![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
114 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
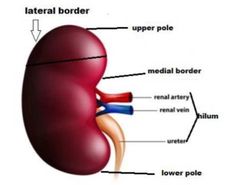
Shape of kidney |
Bean-shaped |
|
|
|
Length of kidney |
4.5 inch |
|
|
|
Breadth of kidney |
2.5 inch |
|
|
|
Thickness of kidney |
1.5 inch |
|
|
|
weight of kidney |
150 grams |
|
|
|
Position of kidney |
Retroperitoneal |
|
|
|
In supine position, kidney extend from? To? |
From T12 superiorly to L3 inferiorly |
|
|
|
Anterior relation of right kidney |
1) Small intestine impression of jejunum 2) Right colic flexure impression of Colon 3) Hepatic impression of liver 4) Suprarenal impression of suprarenal glands 5) Duodenal impression of duodenum |
Saya Cakap Henry Suka Drugs |
|
|
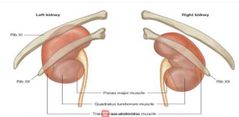
Posterior relation of left & right kidneys |
|
|
|
|
Peritoneal covering of anterior surface of right kidney |
1) Hepatic surface 2) Small intestine area Except: Suprarenal surface, duodenal surface, and colic surface (SDC) |
|
|
|
Peritoneal covering of anterior surface of left kidney |
1) Small intestine area 2) Spleenic surface 3) Gastric surface Except: suprarenal surface, pancreatic area, descending colic area (SPC) |
3 |
|
|
Covering of kidney |
1) Fibrous capsule 2) Perirenal fat 3) Renal fascia (Zuckercandle) 4) Paranephoic fat |
|
|
|
Fibrous capsule of covering of kidney |
→ innermost covering → surrounds kidney → continues to renal sinus |
|
|
|
Perirenal fat covering of kidney |
→ covers fibrous capsule → acts as cushion → helps to hold kidney in relatively fixed position → rapid loss fat can causes renal ptosis (kidney displacement) |
|
|
|
Renal fascia (Zuckercandle) covering of Kidney |
→ condensation of connective tissue → lies outside perirenal fat → encloses kidneys and suprarenal glands → continuous laterally with fascia transversalis |
|
|
|
Paranephric fat of covering of kidney |
→ lies external to renal fascia → contains a large quantity of fat → forms part of retroperitoneal fat |
|
|
|
Which covering of kidney continuous laterally with fascia transversalis? |
Renal fascia ( Zuckercandle fascia) |
|
|
|
Which loss of covering of kidney causes renal ptosis or kidney displacement? |
Perirenal fat |
|
|
|
Which covering of kidney surround kidney and continues to renal sinus? |
Fibrous capsule |
|
|
|
Which covering of kidney form part of retroperitoneal fat? |
Paranephric fat |
|
|
|
Blood supply of kidney |
1) Renal artery 2) Renal vein |
|
|
|
Renal artery arises from |
Abdominal aorta at level Of L2. Each renal artery usually divides into 5 segmental arteries |
|
|
|
Renal vein emerges from? And drains into? |
Renal veins emerge from the hilum in front of the renal artery and drain into inferior vena cava |
|
|
|
Left renal vein also receive from? |
1) Left adrenal vein 2) Branch of inferior phrenic vein 3) Left gonadal vein |
|
|
|
Lymphatic drainage of kidney |
Pass to para-aortic lymph nodes |
|
|
|
Function of ureters |
Two muscular tubes whose peristaltic contractions convey urine from kidneys to urinary bladder |
|
|
|
Length of ureters |
Each one about 25 to 30 cm |
|
|
|
Thickness of ureters |
Thick-walled and narrow lumen, with 3mm diameter |
|
|
|
Beginning of ureters |
Funnel-shaped renal pelvis, which lies within the hilum of kidney at level of L1 |
|
|
|
Termination of ureters |
At posto-superior angles of base of urinary bladder |
|
|
|
Course of Ureters |
1) In front psoas major muscle 2) Birfurcation of common iliac artery 3) Internal iliac artery 4) At Ievel of ischial spine
|
|
|
|
How to identify ureters in computerized tomography (CT) of abdomen? |
