![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
91 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
THORACIC RADIOGRAPHY Always include ______ on radiograph?
|
cranial abdomen
|
|
|
divides thoracic cavity into 2 segments?
|
mediastinum
|
|
|
what is on each side of mediastinum?
|
pleural cavities or pleurae
|
|
|
right lung, name lobes
|
3 visible and 1 hiding; cranial lobe, middle lobe, caudal lobe, and accessory lobe (just medial to caudal lobe)
|
|
|
parts of sternum
|
manubrium (top of the T), body, xiphoid process (caudal)
|
|

What is the structure shown here?
|

tracheoesophageal stripe sign
in x-rays, the DORSAL wall of the TRACHEA and the adjacent ventral wall of the esophagus may be visualized because of air in the esophagus. (trachea is ventral to esophag) |
|
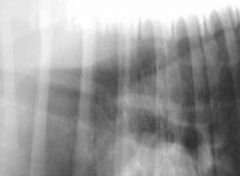
What is the structure shown here?
|

tracheoesophageal stripe sign
in x-rays, the DORSAL wall of the TRACHEA and the adjacent ventral wall of the esophagus may be visualized because of air in the esophagus. (trachea is ventral to esophag) |
|
|
peri-bronchial cuffing”
|
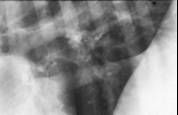
also referred to as peribronchial thickening or bronchial wall thickening is a radiographic sign which occurs when excess fluid or mucus buildup in the small airway passages of the lung causes localized patches of atelectasis (lung collapse). [1] This causes the area around the bronchus to appear more prominent on an xray.
|
|
|
persistent right 4th aortic arch
|
Vascular ring anomaly, caused during development where right INSTEAD of left aortic arch becomes the aorta. Consequently, aorta on wrong side of esophag. (on right), resulting in aorta, ligamentum arteriosum, and base of heart forming ring around esophagus.
So when dog swallows a large amount of food (which is always); dog regurgitates etc. To free esophagus, need to ligated and cut ligamentum arteriosum. |
|
|
Most joints of thorax are ________?
|
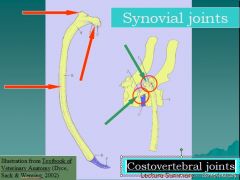
cartilaginous (intervertebral disks are fibrocartilaginous joints) or synovial (Costovertebral joints)
|
|
|
oblique soft tissue opacity due to thymus in ventral part of cranial mediastinum seen in VD/DV views; normal young animals
|
Sail Sign
|
|
|
acquired or congenital dilation of caudal cervical and thoracic esophagus?
|
Megaesophagus; results in ventral displacement of trachea and heart
|
|
|
another name for tracheal bifurcation
|
CARINA
|
|
|
air in pleural space
|
pneumothorax
|
|
|
fluids in pleural space
|
pleural effusions; can lead to scalloped appearance if push lungs away from body wall and fill the lung fissures
|
|
|
interstitial pattern
|
some diseases cause tissue to thicken, become opaque, FUZZY appearing vessels as interstitium. But often b/c radiograph incorrectly taken during expiration.
|
|
|
alveolar pattern
|
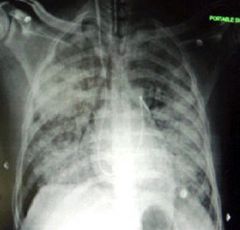
results from lungs filling up with fluid eg. pulmonary edema; vessel no long visible b/c they also have fluid in em.
|
|
|
bronchial pattern
|
enlarged or increased density of bronchial walls. Donuts and tram lines.
|
|
|
name four lobular patterns of lung radiographs
|
interstitial, alveolar, bronchial, and vascular pattern
|
|
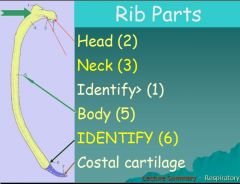
Identify #1 and #6 on image shown
|
Tubercle; Costochondral junction
|
|
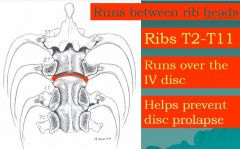
Identify ligament shown here
|
intercapital ligament
|
|
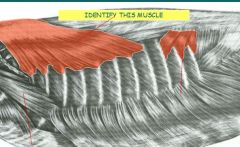
Identify muscle
|
serratus ventralis
|
|
|
What kind of cartilage found in trachea?
