![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
118 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Golden Sentence:
The _______ innervates the posterior aspect of the arm. The _______ innervates the posterior forearm |
The radial n. innervates the posterior aspect of the arm and the deep radial n. innervates the post. forearm
|
|
|
Golden Sentence:
The ____________ innervates the brachialis m., biceps brachii, and coracobrachialis and then becomes the ____________. |
The musculocutaneous n. innervates the brachialis m., biceps brachii, and coracobrachialis and then becomes the lateral cutaneous antebrachial n (aka lateral cutaneous n of forearm).
|
|
|
Golden Sentence:
The ________ innervates the anterior regions of the forearm EXCEPT the _______ and ______________ |
The median n. innervates the anterior regions of the forearm EXCEPT the flexor carpi ulnaris and 2 tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus.
|
|
|
What innervates the flexor carpi ulnaris and 2 tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus?
|
The ulnar n.
|
|
|
suprascauplar notch contents?
|
nerve, artery, and vessels of the same name
|
|
|
Clavicle Shape:
Medial 2/3 is _______ anteriorly and lateral 1/3 is ________ anteriorly. |
S shaped
Medial 2/3 is convex anteriorly and lateral 1/3 is concave anteriorly. |
|
|
cleidocranial dysostosis/dysplasia (CCD)?
Gene involved? |
fx of clavicel btwn middle 1/3 and lateral 1/3
rare autosomal disorder with defective ossification, delayed bone/tooth growth, and craniofacial abnormalities RUNX2 (aka CBFA1) |
|
|
__________ of the clavicle is the weakest point because this is where ______________ ossification occurs here
|
medial-lateral border is weakest point because this is where intramembranous ossification occurs here
|
|
|
sternoclavicular joint is what type of joint?
|
ball and socket synovial joint
|
|
|
acromioclavicular joint is what type of joint?
|
plane-type joint that permits sliding/gliding movements
|
|
|
What type of ossification do the ends of the clavicle undergo?
|
endochondral ossification in second decade of life
|
|
|
Thirds of the clavicle?
|
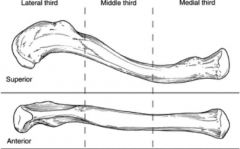
|
|
|
type of ossification at ends of clavicle?
|
endochondral ossification
|
|
|
weakest part of clavicle?
|
medial-lateral border is weakest point because this is where intramembranous ossification occurs here
|
|
|
sternoclavicular joint is what type of joint?
|
ball and socket synovial joint
|
|
|
Acromioclavicular joint
|
plane-type joint
|
|
|
Movements of the shoulder joint?
|
abduction, adduction, anteversion (flexion), retroversion (extension), lateral and medial rotation, and circumduction
|
|
|
Fx of surgical neck of humorous = damage to what nerve?
|
axillary n.
|
|
|
Midshaft humerus injury = damage to what nerve?
|
radial n.
|
|
|
Fx of the medial epicondyle of humerus = damage to what nerve?
|
ulnar n.
|
|
|
Fx of distal end of humorous = damage to what nerve?
|
median n.
|
|
|
What passes through the spiral groove?
|
radial nerve and deep brachial vessels
|
|
|
Colles’ Fracture?
|
Fracture of the distal end of the radius, posterior displacement. Falling on hand with extended arm (eg.: falling on ice).
|
|
|
Colles Fx may be accompanied by?
|
May be accompanied by avulsion of ulnar styloid process.
|
|
|
most frequent bone to fracture among the carpal bones?
most dislocated carpal bone |
Scaphoid bone is the most frequent
bone to fracture among the carpal bones. Lunate is the most dislocated carpal bone |
|
|
Ulnar collateral ligament injury may lead to?
|
abnormal ABDuction of the forearm
|
|
|
Radial collateral ligament injury may lead to?
|
abnormal ADDuction of the forearm
|
|
|
What is Smith's Fracture?
|
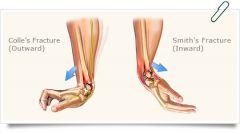
reverse Colles fx.
|
|
|
What is a pulled elbow?
|
aka Nursemaid's elbow, babysitter's elbow
small kids are abruptly pulled up by their arm; causes immature head of radius to dislocate from annular ligament resulting in painful pronation |
|
|
most frequently fractured carpal row?