By the relation of psoas major muscle |
|
|
|
Ureter has three parts which are: |
1) Abdominal part 2) Pelvic part 3) Intramural part |
|
|
|
Posterior relation of abdominal part of left and right ureter |
1) Median border of psoas major and minor muscles 2) Tips of transverse processes of L2,3,4,5 3) Genito-femoral nerve |
|
|
|
Anterior relation of abdominal part of right ureter |
1) 2nd, 3rd parts of duodenum 2) Three vessels : right colic vessels, right ileo colic vessels, right gonadal vessels 3) Three mesenteric related structures: root of mesentery, superior mesenteric vessels, coils of small intestine |
|
|
|
Anterior relation of abdominal part of left ureter |
1) Three vessels : left colic vessels, sigmoidal vessels and left gonadal vessels 2) Apex of sigmoid mesocolon 3) Coils of pelvic colon |
|
|
|
Medial relation of abdominal part of right ureter |
Inferior vena cava |
|
|
|
MediaI part of abdominal part of left ureter |
Inferior Mesenteric vein |
|
|
|
Relation of pelvic part of ureter |
1) External iliac artery and vein 2) Obturator nerve 3) Obturator artery 4) Obturator vein |
3OE |
|
|
Relation of Pelvic part of ureter in male |
Ureter is crossed by vas deferens |
|
|
|
Relation of pelvic part of ureter in female |
The ureter passes above lateral fornix of vagina |
|
|
|
Why the relation between Ureter and ovarian and Uterine blood vessels is very important in female? |
During Oophorectomy (removal of ovary) and hysterectomy (removal of uterus). To remove any organ from body, you have to ligate (tie) its blood supply. If ureters accidentally ligated with blood vessels, it will result in post-operative renal impairment, Which require immediate surgical intervention to relieve ligature from ureters |
|
|
|
Intramural part of ureter |
The ureters pierce the postro-superior angles of the base of the urinary bladder and run obliquely through its wall for a distance of 1.5–2.0 cm before opening at the ureteric orifices |
|
|
|
Importance of arrangement in intramural part of ureter |
To prevent the reflux of urine into ureter when the bladder is full, since intramural ureters are thought to be occluded during increases in bladder pressure at time of micturition. |
|
|
|
Three normal constructions of Ureter course⁷ |
1) At pelvic-ureteric ajunction 2) At bifurcation of common iliac artery 3) At utero-vesical junction |
|
|
|
The sites of ureteric anatomical constrictions represent |
most common site of renal stones impaction |
|
|
|
Arterial blood supply of abdominal part of ureter |
The abdominal part of ureter is supplied by arteries, originating medial to ureter, renal artery, gonadal artery and branches from abdominal aorta. |
|
|
|
Arterial blood supply of pelvic part of ureter |
The pelvic part of ureter is supplied by vessels, originating lateral to ureter by common iliac, internal iliac, vesicle and uterine arteries |
|
|
|
Venous drainage of ureters |
Same as arterial supply |
|
|
|
Why ureter can be safely transected at any level intra operatively? |
Because there's a good longitudinal anastomosis between these branches along the wall of the ureter. |
|
|
|
Lymphatic drainage of ureter |
1) Upper abdominal Part : the collecting lymph vessels join with renal collecting vessels or pass directly to lateral aortic nodes, near the Origin of gonadal artery 2) Lower abdominal part of ureter: drain to common iliac nodes 3) Pelvic part of ureter drain to common, external or internal iliac nodes. |
|
|
|
Nerve supply of ureter |
1) Delivered via the renal, testicular/ovarian and hypogastric plexuses
2) Sympathetic plexus ; from nerve cells lie in T12, L1, L2 from spinal segments.
