|
Give an example of a regional local anesthetic technique:
|
Epidural
|
|
|
Give examples of systemic local anesthetic techniques:
|
IM
IV SQ CRI |
|
|
Three basic parts to an anesthetic molecule:
|
Hydrophobic end
Hydrophilic end Intermediate chain |
|
|
Which is metabolized by hepatic enzymes - amides or esters?
|
Amides
|
|
|
Which undergoes hydrolysis by plasma cholinesterase, amides or esters?
|
Esters
|
|
|
Which is associated with PABA and allergies - esters or amides?
|
Esters
|
|
|
Which is associated with cross reactivities - esters or amides?
|
Esters
|
|
|
True/false: a drug's lipid solubility affects its ability to bind to axonal lipids and thus affects potency.
|
True
|
|
|
True/false: A drugs duration of effect can be affected by protein binding.
|
True
|
|
|
At rest, describe where K and Na relative to each other in/outside of a cell.
|
Na outside
K inside |
|
|
Describe how local anesthetics change neurophysiology.
|
Binds to receptor sites in Na channel to prevent/impede Na movement (and thus effects depolarization)
Electrical impulses reduced; nerve conduction blocked |
|
|
Dissociation ratio is determined by:
|
pH and pKa
|
|
|
Which can bind to a Na receptor, a charged or uncharged cation?
|
Charged --> leads to neural blockade
|
|
|
General parts of a neuron:
|
Cell body
Axon Dendrites |
|
|
Which is blocked first, sensory or sympathetic?
|
Sympathetic
|
|
|
Which is blocked first, sensory or motor?
|
Sensory
|
|
|
Which is blocked first, myelinated or unmyelinated?
|
Myelinated
|
|
|
Which is blocked first, small or larger neurons?
|
Small
|
|
|
Which is blocked first, faster or slower neurons?
|
Faster
|
|
|
Put in order of sensation: Touch, motor, pain, warmth, deep pressure, cold, joint
|
Pain>cold>warmth>touch>joint>deep pressure>motor
|
|
|
Which type of fiber has the slowest conduction velocity?
|
C-fiber
|
|
|
Which type of fiber has the fastest conduction velocity?
|
A-alpha fiber
|
|
|
Put in order of fiber stimulation: Aa, C, Ad, Ag, B, Ab
|
B>C>Ad>Ag>Ab>Aa
|
|
|
True/false: The effects of a neuronal block are reversed as a drug is metabolized and redistributed.
|
True
|
|
|
Procaine, Benzocaine and Proparacaine are all esters or amides?
|
Esters
|
|
|
Another name for Novocaine:
|
Procaine
|
|
|
What is benzocaine used for?
|
Topical wound care
|
|
|
What ester is used for ophthalmic anesthesia?
|
Proparacaine
|
|
|
Lidocaine, Mepivicaine and Bupivicaine are amides or esters?
|
Esters
|
|
|
Another name for Bupivicaine:
|
Marcaine
|
|
|
What can prolong the duration of lidocaine applied topically?
|
Vasoconstriction
|
|
|
Onset for lidocaine:
|
10-15 mins
|
|
|
Does lidocaine have a short or long duration?
|
Short - 1-2 hrs (think of your tooth)
|
|
|
Which has a longer duration of action - Lidocaine or Mepivicaine?
|
Mepivicaine
|
|
|
Which has a very rapid onset - Mepivicaine or Bupivicaine?
|
Mepivicaine - 5-10 mins
|
|
|
What other amide has 4x the potency of lidocaine?
|
Bupivicaine
|
|
|
Which has a lower MOS, and thus you need to carefully calculate doses - Lidocaine or Bupivicaine?
|
Bupivicaine
|
|
|
Which of the amide local anesthetics is the longest acting?
|
Bupivicaine
|
|
|
What is usually the 1st CNS sign seen w/ overdose of anesthetic agent?
|
Muscle twitching
|
|
|
What are some adverse CNS effects seen with local anesthetics?
|
Muscle twitching
Convulsions Unconsciousness Coma Respiratory arrest |
|
|
What are some adverse CV effects seen with local anesthetics?
