![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three main area of the ear and what is their function
|
Outer - Ear - collects sound waves and channels them inwards
Middle - conveys sound vibrations to the oval window Inner - house the receptors for hearing and equilibrium |
|
|
Describe the anatomy of the outer ear
|
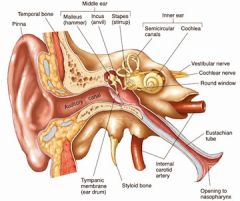
Consists of the Auricle, external auditory canal & tympanic membrane
Ear opening contains hairs and ceruminous glands that secrete cerumen(earwax) to trap dust |
|
|
Describe the anatomy of the middle ear
|
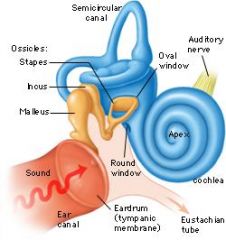
Found in petrous portion of temporal bone
separated from outer and inner ear by tympanic membrane and oval window Contains auditiry ossicles, connected by synovial joints- malleus, incus & stapes Euchachian tube found here connects to nasopharnyx |
|
|
Describe the skeletal muscles found in the middle ear
|
Tensor tympani muscles connect to ossicles and limit movement to prevent damage during loud noises and chewing
|
|
|
What are the three channels of the cochlea
|
Cochlear duct
Scala vestibule scala tymphani |
|
|
what rests on the basilar membrane and what does it contain?
|
The organ of corti, which contains the 16,00- hair cell receptors for hearing
|

