![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
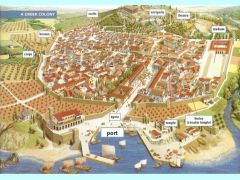
Polis |
City-State consisting of a town and the farms and villages around it. |
|

Acropolis |
Walled fortress where settlement's ruler lives. |
|

Assembly |
A law making group. |
|
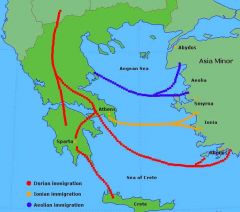
City State |
Ancient Greece consisted of a number of independent city-states such asAthens, Thebes, and Sparta.
|
|

Democracy |
Type of government in which the people rule.
|
|

Oligarchy |
A system of government in which only o few people rule.
|
|
|
Citizen |
People who had the right to participate in government.
|
|
|
Myth |
A story about gods and heroes that try to explain how the world works
|
|
|
Epic |
A system of government in which people are ruled.
|
|
|
Phalanx
|
A battle formation where soldiers formed rows, closely pressed together. |
|
Peloponnesian
League |
An alliance known mainly for being one of the two rivals in the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC).
|
|

Delian League
|
A group of Greek city-states that joined together to fight against the Persian Empire.
|
|

Golden Age of Greece |
A period of great peace, prosperity, and happiness.
|
|
|
Hellenistic Age
|
This Period of Ancient Greece lasted from 323 BCwhen Alexander the Great came to power to 146 BC when Rome conquered Greece.
|
|
|
Persian Wars
|
Series of wars fought between Persia and Greece.
The conflict began when Persia occupied some Greek colonies in Asia Minor. Greece responded by defending the colonies and Persia responded by attacking Greece. |
|

Peloponnesian
Wars |
A War fought between Sparta and Athens.
It lasted 27 years. Sparta and Athens were always in disagreement. |
|

Socrates
|
Greek philosopher who created the "Soctratic method": teaching using questions. Questioned the influences of the gods. interested in finding hawsers by reasoning. |
|

Plato
|
A Greek philosopher who founded the "Academy" in Athens andwrote many philosophical dialogues.
Socrate's student |
|

Aristotle
|
A Greek philosopher who introduced the idea of observing andrecording nature.
He also tutored Alexander the Great and began his own schoolin Athens. |
|

Alexander the Great
|
Alexander the Great was the king of Macedonia or Ancient Greece. He is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history.
|
|

Pericles
|
A leader of Athens during its golden age.
Periclespromoted the arts and literature in the city. He also had many of the majorstructures built including the Parthenon. |
|
|
Homer
|
A Greek epic poet who wrote the Iliad and the Odyssey.
|
|

Philosophers |
People who studied the meaning and knowledge of life ad the unknown. |
|
|
Athens |
Birthplace of democracy. Greek civilization. Thinkers. |
|
|
Sparta |
Military state. |
|

Drama |
The Greeks invented drama from their wild religious ceremonies involving drinking, dancing, and revelry |
|

Tradegy |
Greek tragedy was a popular and influential form of drama performed in theatres across ancient Greece from the late 6th century BCE. The most famous playwrights of the genre were Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides and many of their works were still performed centuries after their initial premiere. |
|

Comedy |
a popular and influential form of theatre performed across ancient Greece from the 6th century BCE. The most famous playwrights of the genre were Aristophanes and Menander and their works, and those of their contemporaries, poked fun at politicians, philosophers, and fellow artists. |
|
|
Significance of: Hellenistic Culture by Alexander the Great |
Blended Eastern and Greek Cultures. Time of learning. Library at Alexandria |
|
|
Contributions of Greece to modern western civilization |
Democracy, Medicine, Science, Mathematics, Literature, Plays |
|
|
Monarchy |
A form of government headed by a king or queen.
|

