![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
206 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Skeletal system components |
Bones Cartilage, ligaments, and connective tissues |
|
|
Skeleton functions |
Support, protection, movement, storage, hematopoiesis |
|
|
Long bone |
-Greater in length than width -shaft with heads situated at both ends -mostly compact -includes all of the bones of the limbs except for wrist, ankle, and kneecap -plate fuses or ossifies at "bone maturity" and is then an epiphyseal line |
|
|
Flat bone |
Plate like Has 2 thin layers of compact bone surrounded by a layer of spongy bone |
|
|
Short bone |
Width and length about the same |
|
|
Sesamoid |
A type of short bone within a tendon (patella) |
|
|
Irregular bone |
No real category (vertebrae) |
|
|
Diaphysis bone |
Shaft, primarily compact |
|
|
Epiphysis |
Ends of long bone, covered with articular cartilage |
|
|
Metaphysis |
Neck |
|
|
Epiphyseal plate |
Growth plate, the site of growth in length of a long bone |
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Produce new bone, make matrix |
|
|
Osteocytes |
Mature bone cells in lacuna, maintain matrix |
|
|
Osteoclasts |
Reabsorb or breakdown bone. Make protons and enzymes |
|
|
Osteoprogenitor |
Stem cell whose divisions produce osteoblasts |
|
|
Tensile strength |
Made by collagen fibers |
|
|
Compressive strength |
Given by hydroxyapetite (Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2) |
|
|
Removing collagen |
Makes brittle bones |
|
|
Removing minerals |
Makes overly flexible bone |
|
|
Compact bone |
Dense, more matrix, less space |
|
|
Lamella |
Collagen arranged in a pattern. |
|
|
Osteon |
Structural unit of compact bone |
|
|
Spongy bone |
Cancellous, less matrix, more space |
|
|
Bone struts |
Trabeculae |
|
|
Diploe |
Flat bones |
|
|
Woven bone |
Random arrangement of collagen fibers. In fetal development |
|
|
Lamellar |
Mature bone. Collagen fibers are parallel to each other and at angles to other lamella |
|
|
Inrramembranous bone growth |
Bone development occurs by replacing membrane with bone |
|
|
Endocbondral bone growth |
Replacing the line cartilage with bone |
|
|
Outer connective tissue sheath |
Periosteum |
|
|
Inner cavity sheath |
Endosteum |
|
|
Chondroblast |
Cell that produces matrix |
|
|
Chondrocyte |
Mature cell in space "Laguna", makes matrix |
|
|
First stage of bone growth |
Hyaline cartilage model |
|
|
Second stage of bone growth |

|
|
|
Third stage of bone growth |

|
|
|
Fourth stage of bone growth |

|
|
|
Final stage of bone growth |

|
|
|
Zones of growth |
Resting (distal) Growth cartilage -hypertrophy Calcification Ossification |
|
|
2 hormones that control calcium levels |
Parathyroid hormone Calcitonin (thyroid) |
|
|
Parathyroid hormone |
Released when blood calcium levels are low |
|
|
Calcitonin |
Released when blood calcium levels are high |
|

|
Epiphyseal artery and vein |
|

|
Metaphyseal artery and vein |
|

|
Periosteum |
|

|
Compact bone |
|

|
Medullary cavity |
|

|
Branches of nutrient artery and vein |
|

|
Periosteum |
|

|
Periosteal arteries and veins |
|

|
Periosteal arteries and veins |
|

|
Connections to superficial osteons |
|

|
Nutrient artery and vein |
|

|
Nutrient foramen |
|

|
Metaphysis |
|

|
Epiphyseal line |
|

|
Metaphyseal artery and vein |
|

|
Cirfumfrential lamellae |
|

|
Osteons |
|

|
Percolating fibers |
|

|
Vein |
|

|
Artery |
|

|
Arteriole |
|

|
Central canal |
|

|
Percolating canal |
|

|
Trabecular of spongy bone |
|

|
Concentric lamellae |
|

|
Interstitial lamellae |
|

|
Periosteum |
|

|
Capillary |
|

|
Venule |
|
|
Bone healing steps |
1) hematoma 2) callus-soft 3) callus-hard, woven 4) remodeling- mature bone |
|
|
Osteoporosis |
Bone loss disease where bone respiration exceeds bone deposition. Common in post-menopausal women because estrogen inhibits osteoclasts |
|
|
Paranasal sinuses |
Hollow portions of bones surrounding the nasal cavity |
|

