![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
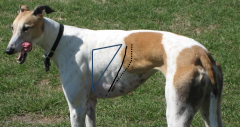
Name the features |
*Dottedline: lineof pleural reflection (~insertion of diaphragm on walls of thorax) *Solidline: caudal extent of the lungs during quiet breathing = cranial extent of costodiaphragmaticrecess (partof thoracic cavity that lung does not fill during quiet inspiration) * Auscultation-percussion triangle (moreuseful in LA) limitedby: triceps, epaxial m, thicknessof lungs caudally(thinnest lung is silent in normal animals) |
|
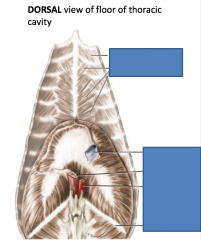
Name the muscles, inlets, and features |
From top to bottom: Intercostalis internus Transversus thoracis caudal vena cava(blue): caval foramen (in the central tendon) esophagus(left lighter pink): esophageal hiatus. The vagal trunks pass through this too. aorta(red): aortic hiatus. The thoracic duct and the azygos vein(as well as the hemiazygos vein) pass through this too. 13th rib Hiatus = gap in muscle belly |
|
What layers is the arrow passing through? |
•Skin -->costal parietal pleura -->visceral pulmonary pleura (entering lung) --> another layer of visceral pulmonary pleura (exiting that lung) --> mediastinal parietal pleura (entering mediastinum) --> another layer of mediatinal parietal pleura (exiting mediastinum) --> visceral pulmonary pleura entering and exiting other lung --> costal parietal pleura --> skin |
|

|
1=Mediastinal parietal plura 2=Connective tissue in mediastinal space 3=fibrous pericardium 4=Parietal Pericardium 5=viceral pericardium/epicardium 6=sternopericardial ligament(in LA). in SA, replaced by the phrenico-pericardiallig.) 7=pericardial cavity 8=sternum |
|
|
What is the order of layers surrounding the heart from most external to most internal? |
Mediastinal parietal pleura-->fibrous pericardium-->parietal pericardium-->fluid->visceral pericardium |
|
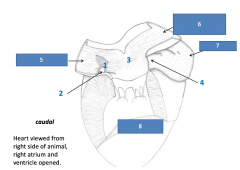
|
Right atrium has internalstructures you need to know 1.Fossa ovale (remnant of fetalforamen ovale) 2.Coronary sinus (openingof greatcardiac vein)3.Terminal crest5. Caudal vena cava 6. Cranial vena cava 7. Right auricle 8.Right ventricl |
|
|
Blood flow through heart |
•Cranialand caudal VC -->RA --> tricuspid valve --> RV --> pulmonary valve --> pulmonary artery--> lungs --> pulmonary vein--> LA--> mitral valve--> LV -->aorta |
|
|
Which aortic arch normally disappears? |
•Right *Persistentright aortic arch=restricted esophagus |
|
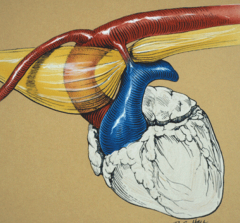
What is happening here? |
•Persistentright aortic arch(PRAA)=restricted esophagus |
|
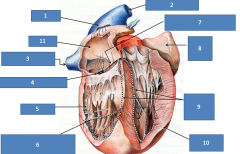
|
1)Sinoatrialnode2)Cranial vena cava3)Caudal vena cava4)Atrioventricular node5)Right ventricle6)Trabecula septomarginale( found in both LV and RV)7)Atrioventricular bundle8)Left auricle9)Left & right bundle branches10)L ventricle11)Right atrium |
|
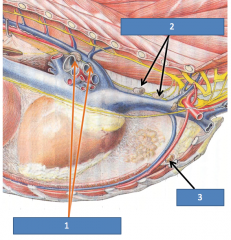
|
Thoracic lymphocenter 1)tracheobronchial lns(FYIO:left, middle & right)drain lungs 2)cranial mediastinal lnsdrain mediastinum, lungs 3)sternal lnsdrain chest wall, diaphragm, crmammary glandsand specifically the third (middle) pair of mammary glands in dogs. |
|
|
What is the name for any lymph node found near the jugular vein and carotid sheath? |
deep cervical lymph node |
|
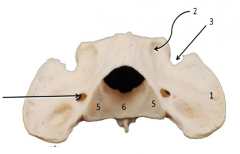
|
1Wing/transverse process of atlas(c1) 2lateral vertebral foramen 3alar notch 5caudal articular surface 6fovea dentis extra arrow:transverse foramen(vertebral vein, art., and nerve) |
|
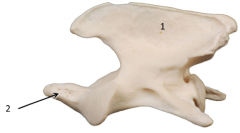
|
1) spinous process 2)dens(articulates with body of atlas dentis&is embryologically from the atlas C2=axis |
|
|
The pes is only composed of the: A.Tarsus and metatarsals B.Tarsus only C.Tarsus, metatarsals and digits D.Tarsus, tibia, and fibula E.Fibula and tibia |
C |
|
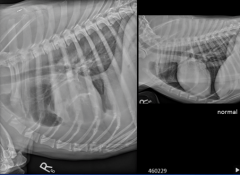
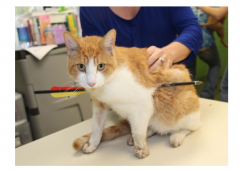
What is wrong with this dog?