3) Parasympathetic plexus, from S2, S3, S4 nerves, which reach kidney through pelvic splanchnic nerves |
|
|
|
Reservoir of urine is? |
Urinary bladder |
|
|
|
Urinary bladder's size, shape, position and relations are vary according to? |
Age, amount of content and state of neighbouring viscera |
|
|
|
Urinary bladder lies posterior to? |
Pubic bones and pubic symphysis |
|
|
|
Nerve supply of Urinary Bladder |
Autonomic fibers from: a) Sympathetic (from 11th, 12th thoracic spinal segments and upper two lumbar segments) - inhibitory to muscle wall and motor to sphincter b) Parasympathetic (from pelvic splanchnic nerve S2, S3,S4) -motor to muscle wall and inhibitory to sphincter |
|
|
|
Atonic bladder results from lesion to sacral spine cord segments or sacral spine nerve roots. Explain its progression. |
Loss of pelvic splanchnic motor innervation causes loss of contraction of detrusor muscle, which results in a full bladder with continuous dribble of urine. |
|
|
|
Spastic bladder results from lesions of Spinal cord above the sacral spinal cord levels. Explain. |
There's a loss of inhibition to parasympathetic innervation to detrusor muscle during filling stage. Thus, the detrusor muscle respond to a minimum amount of stretch, causing urge incontinence (involuntary leakage of urine) . |
|
|
|
Arterial supply of urinary bladder |
1) Superor vesicle arteries → branch of internal iliac artery → supply apex and superior part of bladder 2) Inferior vesicle arteries → supply base and neck of urinary bladder in male 3) Vaginal arteries → branch of uterine arteries → supply base and neck of urinary bladder of female 4) Obturator arteries → branch of internal iliac artery → provide arterial twigs |
SIVO |
|
|
When the bladder is empty, it lies entirely in the lesser pelvis, but as it distends it... |
it expands antero-superiorly into the abdominal cavity |
|
|
|
Lymphatic drainage of urinary bladder |
Drains into the common, external or internal iliac nodes. |
|
|
|
Venous drainage of Urinary bladder |
→ don't follow arteries → create complex plexus on inferolateral surfaces near prostate in male → enters backwards in posterior ligaments of urinary bladder to drain into internal iliac veins → vesical venous plexus interacts with prostatic venous plexus in male → vesical venous plexus interacts with veins at base of broad ligament of uterus in female |
|
|
|
Empty bladder has an apex, neck, base, superior surface and two inferolateral surface. Which of them is the same in relation of Urinary bladder in male and female? |
Apex: median umbilical ligament, attached to anterior abdominal wall Inferolateral surface: Obturator internus muscle, levator ani muscle, obturator nerve, obturator artery and vein, superior vesical artery and vein |
SOLO |
|
|
Base of Urinary bladder in male |
1) Recto-vesical pouch 2) Loops of ilium 3) Two seminal vesicles 4) Two vas deferens |
2TLR |
|
|
Base of urinary bladder in female |
1) Cervix 2) Anterior wall vagina |
AC |
|
|
Relation of neck of urinary bladder in male |
Rests on: 1) Prostate 2) Prostatic venous plexus 3) Ejaculatory duct |
PEP |
|
|
Neck of urinary bladder in female |
Vagina (Posteriorly) |
|
|
|
Superior surface of Urinary bladder in male |
Peritoneum, loops of ileum and sigmoid colon |
PLS! |
|
|
Superior surface of urinary bladder in female |
1) Uterus 2) Utero-vesical pouch 3) loops of ileum 4) Sigmoid colon |
SUUL |
|
|
Peritoneal covering of urinary bladder in male |
Peritoneum covers superior surface and upper part of base of bladder. Then, reflected to rectum, forming recto-vesical pouch. |
|
|
|
Peritoneal covering of urinary bladder in female |
Peritoneum covers anterior part only of superior surface of bladder then reflected to anterior surface of uterus, forming utero-vesical pouch |
|
|
|
True ligament of urinary bladder |