|
hyaline cartilage
|
|
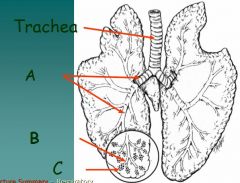
Identify
|
A. Bronchi
B. Bronchioles C. Alveoli |
|
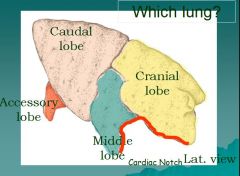
Which lung?
|
Right lung
|
|
|
What serosa covers walls of a cavity?
|
Parietal serosa
|
|
|
What serosa covers an organ?
|
Visceral serosa
|
|
|
What connects parietal and visceral?
|
connecting serosa
|
|
|
What is junction between the two crura?
|
intercrural cleft
|
|
|
anticlinal
|
T11
|
|
|
costochondral junction
|
where ribs meet or become costal cartilage
|
|
|
adult remnant of ductus arteriosus
|
ligamentum arteriosum
|
|
|
adult remnant of foramen ovale?
|
fossa ovale
|
|
|
adult remnant of umbilical arteries
|
round ligament of urinary bladder
|
|
|
adult remnant of umbilical vein
|
round ligament of liver
|
|
|
what seperates lobes of lung?
|
interlobar fissures
|
|
|
2 muscles extending between adj ribs?
|
external and internal intercostal m.
|
|
|
What are junctions between 2 crura?
|
intercrural cleft
crura are 2 sides of diaphragm (left and right) |
|
|
ansa subclavia
|
nerve cord that arises from stella ganglion (cervicothoracic ganglion or star thing)
|
|
|
Left lung
|
2 lobes (looks like 3); number lobes defined by number of secondary bronchi
Left caudal lobe Left cranial lobe, of which there is a cranial and caudal part |
|
|
Right lung
|
cranial, middle, accessory, and caudal lobes
number lobes defined by number of secondary bronchi |
|
|
what forms the thoracic inlet
|
it is cranial thoracic opening formed by 1st pair of ribs, and the vertebrae and sternebrae to which they connect
|
|
|
costal cartilages
|
bars of HYALINE cartilage which serve to prolong the ribs forward (let them move forward) and contribute very materially to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax.
|
|
|
On lateral radiograph where does fundus appear?
pyloric part? |
top, dorsal (air density)
lower, ventral |
|
|
On VD, where does fundus appear?
other air density? |
air density on LEFT (your right) and higher than pyloric part
cecum |
|
|
What is surgical opening of thoracic cavity?
|
Thoracotomy
|
|
|
Where is intercostal space incised to open thorax and why?
|
In center to avoid the vessels caudal to ribs.e.g. internal thoracic artery & vein.
|
|
|
What lung most often problem site for aspiration pneumonia?
What about for light particulate matter (grass cuttings)? |
-Right middle lung lobe
- Cranial right lung lobe - right caudal lobe, str8 shot back |
|
|
What is chylothorax?
|
Lymph in pleural cavity usually from a ruptured lympthatic vessel
(thoracic duct) |
|
|
What are 3 common locations of clinical blockage of esophagus in thorax?
|
1. thoracic inlet
2. base of heart 3. esopageal hiatus of diaphragm (start of esophagus) |
|
|
How far cranially does dome of diaphragm extend?
|
6th intercostal space, just behind the olecranon/ heart
|
|
|
How many pleural sacs are there?
|
2
|
|
|
Whar pleura covering lungs called?
|
Visceral pleura; also pulmonary pleura
I think all the other pleura in thorax is parietal (lines body walls) |
|
|
What is the space just inside the line of pleural reflection?
|
costodiaphragmatic recess
|
|
|
What are holes in the mediastinum called?
|
Fenestrations
Don't exist in young animals for whatever reason |
|
|
What is relationship of basal border of lung and line of pleural reflection?
|
parallel, lung craniodorsal to line (its above it)
|
|
|
A normal expiratory film can be mistaken for what type of pathological lung pattern?
|
interstitial
|
|
|
What does connecting branch of nervous system connect?
|
Spinal nervve and sympathetic trunk/ drains ganglia
|
|
|
What is the surgical opening of the thoracic cavity?
|
Thoracotomy
|
|
|
What is the injection and aspiration of material into and from the trachea for lab work?
|
Transtracheal wash
simple procedure to help evaluate the patient with respiratory tract disease. |
|
|
What is aspiration pneumonia?
|
swallowing foreign material into the lungs and subsequent pneumonia
|
|
|
What is pneumonia?
|
Inflammation of the lungs with consolidation
|
|
|
Which lobe is the most common site for aspiration pneumonia?
