![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
165 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
abrasion |
a scraping or rubbing away of the skin due to friction |
|
|
abscess |
abscess a localized collection of puss in any part of the body.
|
|
|
bedsore (decubitus ulcer) |
an ulcer in the skin over a bony part of the body resulting from a loss of blood supply and oxygen to the area due to pressure on that part of the body. |
|
|
boil |
inflammation of the hair follicles and sebaceous glands, usually by Staphylococcus and streptococcus. |
|
|
callus |
a common, usually painless thickening of the epidermis at sites of external pressure or friction. |
|
|
carbuncle |
inflammation of the skin and deeper tissue containing pus and discharges to the surface. |
|
|
cellulitis |
a diffuse acute infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue having localized heat, deep redness, pain, and swelling. |
|
|
chicken pox |
tiny pustules by herpes varicella, currently preventable by vaccination. |
|
|
contact dermatitis |
itching, redness, and swelling,progressing to blister formation due to contact with chemicals, or poison ivy. Includes diaper rash. |
|
|
contussion |
an injury to a part of the body without a break in the skin |
|
|
corn |
a callus grown inward |
|
|
cryosurgery |
a noninvasive treatment for non-melanoma skin cancer using liquid nitrogen which freezes the tissue. |
|
|
cyst |
a closed sac or pouch in or within the skin that contains fluid, semi-fluid, or solid material. |
|
|
debridement |
removal of debris, foreign objects, and damaged or necrotic tissue from a wound in order to prevent infection and to promote healing. |
|
|
dermatitis |
inflammation of the skin |
|
|
diaphoresis |
the secretion of sweat |
|
|
eczema |
an acute or chronic inflammatory skin condition having erythema, papules, vesicles, pustules, scales, crusts, or scabs with intense itching. |
|
|
exfoliation |
peeling off of tissue cells, as in peeling of the skin after a severe sunburn |
|
|
exoderma pigmentosum |
sun exposure causing extreme freckling |
|
|
fifths disease |
begins with a slapped cheek appearance followed by red spots all over the body lasting for two days caused by HPV. |
|
|
folliculitis |
inflammation of the hair follicle |
|
|
furuncle |
a localized pus- producing infection origination deep in the hair follicle, a boil. |
|
|
gangrene |
death of tissue |
|
|
ichthyosis |
an inherited dermatological condition in which the skin is dry,hyperkeratotic, and fissured, like fish scales. 3 manifestations exist. |
|
|
impetigo |
contagious superficial skin infection characterized by serous vesicles and pustules filled with millions of staphylococcus or streptococcus bacteria, usually forming on the face. |
|
|
keloid |
an enlarged, irregularly shaped and elevated scar that forms due to the presence of large amounts of collagen during the formation of the scar. |
|
|
laceration |
a tear in the skin |
|
|
lesion |
any visible damage to the tissues of the skin, such as a wound,sore, rash, or boil. |
|
|
liver spots |
harmless brown spots on the back of hands, usually found on the elderly, due to increased pigmentation, not due to liver problems. |
|
|
lyme's disease |
large rash resembling a bull's eye on the thighs or trunk caused by a tick |
|
|
mast cell |
a cell, found within the connective tissue, that contains heparin and histamine; these substances are released from the mast cell in response to injury or infection. |
|
|
necrosis |
degeneration of tissue |
|
|
nevus |
a mole |
|
|
onycholysis |
separation of the fingernail from its bed |
|
|
pachyderma |
abnormal thickening of the skin |
|
|
paronychia |
inflammation of the fold of the skin surrounding the fingernail, also called run-around. |
|
|
pediculosis |
infestation with lice |
|
|
pimple |
a papule of the skin |
|
|
polyp |
a small, stalk-like growth that protrudes upward or outward from a mucous membrane surface, like a mushroom stalk |
|
|
pores |
openings of the skin through which substances such as water, salts, and some fatty substances are excreted |
|
|
pruritus |
itching |
|
|
psoriasis |