most frequently and second most freq fractured carpal bone? |
the proximal row
scaphoid followed by triquetral |
|
|
Carpal bones articulate together to form a unit known as
|
the carpal groove
|
|
|
The carpal groove is covered by the ______ forming the ______
|
flexor retinaculum forming the carpal tunnel
|
|
|
Points of insertion of flexor retinaculum?
|
Tubercle of scaphoid, pisiform, tubercle of
Trapezium and hook of Hamate. |
|
|
pathology of carpal tunnel syndrome?
|
compression of median nerve
|
|
|
causes of carpal tunnel syndrome?
|
-pregnancy = increased progesterone = increased fluid
-amyloidosis = amyloid not eliminated = accumlation -hypothyroid = low metabolism = accumulation of fluid/fat -rheumatoid arthritis |
|
|
elbow joint is what type of joint? how many total joints at elbow?
|
synovial; 3 joints:
humeroulnar humeroradial proximal radioulnar |
|
|
wrist joint aka? type of joint?
|
aka radiocarpal joint
ellipsoid-type synovial joint |
|
|
Movement of the carpal joints by row?
|
first (proximal) row has some movement
second row has no movement |
|
|
First carpometacarpal joint type?
|
saddle joint: abduction, adduction, opposition, reposition, and circumduction
|
|
|
metacarpophalangeal joint type?
|
ball-and-socket synovial
restricted movement |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Deltoid |
NN: Axillary N. (C5- C6).
Function: Most important abductor of the arm up to 90 degree. |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Supraspinatus |
Abductor of the arm, belongs to the rotator cuff muscle group.
NN: Suprascapular N. (C4-C6) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Infraspinatus |
Lateral rotator of the arm
belongs to the rotator cuff muscle group. NN: Suprascapular N. (C5-C6) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Teres minor |
Lateral rotator of the arm,
Rotator cuff group, NN: Axillary (circumflex) N. C5-C6 |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Teres major |
adduction and medial rotator of arm
lower sub scapular n. (C6-C7) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Latissimus Dorsi |
medial rotation, extension, and adduction of arm; also coughing
thoracodorsal n. (C6-8) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
subscapularis muscle |
aids in arm adduction and medial rotation
subscapular n. (C5-7) |
|
|
Rotator cuff muscles?
|
supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis
|
|
|
Notable rotator cuff injury?
|
tendinopathy of the supraspinatus, calcification, pain, avulsion of greater tubercle
|
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Coracobrachialis M |
Flexion (anteversion) and adduction of arm,
Musculocutaneous N. (C5,C6,C7). |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Serratus Anterior |
elavation of arm over 90deg; protracts scapula; respiratory muscle
long thoracic nerve (C5-C7) |
|
|
Winged scapula differential?
|
can lift arm above 90deg = damage to dorsal scapular n. (rhomboids)
CANT lift arm above 90deg = damage to long thoracic n. (serratus ant.) |
|
|
What are the causes/signs/symptoms of axillary nerve injury?
|
fx to proximal humerus
limited arm abduction and damaged skin sensation |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Biceps Brachii |
Long head): abductor and medial rotator
of the arm Short head: adductor of the arm Both heads flex (anteroversion) shoulder joint On elbow joint: flexor and strong supinator of the forearm. NN: Musculocutaneous N. (C5- C6) |
|
|
Biceps Jerk?
|
Reflex that tests patency of Musculocutaneous nerve: C5-C6
part of brachial plexus |
|
|
hyperreflexia? indicative of?
|
exaggeration of reflexes
indicates possible upper motor neuron problem |
|
|
hyporeflexia? indicative of?
|
lack of reflex (little to none)
lower motor neuron disease |
|
|
Knee reflex root nerves?
|
L3-L4
|
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Brachialis notable feature? |
Powerful flexor of the elbow joint
NN: Musculocutaneous N. (C5- C6) and radial nerve to some of its lateral part HYBRID muscle |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Triceps Triceps Jerk? |
Function: Chief extensor of elbow joint
Long head acts on 2 joints: Retroversion and adduction of the arm Radial N. (C6- C7- C8) Triceps Jerk: C7- C8 |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Anconeus M: |
assists (extension of the elbow) triceps.