What is the second most common lung lobe? |
Middle right lung lobe (most dependent)
cranial right lung lobe |
|
|
What are 3 common locations of clinical blockage of the esophagus?
|
Thoracic inlet, base of heart, esophageal hiatus of diaphragm (start of esophagus)
Why? |
|
|
The esophagus is normally on what side of aorta?
|
Right side
Aorta is on left; unless dog has a PRAA |
|
|
Where is the intercostal space incised to open the thorax and why?
|
In center to avoid the vessels caudal to ribs
|
|
|
What vessels is of concern in midsternal thoracotomies?
|
Internal thoracic artery and vein
|
|
|
Carotid sheath encloses?
|
carotid artery and vagosympathetic trunk, which consists of vagus n. and sympathetic trunk
|
|
|
What is the clinical significance of the line of pleural reflection?
|
Demarcates the pleural from the peritoneal cavity
|
|
|
What is thoracocentesis?
Where is thoracocentesis done? |
What is pleurocentesis/ thoracocentesis?
Thoracic puncture to withdraw fluid Surgical puncture of the thorax for drainage of fluid In the middle of the intercostal space just dorsal to the costochondral junction, craniodorsal to the diaphragmatic line of pleural reflection |
|
|
How can the pleural cupula be clinically important?
|
Can open the pleural cavity with an incision near the thoracic inlet
|
|
|
pyothorax
|
pyothorax is an accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity. Most pleural empyemas arise from an infection within the lung (pneumonia)
also known as a pleural empyema or purulent pleuritis |
|
|
What theoretically allows a unilateral pneumothorax or pyothorax to become bilateral?
|
fenestration (holes) in the mediastinum, common in the dog
|
|
|
How can infections of the neck migrate to the thorax?
|
Down the deep fascia to the endothoracic fascia
|
|
|
Consolidation
|
clinical term for solidification into a firm, dense mass, specifically used in reference to region of lung tissue that, normally compressible but has filled with liquid,[1] a condition marked by induration (swelling or hardening of normally soft tissue) of a normally aerated lung.
Consolidation occurs through accumulation of fluid in alveoli and adjoining ducts. |
|
|
induration
|
swelling or hardening of normally soft tissue e.g. in lung (alveoli) with pneumonia
|
|
|
exudation
|
fluid that filters from the circulatory system into lesions or areas of inflammation.
|
|
|
What three fetal structures bypass the lungs and liver?
|
Ductus arteriosus and venosus, foramen ovale
|
|
|
What is the adult remnant of the following structures?
Ductus arteriosus? Foramen ovale? Umbilical arteries? Umbilical vein? |
Ligamentum arteriosum
Oval fossa or fossa ovale Round ligaments of urinary bladder Round ligament of liver |
|
|
What glandular structure is in the cranial mediastinum of the young?
|
thymus
|
|
|
What lymph nodes are near the bifurcation of the trachea?
|
Tracheobronchial lymph nodes
|
|
|
What is the lymphatic structure in the cranial mediastinum?
|
Cranial mediastinal lymph node
|
|
|
How do expiratory muscles effect the thorax?
|
Decrease the size of the thorax
|
|
|
what thoracic vertebra usually has the most vertically oriented spine
|
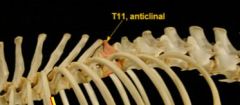
anticlinal vertbra, usually T11 in dog
|
|
|
# what is the parasympathetic innervation to the thorax
|
vagus nerve
|
|
|
How are ruptures of the collateral ligament of the elbow diagnosed?
|
By the amount of supination or pronation allowed, compared to the unaffected arm
|
|
|
Name the main inspiratory muscles
|
Muscles of Inspiration
External Intercostals Diaphragm (Phrenic N.) Scalenus Rectus Thoracis |
|
|
Name the main expiratory muscles
|
Muscles of Expiration
Internal Intercostals Diaphragm (Phrenic N.) Rectus abdominis Transverus Thoracis |
|
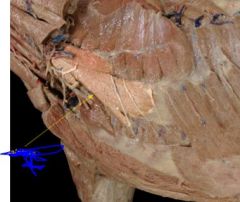
Name this muscle of inspiration
|
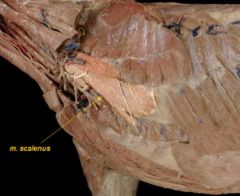
scalenus
|
|
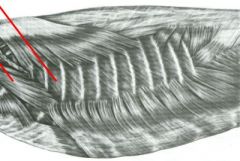
identify muscles
|
Scalenus and External intercostal muscles
|
|
|
What is name of cranial pleural sac extending out thr thoracic inlet?
|
cupula
|

