![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
104 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Endolymph |
Fluid that fills the cochlear duct |
|
|
Annular ligament |
Fastens footpath of stapes to bony wall of oval window |
|
|
Approximately how many hair cells in the organ of corti? |
5,000 inner hair cells and 10,000 outer hair cells |
|
|
What is the normal condition of the eustatian tube? |
Usually closed |
|
|
The ear is most accurately considered to be what? |
The organ of hearing and equillibrium |
|
|
What is the ratio of difference in the size between the tympanic membrane and the oval window? |
17:1 |
|
|
Ceruman has its origin where? |
External auditory meatus |
|
|
The most protruding landmark on the tympanic membrane is what? |
The lateral process of the malleolus |
|
|
The essential parts of the organ of hearing and balance is located where? |
Temporal bone |
|
|
Epitympanic recess |
Also called the attic, filled by head of malleus and much of the incus |
|
|
Perilymph |
A |
|
|
Basilar membrane |
A |
|
|
Ossicular chain |
Made up of the 3 small bones of the inner ear. They serve as a mechanical link between the tympanic membrane and the inner ear |
|

A |
Superior |
|

B |
Anterior |
|

C |
Posterior |
|

D |
Medial |
|

E |
Lateral |
|

F |
Proximal |
|

G |
Distal |
|

H |
Inferior |
|
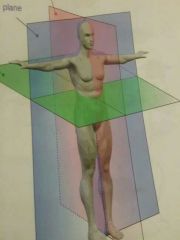
Blue |
Coronal plane |
|