In Male and female: 1) Lateral true ligaments → stretch from lateral wall of bladder to pelvic fascia 2) Median umbilical ligament → fibrous remnant of urachus → goes from apex of bladder to umbilicus → keeps bladder in positon anteriorly and superiorly 3) Posterior ligaments → 2 in number (left and right) → as sheet of loose areolar tissue from side of base of bladder to lateral pelvic wall → enclose vesical venous plexus In male only: 1) Lateral pubo-prostatic ligaments → connect neck of bladder and prostatic sheath with tendinous arch of pelvic fascia 2) Medial pubo-prostate ligaments → connect neck of bladder and prostate sheath with back of pubic bone In female; 1) Lateral pubo-vesical ligaments → connect neck of bladder to tendinous arch of pelvic fascia 2) Medial pubo-vesical ligaments → connect the neck of bladder to back of pubic bone |
|
|
|
False ligaments of urinary bladder |
a) Median umbilical fold → fold of peritoneum over Median umbilical ligament b) Two medial umbilical folds → folds of peritoneum over obliterated umbilical arteries C) Two posterior false ligaments → two peritoneal folds from back of urinary bladder and pass backward on each side of rectum to attach to the front of sacrum False ligaments: (1) Median umbilical fold, (2) Medial umbilical fold, (3) Lateral false ligaments, (4) Posterior false ligaments |
4 |
|
|
Lymphatic drainage of kidney |
Pass to para-aortic lymph nodes |
|
|
|
In renal cell carcinoma, tumor destroy renal vein. If it's in left side, damage of left renal vein results in defect in venous drainage of left gonadal veins, which result in? |
Dilatation of veins surrounding left testes, resulting in varicose of left testis. |
|
|
|
Factors which stabilize kidneys to stay in position |
1) Intra-abdominal pressure and arrangement of adjacent organs 2) Extension of covering fascia and fat 3) Renal vessels connecting kidneys to abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava |
|
|
|
Rapid loss of pre-renal fat tissue may result in drop of kidney in pelvis, which is called ptosis of kidney. This condition can result in? |
Kinking of ureters (sharp twist), results in severe pain. |
|
|
|
Nerve supply of kidney |
1) Renal sympathetic plexus → afferent fibers that travel through renal plexus → enter spinal cord in 10th, 11th and 12th thoracic nerves 2) Parasympathetic fibers → from vagus nerve → reach kidney through plexus |
|
|
|
How can you differentiate between left and right kidney? |
1) Medial border is concave, containing hilum while lateral border is convex. 2) In hilum, renal vein is most anterior structure and renal pelvis is posterior, while renal artery is in between. 3) The ureter passes downward along lower part of medial border |
|
|
|
Surface anatomy of kidney on front of abdomen |
1) The hilum lies on the transpyloric plane, 5 cm from middle line. 2) The upper pole lies 2.5 cm away from middle line and 5 cm above hilum 3) Lower pole lies in below hilum and 7.5 cm from middle line |
|
|
|
Transpyloric plane is |
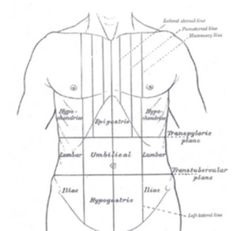
Addison's plane: an imaginary horizontal plane → located halfway between suprasternal notch of manubrium and upper border of symphysis pubis → at level of first lumbar vertebrae L1 |
|
|
|
Renal angle |
→ located on either side of human back between lateral border of erector spinal muscles and inferior borders of 12th ribs → kidney can be felt at this location |
|
|
|
empty bladder is pyramidal in shape, it has? |
an apex, base (posterior surface or fundus), neck, a superior surface and two inferolateral surfaces . |
|
|
|
In females, Superior relation of urinary bladder with uterus, increase the urgency of urination in pregnant females due to |
compression caused by the enlarged uterus over the urinary bladder, so decreasing its capacity |
|
|
|
In females, posterior relation (base) of the urinary bladder with cervix carries an important clinical correlate in cases of cancer cervix. Explain, |
The invasion of the cervical cancer posteriorly to the bladder will result in occlusion of the urinary bladder |
|
|
|