Innervation: Radial N.(C7- C8) |
|
|
common head of forearm flexors?
|
medial epicondyle of the humerus
|
|
|
common head for forearm extensors?
|
dorsal lateral epicondyle
|
|
|
Upper brachial plexus lesion aka? causes?
|
Erb-Duchenne paralysis (C5-C6): Traction on the arm at birth or falling on the shoulder may damage the upper part of the plexus (roots may be pulled out of spinal cord)
|
|
|
Signs of Erb Duchenne?
|
Signs: Deltoid and supraspinatus are paralyzed (no arm abduction)
Infraspinatus paralysis leads to medial rotation of the arm. Biceps and Brachialis are also paralyzed (no elbow flexion) . |
|
|
Lower brachial plexus lesion
|
Klumpke’s paralysis (C8-T1)
|
|
|
Klumpke’s paralysis (C8-T1)
|
Claw hand
Signs: Atrophic paralysis of the forearm and small muscles of hand (Claw hand) and often a sympathetic palsy: eg: a Horner’s syndrome |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Palmaris longus |
Flexes the hand toward the palm,
tenses the palmar aponeurosis, NN: Median N. (C7-T1) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Pronator Teres |
Function: pronation of forearm and flexion at elbow
NN: Median N. (C6- C7) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Flexor carpi radialis |
F: Palmar flexion and Radial abduction of hand
NN: Median N. (C6- C7) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Flexor digitorum superficialis |
Strong flexors of the finger (4 medial) joints;
also flexes the wrist , Runs in the carpal tunnel NN: Median N. (C7, C8, T1) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Flexor carpi ulnaris |
F: Hand (palmar) flexion and adduction
Runs outside of carpal tunnel. NN: Ulnar N. (C7- C8) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Flexor digitorum Profundus |
Runs through the carpal tunnel
Function: it is a flexor of the wrist, midcarpal, metacarpophalangeal and phalangeal joints NN: Median N. (ant. Interosseous branch) laterally (C8 and T1), Ulnar N. medially (C8- T1) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Flexor pollicis longus |
Runs through the carpal tunnel
Has it’s own tendon sheath Flexor of the terminal phalanx (thumb) NN: Median N. (ant. Interosseous branch) C8- T1 |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Pronator quadratus |
Pronates the forearm (with Pronator Teres)
Median N. (ant. Interosseous branch) C8- T1 |
|
|
Structures passing into the tunnel?
|
Flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus,
Flexor pollicis longus and Median nerve. Flexor carpi radialis has its own canal in the groove of trapezium. |
|
|
Palmarcarpal tendon sheeths fxn?
|
prevent friction between tendons in carpal tunnel
|
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Brachioradialis (beer drinking M.) |
It brings the forearm into midposition between
pronation and supination; in this position it acts as a flexor (forearm flexor) NN: Radial N. (C5- C6 and C7) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Extensor carpi radialis longus |
Extensor and abductor of hand at wrist joint
NN: Radial N. (C6- C7) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Extensor carpi radialis brevis |
Extensor and abductor of the hand at wrist joint
NN: Radial N. (deep branch) (C7- C8) |
|
|
Golfer elbow?
|
periostitits = inflammation of medial epicondyle
|
|
|
Tennis elbow?
|
back hand hitting = lateral epicondyle periostits
Tennis players can have both but usual lateral |
|
|
Extensor retinaculum?
|
Covers the carpal bones dorsally and has
septae which produce 6 tendon compartments through which tendon of the extensor muscles and the abductor pollicis longus pass. |
|
|
1st compartment?
|
abductor pollicis longus
extensor pollicis brevis |
|
|
2nd compartment?
|
extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis
|
|
|
Compartment 3?
|
Extensor pollicis longus
|
|
|
Compartment 4?
|
Extensor digitorum and extensor indicis
|
|
|
Compartment 5?
|
extensor digiti minimi
|
|
|
Compartment 6?
|
extensor carpi ulnaris
|
|
|
Thenar muscles? innervated by?
|
All by median n except adductor pollicis
Abductor polloicis brevis Flexor pollicis brevis Adductor Pollicis - deep branch of ulnar n. Opponens pollicis |
|
|
Hypothenar muscles? innervation?
|
All innervated by: deep branch of ulnar N. C8- T1:
Abductor digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi Opponens digiti minimi |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Palmar interossei: 3 muscles |
Function: Adduction of digits, assist lumbricals
Ulnar N. deep branch (C8-T1) |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Dorsal Interossei: 4 muscles |
Function: Abduction of digits
Ulnar N. (deep branch) C8- T1 |
|
|
Fxn & Innervation:
Lumbricals: 4 muscles |
2 lateral ones innervated by Median N. C8-T1
2 medial ones innervated by Ulnar N. C8-T1 |
|
|
Dupuytren’s contracture
|
progressive fibrosis, thickening and shortening of the palmar aponeurosis leads to partial flexion of the ring and small finger (dupuytren's contracture).
