![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where does the ovarian artery travel?
|
*The ovarian artery arises from the abdominal aorta inferior to the renal artery, but considerably superior to the IMA. As it passes inferiorly, the ovarian artery adheres to the parietal peritoneum and runs anterior to the ureter on the posterior abdominal wall, usually giving branches to the ureter.
*We see this anatomy nicely when we perform the robotic cystectomy in a female. |
|
|
Do the seminal vesicles store sperm?
|
No, even though that is what there name implies they do not store sperm. Instead they secrete a thick alkaline fluid that mixes with the sperm as they pass into the ejeaculatory ducts and urethra.
|
|
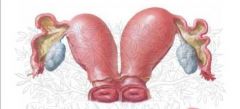
What is this structure?
|
Uterus didelphys (sometimes also uterus didelphis) represents a uterine malformation where the uterus is present as a paired organ as the embryogenetic fusion of the mullerian ducts failed to occur. As a result there is a double uterus with two separate cervices, and often a double vagina as well. Each uterus has a single horn linked to the ipsilateral fallopian tube that faces its ovary.
|
|
|
What is a Cowper's gland and where is it located?
|
*Bulbourethral glands are located posterior and lateral to the membranous portion of the urethra at the base of the penis, between the two layers of the fascia of the urogenital diaphragm, in the deep perineal pouch. They are enclosed by transverse fibers of the sphincter urethrae membranaceae muscle.
*During sexual arousal each gland produces a clear, viscous secretion known as pre-ejaculate. This fluid helps to lubricate the urethra for spermatozoa to pass through, neutralizing traces of acidic urine in urethra[2], and helps flush out any residual urine or foreign matter. It is possible for this fluid to pick up sperm, remaining in the urethral bulb from previous ejaculations, and carry them out prior to the next ejaculation. |