Shape of inferolateral surface of urinary bladder |
Triangle |
|
|
|
Superior surface of urinary bladder forms |
The roof of urinary bladder |
|
|
|
Neck of bladder |
3 to 4 cm. Where base and inferolateral sides meet inferiorly. It is traversed by internal urethral opening .The detrusor muscle runs circularly around the neck, which acts as an involuntary internal sphincter. |
|
|
|
Apex or anterior angle of urinary bladder |
site of attachment of urachus-fibrous remnant of fetal allantois, which is seen as the median umbilical ligament |
|
|
|
Base of urinary bladder, forms the posterior surface : |
1- two ureteric openings at supero - lateral angles
- Internal urethral orifice at the inferior angle 2 - Internal urethral orifice at the inferior angle→ it is surrounded by an internal sphincter, which is an involuntary innervated by autonomic nerves → it is surrounded by an internal sphincter, which is an involuntary innervated by autonomic nerves
3 - Vesical Trigon; → which is a smooth triangular area → formed by three opening, two ureteric, and one urethral opening → The ridge between the two ureteric openings is the interureteric ridge and forms the upper limit of the trigon |
VIT |
|
|
The part of the urogenital ridge that gives rise to the urinary system is called |
Nephrogenic cord |
|
|
|
After folding of the embryo, the intermediate mesoderm is carried |
ventrally |
|
|
|
the urogenital ridge is formed on each side of |
the dorsal aorta |
|
|
|
The pronephroi phase |
→transitory, nonfunctional structures appear in the 4th week →represented as a few cell clusters and tubular structures in the neck region opposite to the 7th to the14th somites →pronephric ducts run caudally and open into the cloaca → rudimentary pronephroi are degenerate → most of the pronephric ducts persist and are utilized by the next set of the kidneys and its name is changed and called mesonephric ducts
|
|
|
|
The Mesonephroi phase |
→large; elongated; excretory organs appear late in the 4th week caudal to the rudimentary pronephroi →appears at a lower-level opposite to 14th to 28th somites in the thoracic and upper lumbar region of the embryo →well developed and function as transient kidneys for about 4 weeks →consists of glomeruli and mesonephric tubules ( tubules open into the mesonephric ducts which open into the cloaca ) → mesonephroi degenerate toward the end of the 1st trimester |
|
|
|
What's the difference of mesonephric tubules development in male and female? |
☆ In male, the mesonephric tubules become the efferent ductules of the testes. ☆ Mesonephric duct gives rise to PADDU PCCES → paradidymis → appendix of epididymis → duct of epididymis → ductus deferens→ ureter → pelvis → calices→ collecting tubules; ejaculatory duct and seminal gland ☆ In female, the mesonephric tubules become the Epoophoron and Paroophoron ☆The mesonephric duct gives rise to ADDUP2C → appendix vesiculosa → duct of epoophron → duct of Gartner → ureter → pelvis → calices and collecting tubules |
|
|
|
Metanephroi phase |
→ primordia of permanent kidneys which begin to develop early in the 5th week and start to function about 4 weeks later → permanent kidneys develop from 2 sources: ureteric bud & metanephric mass → primordia of the metanephros are of mesodermal origin |
|
|
|
Permanent kidneys develop from 2 sources, Which are |
ureteric bud and metanephric mass |
|
|
|
Expanded cranial and of stalk of mesonephric duct becomes? |
Renal pelvic |
|
|
|
straight collecting tubules undergo repeated branching, forming ? |
generations of tubules, major calices, minor calices and collecting tubules |
|
|
|
Fetal kidneys |
→divided into lobes → lobulation diminishes toward the end of fetal period, but the lobes are still inducated in the kidneys of a newborn infant →lobulation disappears by the end of the first postnatal year during infancy as the nephrons increase and grow →increase in kidney size after birth results mainly from the elongation of the proximal convoluted tubules as well as an increase of interstitial tissue → functional maturation of the kidneys occurs after birth |