mimics claw hand but NO nerve damage |
|
|
Radial n injury at proximal origin of Triceps
|
Flexed elbow and wrist drop with flexed/adducted thumb
|
|
|
Sensory loss occurs where with proximal radial n injury?
|
dorsolateral lower brachial region
posterior forearm dorsal hand radial side of the proximal phalanges |
|
|
injury at the radial groove
what nerve? |
radial n injury (humerus fx)
triceps is working (already innervated) = elbow movement wrist drop present sensory loss in dorsolateral arm/hand |
|
|
forearm radial nerve injury
|
deep radial nerve is damaged
wrist drop no sensory loss |
|
|
Median Nerve injury
Above the elbow? |
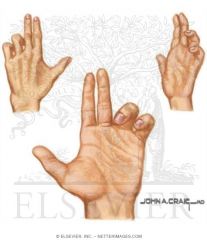
Muscles in the arm are not affected
Forearm and hand muscles are affected Flexors are mainly affected HAND OF PAPAL BENEDICTION Pronation of forearm paralyzed and sensory loss over the median N. area |
|
|
Median Nerve injury
Injury at wrist Joint |
APE Hand
(suicide or injury e.g.: hand out of car’s window) Short muscles of the thumb paralyzed, not adductor. Thenar muscles atrophy (flattened, APE HAND) Flexor pollicis longus functioning Sensory loss over Medial N. area |
|
|
Ulnar nerve injury
At wrist |
Claw hand
flexion of the ring and little finger is not possible at distal phalangeal joints Small muscles of the little finger are paralyzed Abduction and Adduction of the fingers are impaired ( paralysis of interossei MM, piano playing, writing.. Impaired) Sensory loss over ulnar innervating area. |
|
|
Ulnar nerve injury at elbow?
|
Injury at elbow:
Paralysis of flexor carpi ulnaris and medial portion of Flexor digitorum profundus hand is abducted and extended claw hand |
|
|
logic statement for papal benediction and ape hand?
|
any time you have papl benediction you have ape hand but when you have ape hand you don’t always have papal benediction
|
|
|
Upper limb blood supply start to radial/ulnar a.
|
Aorta > Subclavian > passes through scalene gap/below clavicle > axillary artery (6 branches) > passes margin or teres/lat dorsi > brachial artery (deep brachial a. branches posteriorly) > divides in elbow region into radial and ulnar
|
|
|
blood supply of upper limb from radial and ulnar
|
ulnar artery > interosseous artery
radial and ulnar artery join to form deep palmar arch and superficial palmar arches > palmar arteries |
|
|
6 Branches of the axillary a.?
|
SLAP STuff:
Superior Thoracic a. Lateral Thoracic a. Anterior Circumflex a. Posterior Circumflex a. Subscapular a. Thoracoacromial a. |
|
|
Breast Cancers may
give metastasis to the _____ |
axillary lymph node
|
|
|
Quaderangular space
Contents? Borders? |
Contents:
Axilary nerve Post. Circumflex humeral artery Borders: Teres Minor Teres Major Humerus Long head of Triceps |
|
|
Guyons canal?
|
ulnar nerve and vessels pass through between the two layers of the retinaculum (fig 6-40 pg 367)
located anteriorly |
|
|
Snuffbox: borders:
|
Tendon of extensor pollicis longus (superior)
tendons of the ext. pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus (inferiorly). |
|
|
Contents of snuffbox:
|
Radial artery
Superficial radial N. |
|
|
Snuff box picture
|
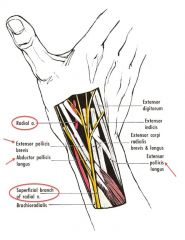
|
|
|
What goes through the carpal tunnel
|
flexor digitorum superficialis
flexor digitorum profundus flexor pollicis longus median n |
|
|
The flexor pollicis brevis is innervated by ?
|
median n. (superficial) and ulnar n. (deep)
hybrid |
|
|
Deep Radial n. runs between two heads of ____
|
supinator m
|
|
|
3 muscles that insert on coracoid process?
|
short head of biceps brachii
coracobrachialis pectoralis minor |
|
|
Volkmann's contracture?
|
ischemic contracture when brachial artery is lacerated or completely compressed for too long.
Causes loss of finger contraction & wrist flexion |