|
Maxillary sinus |
|

|
Sphenoidal sinus |
|

|
Ethmoid sinus |
|

|
Frontal sinus |
|
|
Fontanelle |
The infant skull. Areas between bone are fibrous connective tissue |
|
|
Vertebral column |
Spine. Protects spinal cord. |
|
|
Sacrum |
5 fused in spine |
|
|
Coccyx |
3-5 fused |
|
|
Curvature of vertebral column |
Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral |
|
|
Abnormal curves |
Hyperlordosis, hyperkyphosis (anterior posterior) Scoliosis (lateral) |
|
|
Joints |
Articulation where two or more bones meet |
|
|
Joint functions |
Holds bones together and allow for mobility |
|
|
Synarthroses |
Immovable joints |
|
|
Amphiarthroses |
Slightly movable joints |
|
|
Diarthroses |
Freely movable joints |
|
|
Fibrous joints |
Generally immovable |
|
|
Cartilaginous joints |
Immovable or slightly movable |
|
|
Synovial joints |
Freely movable |
|
|
Distinguishing features of synovial joints |
Articular cartilage Articular capsule Joint cavity Reinforcing ligaments |
|
|
Accessory structures of synovial joints |
Tendons Ligaments Capsule Bursa |
|
|
Tendon |
Attach to muscles around joint |
|
|
Ligament |
Attach bone to bone |
|
|
Capsule |
Surrounds the joint and is lined by synovial membrane |
|
|
Bursa |
Flattened sacs of synovial membrane |
|
|
Weight bearing part of spine |
Joints anterior to spinal cord |
|
|
Movement part of spine |
Joints posterior to spinal cord |
|
|
Parts of discs between vertebrae |
Inner gel like nucleus pulposis and outer annular fibers |
|
|
Gout |
Uric acid crystals |
|
|
Arthritis |
All forms of rheumatism that damage articular cartilage of synovial joints |
|
|
Osteoarthritis |
Caused by wear and tear of joint surfaces or genetic factors affecting collagen formation |
|
|
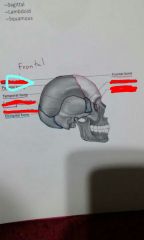
Coronal structure |
|

|
Lambdoid sature |
|

|
Squamous suture |
|

|
Ethmoid bone |
|

|
Sphenoid bone |
|

|
Sphenoid bone |
|

|
Ethmoid bone |
|

|
Mandible |
|

|
Maxilla |
|

|
Vomer |
|

|
Inferior nasal concha |
|

|
Middle nasal conch of ethmoid bone |
|

|
Zygomatic bone |
|

|
Lacrimal bone |
|

|
Mental foramen |
|

|
Perpendicular plate |
|

|
Middle nasal concha of ethmoid bone |
|

|
Inferior orbital |
|

|
Optic canal |
|

|
Superior orbital fissure |
|

|
External acoustic meatus |
|

|
Mastoid process |
|

|
Styloid process |
|

|
Foramen rotundum |
|

|
Internal acoustic meatus |
|

|
Foramen magnum |
|

|
Jugular foramen |
|

|
Foramen spinosum |
|

|
Foramen ovale |
|

|
Sella turcica |
|

|
Optic canal |
|

|
Crista galli |
|

|
Cribriform plate |
|

|
Jugular foramen |
|

|
Occipital condyle |
|

|
Ptertgoid processes |
|

|
Palatine bone |
|

|
Cribniform plate |
|

|
Perpendicular plate |
|

|
Middle nasal concha |
|

|
Crista galli |
|

|
Lesser wing |
|

|
Orbital surface of greater wing |
|

|
Pterygoid canal |
|

|
Pterygoid process |
|

|
Medial plate |
|

|
Lateral plate |
|

|
Foramen rotundum |
|

|
Greater wing |
|

|
Superior orbital fissure |
|

|
Sphenoid |
|

|
Sphenoid sinus |
|

|
Sphenoid spine |
|

|
Sella turcica |
|

|
Optic groove |
|

|
Posterior clinoid process |
|
|
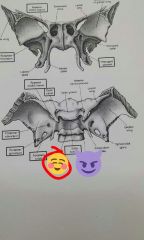
Dorsum sellae |
|

|
Mandibular notch |
|

|
Mandibular condyle |
|

|
Ramus of mandible |
|

|
Mandibular angle |
|

|
Body of mandible |
|

|
Alveolar margin |
|
|
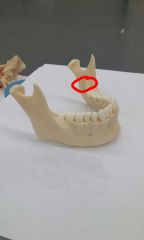
Mandibular foramen |
|

|
Mandibular does a of temporal bone |
|

|
Coronoid process |
|

|
Mandibular fossa of temporal bone |
|
|
Muscle tissue function |
Contraction |
|
|
Skeletal muscle functions |
Produce skeletal movement, maintain body position Support soft tissues Guard openings Maintain body temperature Store nutrient reserves |
|

|
Blood vessel |
|

|
Perimysium |
|

|
Epimysium |
|

|
Bone |
|

|
Endomysium |
|

|
Tendon |
|

|
Fascicle |
|

|
Muscle fiber |
|
|
Sarcoplasm |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
Sarcolemma |
Plasma membrane |
|
|
Transverse tubule |
Invagination of sarcolemma |
|
|
Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
Specialized ER that stores and releases calcium, surrounding myofibrils |
|
|
Terminal cisterna |
Enlarged sacs of SR near transverse tubules |
|

|
Mitochondria |
|

|
Sarcolemma |
|

|
Myofibril |
|

|
Thin filament |
|

|
Thick filament |
|

|
Triad |
|

|
Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|

|
T tubules |
|

|
Myofibrils |
|

|
Sarcoplasm |
|

|
Sarcolemma |
|

|
Terminal cisterna |
|
|
Contraction proteins |
Actin and myosin |
|
|
Regulatory |
Troponin and tropomyosin |
|
|
Muscle contraction |
Calcium release initiates this and results in conformational change |
|
|
Bone matrix makeup |
65% inorganic 35% organic |
|
|
Haversian system |
Compact vs spongy bone classification |
|
|
Joint classification |
Function and structure |
|
|
Sprain |
Ligament or capsule injury |
|
|
Strain |
Muscle or tendon injury |