A.Airin the pleural cavity B.Fluidin the lungsC.Fluidin the pleural cavity D.Fatin the thoracic cavity |
C |
|
|
What does the mediastinum include? |
•Trachea•Esophagus•Thymus•Heart •Greatvessels•Nerves•Lymph nodes |
|

|
1.Thymus2.Heart3.Phrenicnerve4.esophagus |
|
|
What divides the thoracic cavityinto L and R sides? |
•Mediastinum |
|
|
Define the thoracic cavity |
•spacebetween thoracic inlet, ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and diaphragm caudally |
|
|
What are the inspiratory muscles? |
•Scalenus•Externalintercostals (when breathing deeply or hard)•Cranialdorsal serratus•Rectusthoracis•Diaphragm(most important) |
|
|
What are the expiratory muscles |
•Internalintercostals•Caudaldorsal serratus•Transversusthoracis (inside chest) |
|
|
What happens when the diaphragmcontracts? |
•Thedome flattens out, increasing the size of the thoracic cavity |
|
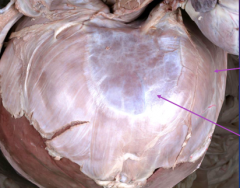
What are the arrows pointing to? |
Top=muscular periphery bottom=tendinous center of the diaphragm |
|
|
What are the diaphragmatic hiatuses? |
•CaudalVena Cava: cavalforamen•Esophagus:esophagealhiatus (including the vagal trunk)•Aorta:aortichiatus (including the thoracic duct,azygos vein, and hemiazygos vein) |
|
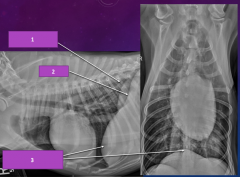
|
1)right crus 2)left crus 3)dome of diaphragm |
|
|
Define Pleura and Pleural Cavity |
•Thethin continuous serous membrane lining the walls of the thoracic cavity(including the mediastinum), and covering the lungs. Because it is continuousand folded upon itself, it is like a bag interposed between the lungs and thewalls of the thoracic cavity•Bonusquestion: what does the inside of the “bag” form?•Pleuralcavity (only contains a few mLs ofpleural fluid) |
|
|
What does the visceral pleuracover? |
•Directlycovers the lungs and other organs such as the thymus |
|
|
What does the parietal pleuracover? |
•Coversthe walls of the thoracic cavity including the mediastinum |
|
|
What does the costal pleura cover? |
ribs and intercostal muscles |
|
|
What does the diaphragmatic pleuracover? What about the pulmonary pleura? |
diaphragm lungs |
|
|
What two components make up thefolds of the pleura? |
•Pulmonaryligament•PlicaVena Cava |
|
|
Is inspiration passive or active? |
active |
|
|
What links the parietal andvisceral pleurae? |
pleural fluid |
|
|
Inspiration: |
•Contractionof external intercostals (and ventral part of internal intercostals) rotatesribs cranially (like a bucket handle), widening the chest.•Thediaphragm contracts and flattens (like an opening umbrella), lengthening thethoracic cavity.•Thethoracic cavity thus gets larger.•Theparietal and visceral pleurae are linked by the pleural fluid and passivelyfollow, pulling the lungs after them. |
|
|
What occurs during expiration? |
•Musclesrelax, and the thoracic cavity returns to its normal size.•Lungspartially collapse, expelling air. |
|
|
What are the 2 breath components of the lungs that are not visible with external dissection? |
•Airways(tracheobronchial tree)•Parenchyma(gas exchange units) |
|
|
T/f The left lung has 4 lobes. |
•FALSE!•Leftlung has 2 lobes•Cranialand caudal•Rightlungs has 4 lobes•Cranial•Middle•Caudal |
|
|
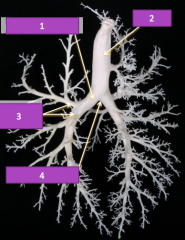
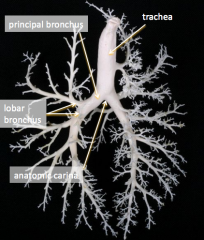
What are the major components of the lungs?* check echo lecture from 10/12 to clarify |
•Principalbronchi•6lobar bronchi, one for each lobe •Manygenerations of smaller bronchi•Bloodvessels (pulmonary arteries and veins) follow the bronchi |
|
|
|
|
|
What is the cupula pleurae? *check this |
•Extensionof both pleural sacs cranial to the thoracic inlet |
|
|