a common,noninfectious, chronic disorder of the skin manifested by silvery-white scales over round, raised, reddened plaques producing pruritus. |
|
|
pustule |
a small elevation of the skin filled with pus, a small abscess |
|
|
scarlet fever |
sunburn like rash that begins near the ears and spreads to the face and abdomen caused by streptococcus pyogenes |
|
|
sebaceous cyst |
a cyst filled with a cheesy material composed of sebum and epithelial debris that has formed in the duct of a sebaceous gland, also known as an epidermoid cyst. |
|
|
seborrhea |
excessive secretion of sebum , resulting in excessive oiliness or dry scales |
|
|
skin tags |
a small brownish colored or flesh colored outgrowth of skin occurring frequently on the neck. |
|
|
systematic lupus erythematosus (SLE) |
a chronic, multisystem, inflammatory disease characterized by lesions of the nervous system and kin, renal problems, an vasculitis. (butterfly rash on face) |
|
|
tinea |
ringworm; a chronic fungal infection of the skin that is characterized by scaling, itching, and sometimes painful lesions |
|
|
tinea capiitis |
ringworm of the scalp |
|
|
tinea corporis |
ringworm of the body |
|
|
tinea cruris |
ringworm of the groin |
|
|
tinea pedis |
ring worm of the foot or athlete's foot |
|
|
vesicle |
a small, thin-walled, skin lesion containing clear fluid;a blister |
|
|
vitiligo |
a skin disorder characterized by non-pigmented white patches of skin of varying sizes that are surrounded by skin with normal pigmentation. |
|
|
wart |
a benign, elevated skin lesion that results from hypertrophy of the epidermis; caused by HPV |
|
|
wheal |
a circumscribed, slightly elevated lesion of the skin that is paler in the center that its surrounding edges; hives |
|
|
hemagioma |
blood-like blister that comes to surface |
|
|
hypertrichosis |
a genetic disorder, excessive growth of hair |
|
|
tinea versicolor |
white patches
|
|
|
tinea barbae |
ringworm of the beard |
|
|
dorsal |
pertaining to the back |
|
|
ventral |
pertaining to the underside |
|
|
lateral |
to the side |
|
|
ipsilateral |
same side |
|
|
contralateral |
opposite sides |
|
|
anterior |
front end |
|
|
posterior |
rear end |
|
|
superior |
above another part or closer to the head |
|
|
inferior |
below another part or closer to the feet |
|
|
medial |
towards imaginary midline |
|
|
central |
middle |
|
|
peripheral |
nearest surface |
|
|
proximal |
nearest main mass or nearest point of attachment |
|
|
distal |
further from point of attachment or away from main mass (fingers are distal to wrist) |
|
|
superficial |
on the surface |
|
|
deep |
most internal |
|
|
cephalic |
head |
|
|
celiac |
abdomen |
|
|
carpal |
wrist |
|
|
caudal |
tail |
|
|
abdominal |
between the thorax and abdomen |
|
|
acromial |
point of the shoulder |
|
|
antebrachial |
forearm |
|
|
antecubital |
front of the elbow |
|
|
axillary |
under arms |
|
|
buccal |
cheek |
|
|
brachial |
upper arm |
|
|
cervical |
neck |
|
|
costal |
ribs |
|
|
coxal |
hip |
|
|
crural |
leg |
|
|
cubital |
elbow |
|
|
digital |
finger |
|
|
frotnal |
forehead |
|
|
femoral |
thigh |
|
|
genital |
reproductive organs |
|
|
gluteal |
near buttocks |
|
|
inguinal |
near groin |
|
|
lumbar |
lower back |
|
|
nasal |
nose |
|
|
mammary |
breast |
|
|
mental |
chin |
|
|
ooccipital |
back of skull |
|
|
oral |
mouth |
|
|
orbital |
eye cavity |
|
|
otic |
ear |
|
|
palmar |
palm |
|
|
perineal |
region between anus and external reproductive organs |
|
|
pectoral |
chest |
|
|
pedal |
foot |
|
|
pelvic |
hips |
|
|
plantar |
sole of foot |
|
|
popliteal |
area behind knee |
|
|
sacral |
between hipbones |
|
|
sternal |
middle of thorax |
|
|
tarsal |
instep |
|
|
umbilical |
navel |
|
|
vertebral |
spinal column |
|
|
supination |
palm up |
|
|
pronation |
palm down |
|
|
abduction |
away from the midline |
|
|
adduction |
towards the midline |
|
|
flexion |
decrease angle |
|
|
extesion |
increase angle |
|
|
circumduction |
moving in a circular path |
|
|
dorsiflexion |
bending foot upward |
|
|
plantar flexion |
bending foot downwards |
|
|
protraction |
moving part forward |
|
|
retraction |
moving part backwards |
|
|
rotation |
moving around on an axis |
|
|
hyperextension |