|
|
|
Positional Changes of Kidneys |
→ Initially the metanephric kidneys lie close to each other in the pelvis ventral to the sacrum →As the abdomen and pelvis grow, the kidneys gradually come to lie in the abdomen and move farther apart and attain their adult position by 9th week →Initially the hilum faces ventrally however, as the kidney ascends it rotates medially 90 degrees →By the 9th week the hilum is directed anteromedially |
|
|
|
Congenital Anomalies of the kidney CHER |
1) Cystic kidney disease (A) Polycystic kidney (B) Multi-cystic dysplastic kidney disease Horseshoe kidney 2) Horseshoe kidney3) Ectopic pelvic kidney4) Renal agenesis 3) Ectopic pelvic kidney Horseshoe kidney3) Ectopic pelvic kidney4) Renal agenesis Horseshoe kidney3) Ectopic pelvic kidney4) Renal agenesis Horseshoe kidney3) Ectopic pelvic kidney4) Renal agenesis 4) Renal agenesis |
|
|
|
Polycystic kidney |
→ is cystic kidney disease → autosomal disorder →diagnosed at birth by ultrasonography → both kidneys contain many hundred small cysts which results in renal insufficiency. → death of infant usually occurs short after birth |
|
|
|
Horseshoe kidney |
→results from fusion of caudal ends of both kidneys →interconnecting bridge becomes trapped behind the inferior mesenteric artery so that the kidneys come to rest in low lumbar region |
|
|
|
Ectopic pelvic kidney |
→kidney is arrested in some part of its normal ascent →usually is found at the pelvic brim |
|
|
|
Renal agenesis |
→unilateral renal agenesis results due to absence of formation of one ureteric bud
→often causes no symptoms
→ Bilateral renal agenesis is associate with oligohydramnios → absence of one or both kidneys |
|
|
|
The urogenital system develops from |
Intraembryonic mesoderm |
|
|
|
Development of the kidneys passes through 3 stages, which are? |
1) The pronephroi 2) The mesonephroi 3) The metanephroi |
|
|
|
Metanephric diverticulum development |
→ outgrowth from the mesonephric duct near its entrance into the cloaca →primordium of the ureter → renal pelvis → calices and collecting tubules →as it elongates, it penetrates the metanephric mass of the intermediate mesoderm → the stalk of it becomes the ureter and its expanded cranial end forms the renal pelvis. → the straight collecting tubules undergo repeated branching, forming generations of tubules, major calices, minor calices and collecting tubules |
|
|
|
Metanephric tubules (primordia of nephron) development |
→ mass of the intermediate mesoderm derived from the caudal part of the nephrogenic cord →end of each arched collecting tubule form metanephric vesicles →metanephric vesicles elongate and become metanephric tubules →proximal ends of these tubules are invaginated by glomeruli →glomerular filtration begins around the 9th fetal week → their number increases until the 32 week with increase in the rate of filtration after birth →renal corpuscle and its proximal convoluted tubules; loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubule constitute a nephron → nephrons become continuous with the collecting tubules to form the uriniferous tubules |
|
|
|
Changes in Blood Supply of kidneys |
➢ Initially, the renal arteries are branches of the common iliac and median sacral arteries ➢ As the kidneys ascend, they receive their blood supply from the distal end of the aorta. ➢ Then, they receive new branches from the aorta. ➢ The most cranial arterial branches from the abdominal aorta become the permanent renal arteries ➢When the kidneys become in contact with the suprarenal glands in the 9th week their ascend stops ➢ Normally, the caudal branches undergo involution and disappear |
|
|
|
Multi-cystic dysplastic kidney disease (MDK) |
→ results from dysmorphology (defect) during development of the renal system → outcome is generally good |
|
|
|
The stalk of mesonephric duct becomes? |
Ureter |
|