Green |
Transverse plane |
|

Pink |
Saggittal plane |
|
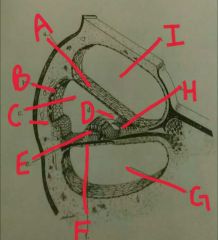
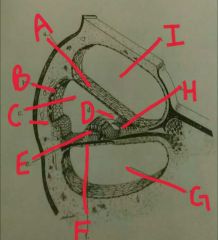
A |
Reissner's membrane |
|
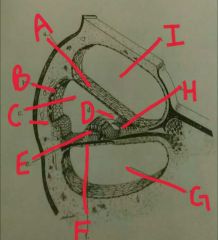
B |
Stria vascularis |
|
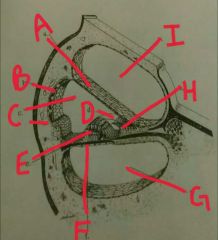
C |
Scala media |
|
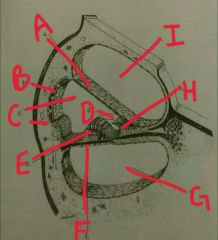
D |
Tectonics membrane |
|
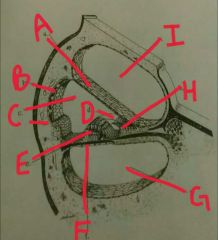
E |
Organ of corti |
|
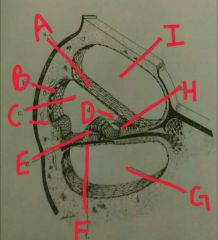
F |
Basilar membrane |
|
F |
Basilar membrane |
|
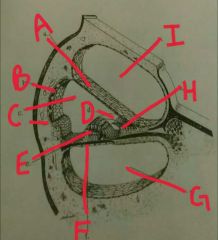
G |
Scala tympani |
|
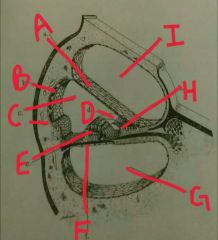
H |
Spiral limbus |
|
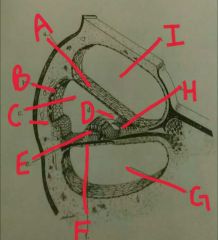
I |
Scala vestibulli |
|
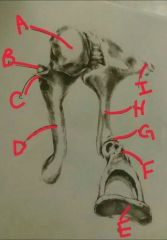
A, B, C |
A- head or shoulder of malleus B- anterior process of the malleus C- lateral process of the malleus |
|
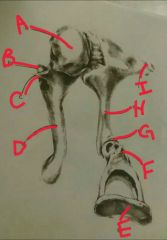
D, E, F |
D- mannerism of malleus E- footplate of stapes |
|
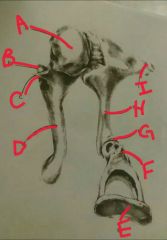
F, G, h, i |
F - head or neck of stapes G - incudostapedial joint or junction H- long process of the incus Ì short process of the incus |
|
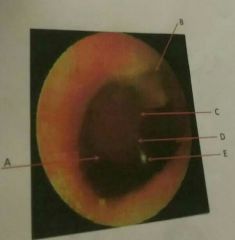
A |
Pars tensa |
|
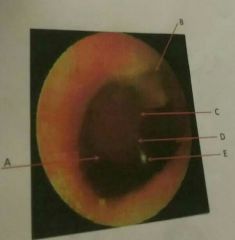
B |
Pars flaccid a or sharpness membrane |
|
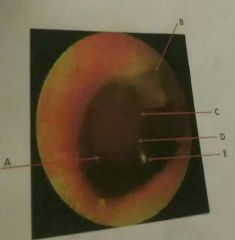
D |
Shadow of the malleus or manubrium of the malleus |
|
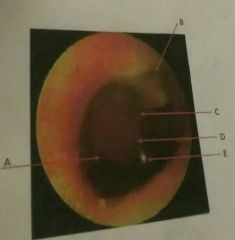
E |
Cone of light |
|
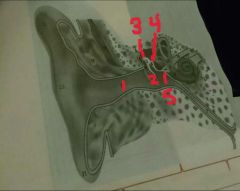
1, 2, 3, 4, 5 |
1-external auditory meatus or canal 2-tympanic membrane or eardrum 3-malleus 4-incus 5-stapes |
|
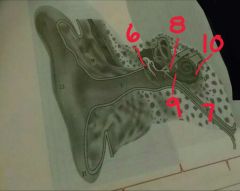
6, 7, 8, 9, 10 |
6- ligament 7-eustaciah tube 8-oval window 9-round window 10-cochlea |
|
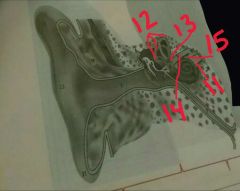
11, 12, 13, 14, 15 |
10-cochlea nerve 12-semicircular canals 13-utricle 14-balance/vestibular nerve 15-balance/vestibular nerve |
|
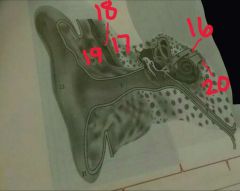
16, 17, 18, 18, 20 |
16-facial nerve17-temporal bone18-muscle19-cartilage20-internal auditory meatus or canal |
|
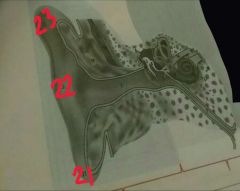
21, 22, 23 |
21-earlobe or lobule 22-external ear, pinna, auricle 23-pinna or helix |
|
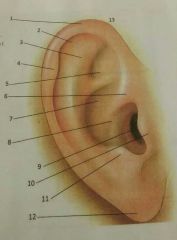
1, 2, 3 |
1-helix 2-scaphoid fossa 3-antihelix |
|
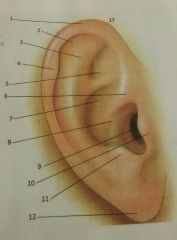
4, 5, 6 |
4-darwin's turbercle 5-triangular fossa 6-crus |
|
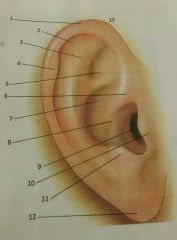
7, 8, 9 |
7-cymba of concha 8-cavum of concha 9-aperature |
|
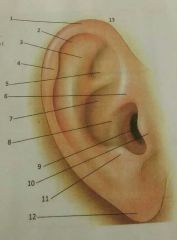
10, 11, 12, 13 |
10-tragus 11-anti-tragus 12-lobule 13-pinna |
|
|
What is the shape of the ear canal? |
S shaped, backward and upward, then slightly forward and downward |
|
|
Where is the ear canal the most narrow? |
At the isthmus |
|
|
What are the dimensions of the adult ear? |
28-30mm in length 6-8mm in diameter |
|
|
What is Arnolds branch? |
A branch of the vagus nerve along the floor of the ear canal, can cause reflex such as cough, sneeze, pain, ill feeling. |
|
|
How much of the external ear is cartilage? |
1/2-2/3 |
|
|
How much of the external ear is the Osseous (boney) portion? |
1/2-1/3 |
|
|
What 3 things are found in the ear canal? |
Sebaceous glads, ceruman glands, and hair cells. |
|
|
What purpose does the cartilaginous portion of the ear serve? (3 things) |
-protects ear canal from drying out -secretions and hairs act as a bug repellant -hairs, jaw movement, and lateral migration of skin move dry particles towards entrace |
|
|
What purpose does the Osseous (boney) portion of the ear canal serve? (2 things) |
-Keeps canal from collapsing -helps protect internal ear strucures |
|
|
What purpose does the EAC serve? (3 things) |
-directs sound -protects -natural amplification |
|
|
Most adult EAC'S resonate between |
2000-3000Hz |
|
|
The pinna naturally resonates between |
2000-5000Hz |
|
|
On average, the EAC and pinna together, have a natural resonance of what? It will provide a boost in sound up to what? |
2700Hz 15dB |
|
|
Middle ear consists of (4 things) |
Tympanic membrane Ossicular chain Tensor tympani muscle Stapedius muscle |
|
|
Where is the Ossicular chain housed? |
Epitympanic recess / attic |
|
|
Characteristics of the tympanic membrane (list 6) |
Oval shape Slightly convex Separates ear canal from middle ear About .1mm thick 45-55 degree angle Made up of 3-4 layers |
|
|
Describe the outer layer of the tympanic membrane |
Thick cutaneous layer continuous with skin of ear canal |
|
|
Describe the 2 middle layers of the tympanic membrane |
Both are fiberous Inner layer is concentric rings Outer layer fibers radiate from center out |
|
|
What are the four quadrants of the tympanic membrane |
Posterior superior Anterior superior Posterior inferior Anterior inferior |
|
|
Cone of light |