movement beyond normal position |
|
|
inversion |
moving the sole inward |
|
|
eversion |
moving the sole outward |
|
|
elevation |
raising a part |
|
|
depression |
lowering a part |
|
|
epigastric |
left lobe and medial part of the right lobe of the liver, pyloric portion and lesser curvature of the stomach, superior and descending portions of the duodenum, body and superior portion of the head of the pancreas, right and left adrenal glands |
|
|
right hypchondriac |
right lobe of the liver, gallbladder, superior third of right kidney |
|
|
left hypochondriac |
body of the stomach, spleen, left colic (splenic), flexure, superior two-thirds of left kidney, and tail of pancreas |
|
|
umbilical |
middle portion of transverse colon,inferior part of duodenum, jejunum, ileum, and bifurcation (branching) of abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava |
|
|
right lumbar |
superior part of cecum, ascending colon, right colic (hepatic) flexure, inferior lateral portion of right kidney, and small intestine. |
|
|
left lumbar |
descending colon, inferior third of left kidney, and small intestine |
|
|
hypogastric (pubic) |
urinary bladder when full, small intestine, and part of sigmoid colon |
|
|
right iliac (inguinal) |
lower end of cecum, appendix,and small intestine |
|
|
left iliac (inguinal) |
junction of descending and sigmoid parts of colon small intestine |
|
|
the quadrants |
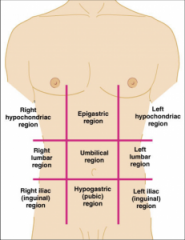
|
|
|
oral cavity |
contains teeth and tongue |
|
|
nasal cavity |
located withing the nose and divided into the right and left portion of the nasal septum. |
|
|
orbital cavity |
contains the eyes, associated muscles and nerves. |
|
|
middle ear cavity |
bones and structures of the middle ear |
|
|
disease |
any change in the state of health in which part or all of the body is not carrying out its normal function |
|
|
local disease |
affects one part or a limited area of the body |
|
|
systematic diasease |
affects either the entire body or several parts |
|
|
symptom |
a subjective change in body functions not apparent to an observer |
|
|
syndrome |
a specific group of symptoms and signs accompanying a particular disease |
|
|
epidemiology |
why, when, and where diseases occur and how they are transmitted |
|
|
pharmacology |
the effects and use of drugs in the treatment of disease |
|
|
diagnosis |
distinguishing one disease from another or determining the nature of a disease |
|
|
computed tomography scanning (CT scan) |
combines computer technology and principles of x-ray technology. CT scans are 10-20 times more detailed than conventional x-rays. used to detect blood clots, tumors, aneurysms, kidney stones, gallstones, tissue damage, and deformities. however,it does not tell how an organ is functioning. |
|
|
positron emission tomography (PET scan) |
reveals the metabolic state of an organ by measuring the rate at which tissues consume chemical substances such as glucose. Used to diagnose cancer, cardiovascular problems, brain disorders. |
|
|
dynamic spatial re-constructor (DSR) |
produces 3-D computer generated images to reveal the flow of blood thorough the brain. may be used to prevent impending strokes. |
|
|
magnetic resonance imaging (MSR) (NMR) |
envelopes the patient in a strong magnetic field to detect differences n healthy and unhealthy tissue. no x-ray or dyes or radioactive tracers, does not register bone that obscures soft tissue, can detect damaged myelin sheaths,detects build-up of fatty tissues around vessels, detects atherosclerosis, detects brain tumors. |
|
|
digital subtraction angiography (DSA) |
uses a computer to show blockages of blood vessels as well as determine flow rates. useful in predicting heart attacks. |
|
|
ultrasound |
sends pulses of high freq. sound waves into designated body regions. used to look at compact organs such as the lungs. differentiated between healthy and non-healthy tissue, look at fetus, detect ectopic and multiple pregnancies, fetal surgery, reveals birth defects. |
|
|
thermography |
reveals chemical reactions that are taking place within the body based on heat changes in the skin. Used to detect cancer, arthritis, and circulation problems. |