What are the limits of theauscultation-percussion triangle? |
•Triceps•Epaxial m•Thicknessof lungs caudally (thinnest lung is silent in normal animals) |
|

|

|
|

|
Persistant/patent ductusarteriosus (PDA) is the most common congenital heart defect in dogs |
|
|
Which of the following is not a structure on the ulna? a. Medial coronoid process b. Anconeal process c. Lateral styloid process d. Medial styloid process e. Lateral coronoid process |
D. The medial styloid process is on the radius |
|
|
True/false: The supratrochlear foramen is a hole passing through the distal end of the humerusthrough which several tendons pass. |
False. No structures pass through it, but it receives the anconeal process of the ulna. *Supracondylar foramen in cats allows for passage of the brachial vessels and the median nerve. |
|
|
Which of the following is not a structure in the humerus? a. Trochlea b. Capitulum c. Supratrochlear foramen d. Medial condyle e. Radial fossa |
D. Medial condyle is on the femur. In the humerus, the humeral condyle consists of trochlea, fossae,epicondyles and capitulum |
|
|
True/false: Each metacarpus has a proximal head and a distal base. |
False. The Head is distal and the base is proximal. They are named for shape and not position. |
|
|
Which of the following muscles does not originate somewhere on the scapula? a. Subscapularis b. Biceps brachii c. Trapezius d. Omotransversarius e. Deltoideus |
C. Trapezius inserts there |
|
|
The radioulnar joint is a ________ joint that causes the movements _________ and _________. |
pivot,supination, pronation |
|
|
What 3 joints are combined in the elbow joint? Which bears most of the weight? Which providesstability? |
Hinge joint between humerus/radius, hinge joint between humerus/ulna, and pivotal joint between radius/ulna. All 3 are contained in a common capsule. Humeroradial bears the most weight. |
|
|
Which of the following muscles does not have the action of flexing the shoulder joint? a. Deltoideus b. Supraspinatus c. Teres Minor d. Triceps brachii long head e. Teres major |
B. The supraspinatus extends and stabilizes the shoulder |
|
|
Which of the following is not innervated by the accessory nerve? a. Trapezius b. Omotransversarius c. Latissimus dorsi d. Brachiocephalicus |
C. The latisimus dorsi is innervated by the thoracodorsal nerve |
|
|
Which of the following does not pass through the carpal canal? a. Median nerve b. Median artery c. Deep digital flexor d. Common digital extensor tendon |
D. The carpal Canal is on the Palmer surface whereas the common digital extensor tendon is on the dorsal surface. |
|
|
Which of the following inserts the most distally? a. Superficial digital flexor b. Deep digital flexor c. Flexor carpi ulnaris d. Flexor carpi radialis |
B. the deep digital flexor inserts on PIII
|
|
|
If you pinch the lateral digit, you are testing the _______ nerve. |
ulnar |
|
|
The os coxae are each made up of 3 bones called ______, _______, and _______. All 3 plus afourth ________ bone contribute to the acetabulum. The conceptual hole formed by the os coxae andthe sacrum is the ________ ________ caudally and the ________ _______ cranially. |
pubis, ilium, ischium. Acetabular. Pelvic outlet, pelvic inlet. |
|
|
There are 3 trochanters on the ______. Which are medial and which are lateral? |
Femur. The greater trochanter and third trochanter are on the lateral surface of the femur whereas the lesser trochanter is on the medial surface.
|
|
|
True/false: The femur is similar to the humerus because they both have 2 epicondyles, 2 condyles,and a trochlea. |
False. The humorous only has one condyle which is really referring to the total distal extremity.