|
Profound vasodilation
Profound hypotension Direct myocardial depression Decreased ventricular contractility |
|
|
If you have an adverse effect associated with a local anesthetic, what do you do?
|
Fluids
Diazepam if seizuring Intubate 100% O2 |
|
|
An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience (perception) associated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of such damage is AKA:
|
Pain
|
|
|
The reception, conduction and CNS processing of nerve signals generated by nociceptors leading to the perception of pain is AKA:
|
Nociception
|
|
|
True/false: Nociception is the process that leads to the perception of pain.
|
True
|
|
|
What are the two types of nociceptors that convert chemical, mechanical or thermal energy into electrical impulses?
|
Free A-delta and C nerve fibers
|
|
|
Which nociceptors are composed of mechanoreceptors and mechanothermal receptors?
|
A-delta nociceptors
|
|
|
Describe a high threshold A-delta nociceptor.
|
(<25%) - responds only to tissue damaging stimuli
|
|
|
A-delta nociceptors can be broken into 2 subtypes:
|
High threshold (<75%)
Low threshold (<25%) |
|
|
Which discharges at a faster rate, A-delta nociceptors or C-fiber nociceptors?
|
A-delta
|
|
|
Which provides more discriminative information to the CNS - A-delta fibers or C-fibers?
|
A-delta fibers
|
|
|
Which is associated with 'first pain', the pricking or sharp quality, A-delta fibers or C-fibers?
|
A-delta
|
|
|
True/false: Almost all C-fibers are high threshold and respond to different types of stimuli (are polymodal)?
|
True
|
|
|
Which nerve fiber is associated with second pain?
|
C-fiber
|
|
|
What are the qualities of second pain, associated with C-fibers?
|
Burning and aching qualities
Signals tissue damage and inflammation that initiates self preservation behaviors |
|
|
What are silent, or sleeping nociceptors important for?
|
Peripheral sensitization
|
|
|
Describe silent/sleeping nociceptors.
|
A-delta and C-fiber nociceptors that are activated by tissue damaging events
Important role in peripheral sensitization |
|
|
The conversion of mechanical, chemical or thermal energy to an electrical impulse is what part of the pain pathway?
|
Induction
|
|
|
When eletrical signals are transmitted via nociceptors to the spinal cord, this process is AKA:
|
Transmission
|
|
|
Which is myelinated, A-delta fibers or C-fibers?
|
A-delta
|
|
|
Which has a smaller diameter, A-delta fibers or C-fibers?
|
C-fibers
|
|
|
Which has fast conduction, A-delta fibers or C-fibers?
|
A-delta
|
|
|
Which transmits well localized, sharp pricking pain, A-delta fibers or C-fibers?
|
A-delta fibers
|
|
|
Which is involved in second pain, A-delta fibers or C-fibers?
|
C-fibers
|
|
|
Amplification or supression of peripheral sensory nerve impulses at the level of the spinal cord is AKA:
|
Modulation
|
|
|
What is the role of interneurons?
|
Part of modulation
Excitatory or inhibitory Transmit sensory information for a short distance in the spinal cord |
|
|
What are propriospinal neurons involved in?
|
Modulation
Segmental reflex activity - generate a simple motor withdrawl response |
|
|
Where do projection neurons synpase with 3rd order neurons?
|
Medulla
Pons Midbrain Thalamus Hypothalamus Cerebral cortex |
|
|
What are the three types of neurons associated with modulation?
|
Interneurons
Propriospinal neurons Projection neurons |
|
|
Integration, processing and recognition of sensory information is AKA:
|
Perception
|
|
|
The descending pathway invovles which endogenous opioids?
|
Dynorphins
Endorphins Enkephalins |
|
|
The descending pathway begins where in the brain?
|
Amigdala
Cortex Thalamus |
|
|
Describe the progression of a signal down the descending pathway?
|
Begins in Cortex, amigdala, thalamus
Goes to midbrain Goes to dorsal horn of the spinal cord Inhibition of transmission of impulses |
|
|
Pain due to a stimulus which does not normally provoke pain and can be either static or mechanical is AKA:
|
Allodynia
|
|
|
Allodynia is associated with:
|
Central sensitization
|
|
|
Alteration in the excitability of the neurons in the brain and in the spinal cord caused by severe or chronic painful stimuli that activates A-delta and C-receptors is AKA:
|
Central sensitization
|
|
|
What is hyperalgesia and what is it associated with?