Light reflect on the tympanic membrane during otoscopy |
|
|
Annulus |
Incomplete ring of bone holding the tympanic membrane in place |
|
|
Umbo |
Manubrium of the malleus |
|
|
Pars flaccida |
Small flaccid triangular shaped area at the top edge of the tympanic membrane |
|
|
Pars tensa |
The tense greater part of the eardrum |
|
|
When performing otoscopy what things do you need to look for on the tympanic membrane? (List 5) |
-grayish or pinkish in color -more concave than convex -a shadow of manubrium of malleus -umbo -cone of light |
|
|
Malleus |
Largest of the three bones in the middle ear, I'm bedded in the fiberous layer of the eardrum |
|
|
Incus |
One of the bones of the middle ear, joins the malleus to the stapes |
|
|
Stapes |
Smallest bones in the human body, connects to the incus in the Ossicular xhair. The footpath of the stapes is fixed in the oval window of the inner ear |
|
|
Ossicular vibration |
The vibration of the eardrum is transmitted to the oval window of the inner ear by means of the ossicles |
|
|
What is the primary function of the ossicles? |
Compensate for the impedance mismatch between the low impedance of acoustic energy (air pressure waves) and the high impedance of the hydraulic, fluid filled system of the cochlea. |
|
|
How does the middle ear overcome impedance mismatch? (List 3) |
-Funneling action from eardrum to oval window provides a 15-20dB boost to sound as it travels through the inner ear -the malleus provides a fulcrum like action, which magnifies sound about 5dB -the buckling effect of the tympanic membrane, as a result of not being completely attached to the malleus, creating a 10dB boost |
|
|
Basilar membranr |
Separates cochlear duct from the scala tympani |
|
|
Organ of corti (list 3) |
-Sits on the basilar membrane in the scala media -contains 4-6 rows of hair cells -above the hair cells is the tectonics membrane
|
|
|
The Ossicular chain is supported by |
Ligaments and two muscles; the stapedius, and the tensor tympani. |
|
|
Stapedius |
Muscle that attaches to the stapes and draws the stapes in a posterior direction when it contracts |
|
|
Tensor tympani |
Muscle that atravges to the malleus, when contracted it pulls in opposition to the stapedius muscle, thereby tightening the tympanic membrane |
|
|
What is impedance mismatch? |
Resistance to flow due to the difference of air and fluid |
|
|
What would happen if we did not have a middle ear? |
Everyone would have a 30-40dB hearing loss |
|
|
Because of the delicate nature of the suspension within the middle ear cavity, it is vulnerable to |
Trauma and disease |
|
|
Acoustic reflex |
provides some protection to the ear from loud sounds, only occurs for signals around 85dB or louder. |
|
|
Explain the eustachian tube |
-The middle ears air pressure equalization system -runs from middle ear cavity down to the josopharynx (upper part of the throat, behind the nose) -is normally closed, but opens about every 2-3 you swallow |
|
|
What happens If the eustachian tube does not function properly (list 4) |
-the middle ear remains in a state of negative pressure or a partial vacuum -the TV retracts -Ossicular chain doesn't work as well -the negative pressure draws fluid from the mucous membrane lining from middle ear cavity |
|
|
What is the bony labyrinth? |
A series if channels and chambers embedded within the temporal bone |
|
|
The cochlea changes mechanical sound energy into what? |
A sequence of electrical discharges that is the language of the auditory nervous system. |
|
|
The cochlea is divided lengthwise into three channels by what two membranes? |
Basilar membrane and reissner's membrane |
|
|
What are the three channels of the cochlea? |
Scala vestibule Scala tympani Cochlear duct |
|
|
Scala vestibule |
-The channel formed by the upper bony wall of the cochlea -filled with perilymph |
|
|
Scala tympani |
-The channel between the basilar membrane and the lower bony wall -filled with perilymph |
|
|
Scala media {Cochlear duct} (list 3) |
-The third channel which separates the Scala tympani and the scala vestibule -lies between the basilar membrane and the reissner's membrane - filled with endolymph |
|
|
The oval window leads from where, to where? |
From the missile ear directly into the scala vestibuli |
|
|
Round window |
Leads directly into the scala tympani, on the other side of the cochlear duct, opposite the oval window |
|
|
Membraneous labyrinth (2 parts) |
Fluid filled membrane that sits inside the bony labyrinth, which houses the functional part of the cochlea |
|
|
What is known to be true about otosclerosis? (List 3) |
It is more common in women than men Reduced ability to understand children Difficulty hearing in noisy and quiet environments |
|
|
What is the isthmus? |
Where the canal narrows to enter the temporal bone |