|
|
|
There are 3 gluteal muscles. Which originates only on the ilium? Which two insert on the greatertrochanter of the femur? Which one is not innervated by the cranial gluteal nerve? |
Middle gluteal. Deep & middle. Superficial gluteal.
|
|
|
What muscles rotate the limb literally at hip? |
Internal obturator, external obturator, quadratus femoris, gemelli
|
|
|
What nerve innervates the adductor, pectineus, and gracilis? |
obturator |
|
|
What is the action of the popliteus? |
Rotate the leg medially and flexed the stifle
|
|
|
What does the fibular (peroneal) nerve innervate? Also, each of these muscles has 2 functions.One function is common to all- what is it? |
Cranial tibial, Long digital extensor, fibularis longus. All flex the tarsus.
|
|
|
Why do guys hate the gracilis, pectineus, and adductor? |
They keep your legs closed(adduct the limb). Damn PAG
|
|
|
How can the Sartorius both flex and extend the stifle joint? |
The cranial part extends the stifle joint whereas the Cauda part flexes the stifle joint. The sartorius also flexes the hip joint.
|
|
|
What are the 5 components of the common calcanean tendon? |
Gastroc, superficial digital flexor, biceps femoris, semitendinosus, gracilis |
|
|
Ifa cranial drawer is apparent in a dog’s hind limb, what is affected? a. Caudal cruciate ligament b. Cranial cruciate ligament c. Medial collateral ligament d. Patellar ligament |
B |
|
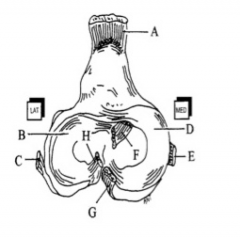
Which letter represents the caudal cruciate? The patellar ligament? |
G,A |
|
|
Thesupratrochlear foramen receives the… a. Medial artery b. Radial nerve c. Anconeal process d. Olecranon process |
C |
|
|
T/F:The humerus has medial and lateral condyles. |
False |
|
|
Whatpasses through the supracondylar foramen of a cat? a. Brachial vessels and median nerve b. Brachial vessels and radial nerve c. Axillary nerve d. None of the above |
A |
|
|
Thetendon of origin of which muscle contain fabella? a. Quadriceps b. Superficial digital flexor c. Gracilis d. Gastrocnemius |
D |
|
|
There are _____ rows of carpal bones and _____rows of tarsal bones. a. 4, 3 b. 2, 3 c. 3, 4 |
B |
|
|
Inwhich direction is the elbow more likely to dislocate due to an injury? a. Lateral b. Medial c. Cranial d. Caudal |
A |
|
|
The popliteal sesamoid articulates with the_______ tibial condyle. a. Medial b. Lateral c. Inferior d. Cranial |
B |
|
|
Wheredoes the axillary artery become the brachial artery? a. At the teres tuberosity b. At the ulnar tuberosity c. At the olecranon fossa d. At the glenoid fossa |
A |
|
|
Which artery in the forelimb passes through thecarpal canal, enabling blood supply even if the paw is caught in a trap? a. Brachial b. Ulnar c. Median d. Axillary |
C |
|
|
Whatis the preferred site for venipuncture in the forelimb? a. Cephalic vein b. Saphenous vein c. Ulnar vein d. Deep brachial vein |
A |
|
|
What is the preferred site for venipuncture inthe hindlimb of a dog? a. Femoral b. Lateral Saphenous c. Cranial tibial d. Medial Saphenous |
B |
|
|
What is the preferred site for venipuncture inthe hindlimb of a cat? a. Femoral b. Lateral Saphenous c. Cranial tibial d. Medial Saphenous |
D |
|
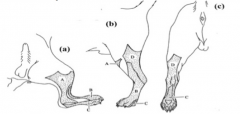
1. Ifyou were to pinch the shaded area labeled A and got no response from the dog,which nerve has been injured? a. Tibial b. Fibular c. Sciatic d. Saphenous 1. Ifyou pinched the shaded area labeled B and got a response from the dog, youcould safely assume that which nerve is still intact?a. Tibial b. Fibular c. Sciatic d. Saphenous |
D,B |
|
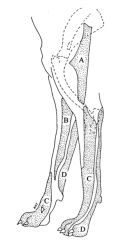
1. Ifyou pinched the shaded area labeled D and got a response from the dog, you couldsafely assume that which nerve is still intact? a. Ulnar b. Radial c. Axillary d. Musculocutaneous 2. Ifyou were to pinch the shaded area labeled B and got no response from the dog, whichnerve has been injured? a. Ulnar b. Radial c. Axillary d. Musculocutaneous |
A,D |
|
|