|
Intensification of pain associated with central sensitization
|
|
|
What are the two general ways we can classify pain?
|
Duration
Origin |
|
|
Which is usually related to trauma, surgery or infection, acute or chronic pain?
|
Acute
|
|
|
What type of pain persists beyond a reasonable time for the course of disease or injury?
|
Chronic pain
|
|
|
If you say your pain is somatic in origin, what does this mean?
|
Originates from damage to somatic tissues - bones, joints, muscle, skin
|
|
|
Is somatic pain well localized or not?
|
YES, visceral pain is not
|
|
|
Which can be associated with nausea or vomiting, somatic or visceral pain?
|
Visceral
|
|
|
What type of pain arises from visceral injury and is not well localized?
|
Visceral pain
|
|
|
What type of pain is associated with direct damage to the peripheral nerves or spinal cord?
|
Neuropathic
|
|
|
Describe neuropathic pain sensation:
|
Burning or shooting pain
Difficult to treat |
|
|
How is the immune system affected by pain?
|
Increased cortisol levels impair wound healing and decrease immune function
|
|
|
Describe how the neuroendocrine system is affected by pain:
|
Activated by pain
Gluconeogenesis is favored Impaired metabolism results in catabolism and cachexia |
|
|
Describe how the GI system is affected by pain:
|
Sympathetic stimulation can cause shunting of blood, decreased motility and decreased mucosal integrity
|
|
|
With pain, the CV system can be affected by initiation of R-A-A, what is the effect of this?
|
Fluid retention
Elevated BP Decreased renal profusion Increased HR, SV, CO and myocardial O2 consumption |
|
|
What are the psychological effects associated with pain?
|
Patient's quality of life is decreased
Owner gets angry, guilty and fearful of procedures Caregivers feel guilt if unable to treat pain |
|
|
What is the 4th vital sign?
|
Pain
|
|
|
True/false: Pain assessment is considered part of every patient evaluation, regardless of presenting complaint.
|
True
|
|
|
What are the four general signs of pain?
|
Loss of normal behavior
Expression of abnormal behaviors Reaction to touch Change in physiologic parameters |
|
|
Give some examples of loss of normal behavior associated with pain.
|
Decreased ambulation
Decreased appetite Decreased grooming (cat) Lethargic attitude |
|
|
True/false: a change in normal behaviors associated with pain is difficult to assess in the hospital.
|
True
|
|
|
Describe some abnormal behaviors that may be expressed if an animal is in pain.
|
Vocalization
Inappropriate elimination Aggression Altered facial expression Decreased interaction w/ pets and family members Altered posture Restlessness Hiding (cats) |
|
|
How might your physiologic parameters change in association with pain?
|
Increased HR, BP, RR, temp
Pupil dilation (mydriasis) |
|
|
What type of pain scale is this?
|
Numerical - just like a simple descriptive scale except it has numbers also
|
|

What type of pain scale is this?
|
Simple descriptive
|
|
|
How can you improve the use of a visual analogue pain scale?
|
Specify procedure: Worst possible pain for THIS...
|
|
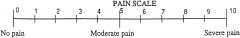
What type of pain scale is this?
|
Visual analogue
|
|
|
True/false: Pain scoring systems are very subjective with user variability.
|
True
|
|
|
Describe the Dynamic and Interactive Visual Analogue Scale (DIVAS).
|
Observation from a distance undisturbed
Approached, handled and encouraged to walk Palpation of surgical incision and surrounding area Final overall assessment of sedation and pain |
|
|
Describe the Glasgow composite measures pain score.
|
47 well defined words or expressions that could define pain
One physiologic and 7 behavioral categories |
|
|
What are the 7 behavioral categories associated with the Glasgow Composite Measures Pain Score?
|
Posture
Comfort Vocalization Attention to Wound Mobility Demeanor and Response to Humans Response to Touch |
|
|
Which quantitative pain scoring system looks at physiologic data and behavioral responses, and gives a pain score between 0 and 27?
