![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
State the two functions of the crystalline lens |
Provides +20.00D approx of the refractive power of the eye to focus images clearly onto the macula Change shape in accommodation to become more powerful |
|
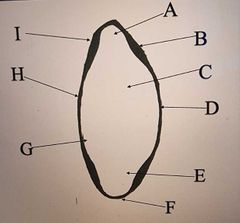
Label the Crystalline Lens |
A: Lamellae of fibres/cortex B: Capsule thickens at insertion of zonular fibres C: Lens Nucleus D: Posterior Pole E: Lens Bow F: Equator (new cells formed here) G: Cuboidal Epithelium (single layer) H: Anterior Pole (thinnest region of capsule) I: Lens Capsule |
|
|
Where does the Capsule thickness increase towards? |
The equator |
|
|
Where does the crystalline lens sit? |
The patellar Fossa |
|
|
What is the radii of curvature of the lens anteriorly and Posteriorly. Include unaccomodated and accommodated states |
Unaccommodated: Anterior: 10mm Posterior: 6mm approx Accommodated Anterior: 6mm Posterior: 6mm approx |
|
|
What is the thickness of the crystalline lens? |
4mm approx |
|
|
What is the horizontal diameter of the crystalline lens? |
9mm approx |
|
|
What is the refractive index of the lens at the cortex and at the Nucleus? |
Cortex: 1.36 - 1.38 Nucleus: >~1.4 |
|
|
Why does the refractive index of the lens increase towards the Nucleus? |
Denser concentrations of fibres towards the Nucleus |