Ifan animal is unable to bear weight on its forelimb, which nerve is likelyinjured? a. Radial b. Axillary c. Ulnar d. Musculocutaneous |
A |
|
|
Whichmain ligament runs from the transverse processes of the last sacral and firstcaudal vertebrae to the ischiatic tuberosity? a. Sacroiliac b. Sacrotuberous c. Transverse acetabular d. Pubosacral |
B(not in cats) |
|
|
Theextensor retinaculum of the forelimb secures all the these tendons EXCEPT: a. Extensor carpi radialis b. Common digital extensor c. Long digital extensor d. Lateral digital extensor e. Ulnaris lateralis |
c |
|
|
Whichstructure forms the roof of the carpal canal? a. Flexor retinaculum b. Extensor retinaculum c. Superficial digital flexor d. Deep digital flexor |
A |
|
|
Thepatella glides in the _________ groove. a. Femoral b. Tibial c. Trochlear d. Patellar |
C |
|
|
Inwhich direction is the head of the femur generally displaced when it isdislocated? a. Ventral & cranial b. Dorsal & cranial c. Medial & caudal d. Ventral & caudal |
B |
|
|
Thesupraspinatous and infraspinatous muscles both insert on the ___________ andare both innervated by ____________ nerve. a. Lesser tubercle of the humerus; subscapular b. Olecranon process; accessory c. Greater tubercle of the humerus; suprascapular d. Head of the humerus; suprascapular |
C |
|
|
Allof the following muscles play a role in stabilizing the shoulder joint EXCEPT: a. Infraspinatous b. Latissimus dorsi c. Subscapularis d. Supraspinatus |
B |
|
|
Theorigin of the brachiocephalicus is the… a. Atlas b. Spine of the scapula c. Clavicular tendon d. Greater tubercle of humerus |
C |
|
|
Allof the following muscles are innervated by the radial nerve EXCEPT: a. Biceps brachii b. Triceps brachii c. Extensor carpi radialis d. Lateral digital extensor |
A |
|
|
Whichof the following muscles originate on the medial epicondyle of the humerus? a. Superficial digital flexor b. Flexor carpi radialis c. Ulnaris lateralis d. Deep digital flexor e. A and B f. A, B, and D g. A, C, and D h. All of the above |
F |
|
|
1. T/F:The internal iliac artery gives rise to the caudal gluteal artery. 2. T/F:If the sciatic nerve is cut, the dog will not be able to bear weight on theaffected hind limb. |
True, false |
|
|
Whichgluteal muscle is innervated by the caudal gluteal nerve and inserts on the 3rdtrochanter of the femur? a. Middle b. Deep c. Superficial d. Lateral |
C |
|
|
Allof these muscles insert on the greater trochanter of the femur EXCEPT: a. Deep gluteal b. Superficial gluteal c. Middle gluteal |
B |
|
|
1. Which4 muscles are innervated by the obturator nerve? |
Pectineus, adductor, gracilis, external obturator(Page the Obturator) |
|
|
1. Allof the following muscles make up the calcaneon tendon EXCEPT: a. Biceps femoris b. Semitendinosus c. Semimembranosus d. Gastrocnemius e. Superficial Digital Flexor f. Gracilis |
C; Big STupid Giraffes SUck Grapes |
|
|
1. Whichof the following is NOT innervated by the sciatic nerve? a. Semitendinosus b. Internal obturator c. Quadriceps femoris d. Semimembranosus |
C |
|
|
1. Whichmuscle is the major flexor of the hip? a. Iliopsoas b. Pectineus c. Gracilis d. Adductor |
A |
|
|
1. Whatis the major action of the cranial tibial muscle? a. Flex carpus b. Flex digits c. Flex tarsus d. Flex stifle |
C |
|
|
Thedeep digital flexor of the hindlimb inserts on the _______ phalanges. a. Proximal b. Distal c. Lateral d. Medial |
B |
|
|
Whichof the following extends the tarsus AND flexes the stifle joint? a. Gastrocnemius b. Long digital extensor c. Gracilis d. Deep digital flexor |
A |
|
|
Forelimb arteries: |
Subclavian > Axillary > Brachial > (ulnarbranches off) > Median > (Radial branches off) |
|
|
Hindlimb arteries: |
Externaliliac > Femoral > (Saphenous branches off) > Popliteal > CranialTibial > Dorsal Pedal |
|
|
Ifan animal is unable to bear weight on its hind limb, which nerve is likelyinjured? a. Obturator b. Saphenous c. Sciatic d. Femoral |
D |