|
University of Melbourne Pain Scale (UMPS)
|
|
|
What are the four general ways you can treat pain?
|
Inhibit transduction
Inhibit transmission Inhibit modulation Inhibit perception |
|
|
What are full Mu agonist opioids generally used for?
|
Moderate to severe pain
|
|
|
What are the full agonist opioids?
|
Morphine
Oxymorphone Hydromorphone Fentanyl Methadone |
|
|
Which opioid would I pick for very mild pain?
|
Agonist-antagonist
Butorphanol |
|
|
Which opioid would I pick for moderate pain?
|
Partial Mu agonist
Buprenorphine |
|
|
Which opioid is a partial Mu agonist?
|
Buprenorphine
|
|
|
Which opioid is an agonist-antagonist, and is used for mild pain?
|
Butorphanol
|
|
|
True/false: NSAIDS are inhibitors of COX-1 and COX-2 pathways.
|
True
|
|
|
What is the general mechanism of NSAIDS?
|
By inhibiting the COX-1 and COX-2 pathways, they prevent the conversion of arachadonic acid to prostanoids
|
|
|
Should I use an NSAID with renal or hepatic insufficiency?
|
NO
|
|
|
What are some contraindications for NSAID usage?
|
Renal/hepatic problems
Dehydration/hypotension/shock Active GI disease Coagulopathy Current use of steroids or other NSAIDS Pregnancy |
|
|
True/false: NSAID usage is contraindicated in pregnancy.
|
True
|
|
|
Which classes of drugs provide analgesia?
|
Opioids
Alpha-2-agonists Dissociatives NSAIDS |
|
|
Which parts of the pain pathway do local anesthetics act on?
|
Transduction
Transmission |
|
|
Which can you use IV, lidocaine or bupivicaine?
|
Lidocaine
|
|
|
True/false: IV Lidocaine provides good visceral analgesia to horses in colic.
|
True
|
|
|
Central sensitization and hyperalgesia is common with what injury?
|
Burn
|
|
|
Can ketamine be used to prevent and treat central sensitization?
|
YES (hence why it is used to treat burns)
|
|
|
Name the routes by which ketamine can be given?
|
IV, IM, SQ, epidural
|
|
|
Name an adjuvant drug that is OFTEN used as a sedative.
|
Ace
|
|
|
What tricyclic antidepressant is often used as an adjuvant drug?
|
Amitryptylline
|
|
|
What is the nature of Gabapentin (i.e. what might it be used for)?
|
Anticonvulsant
|
|
|
How does tramadol affect GABA and serotonin?
|
Increase them
|
|
|
What is the benefit of using an opioid CRI, rather than just an injection prior to surgery?
|
More constant plasma levels
Eliminates the need for repeated administration via other routes |
|
|
Which opioid is given as a buccal transmucosal?
|
Burprenorphine
|
|
|
True/false: There is a big difference between giving something (like Buprenorphine) orally and giving it transmucosal in the buccal cavity.
|
True! - With buccal transmucosal administration, there is NO first pass effect
|
|
|
The peak effect of transdermal Fentanyl is felt in how many hours?
|
12-24 (lasts about 72 hrs)
|
|
|
What are the advantages to doing an epidural?
|
Prolonged segmental analgesia
Minimal sedation Decreased MAC |
|
|
What are the disadvantages to doing an epidural?
|
Technical expertise required
Spinal needle necessary |
|
|
What are some side effects of epidural usage?
|
Urinary retention
Pruritis Vomiting Hypotension |
|
|
When is an epidural contraindicated?
|
Sepsis
Coagulopathies |
|
|
True/false: Hematomas, abscesses and ineffective analgesia can all be complications associated with epidural usage.
|
True
|
|
|
I want to do a brachial plexus block. This means I want to work on what part of the leg?
|
Within or below the elbow
|
|
|
When might I use an intercostal nerve block?
|
Rib fractures
Lateral intercostal thoracotomy |
|
|
When you do an intercostal nerve block, do you go cranially or caudally to the rib?
|
Caudal border of the rib
|
|
|
When might I use interpleural analgesia?
|
Thoracotomy
Rib fractures Pancreatitis Cholecystectomy Metastasis in the region |

