![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
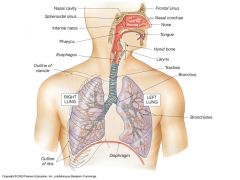
Locate oral cavity, nasal cavity, pharynx (throat) larynx (voice box), trachea (windpipe), two bronchi, and bronchioles
|
|
|
|
The trachea and bronchi are lined with cartilage. Once the cartliage stops, this extension of the bronchi is called ?
|
Bronchioles
|
|
|
Oxygen is transported into the ___ from the bronchioles?
|
alveoli
|
|
|
the alveoli allow Oxygen molecules to cross a thin membrane to oxygenate __________
|
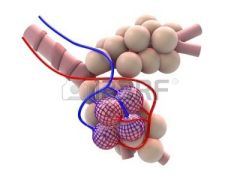
To oxygenate the blood from the pulmonary arteries so that the pulmonary veins can feed oxygenate blood back to the heart
|
|
|
Breathing:
Upon inhalation or inspiration, the thoracic diaphragm _______ and what happens? |
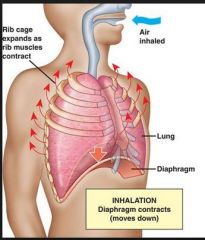
the thoracic diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, the diaphragm moves
down, the thoracic volume increases, the pressure decreases and air is drawn into the lungs. |
|
|
experation or exhale is when the muscles _____
|
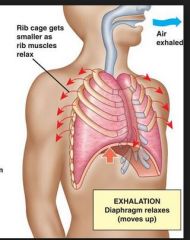
the muscles relax, the diaphragm moves upwards, the thoracic volume decreases, the thoracic pressure increases and the lungs deflate.
|
|
|
oxygen is transported through the alveoli into the blood due to ____
|
Diffusion of gases in the alveoli is aided
by a large surface area (total is 75 square meters!), very thin walls, moist lining and good blood supply. |
|
|
Oxygen within the blood is absorbed by red blood cells because they contain _____
|
Hemoglobin
|
|
|
hemoglobin is a _______ that can carry how many oxygen molecules? Why?
|
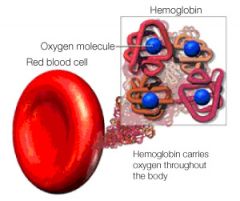
Heomglobin is a protein made of 4 subunits or amino acid chains (2 alpha and 2 beta) each subunit contains a heme molecule that contains an iron ion which can bind oxygen.
In binding, oxygen temporarily and reversibly oxidizes (Fe2+) to (Fe3+) therefor, one hemoglobin protein can carry 4 oxygen atoms. |
|
|
what happens to the carbon dioxide?
|
carbon dioxide from respiring cells is carried away as hydrogen carbonate ions and released from the pulmonary artery into the alveoli and we exhale the CO2
|
|
|
hemoglobin exhibits cooperative binding. What does that mean?
|
cooperative binding is when one oxygen atom binds to one heme group, then the conformation of the hemoglobin molecule changes so that the other 3 heme groups bind oxygen better and easier
|
|
|
allosteric regulation of an enzyme is
|
allosteric regulation is the regulation of an enzyme or other protein by binding an effector molecule at the protein's allosteric site (that is, a site other than the protein's active site). Effectors that enhance the protein's activity are referred to as allosteric activators, whereas those that decrease the protein's activity are called allosteric inhibitors.
|
|
|
hemoglobin is allosterically binds to ______
|
CO2 and Hydrogen ions. with higher co2 concentration and higher acidity, hemoglobin releases its oxygen
|
|
|
a blood type is defined by
|
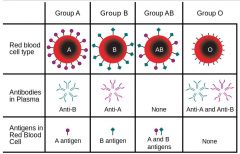
classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs).
|
|
|
the antibodies associated with the red blood cells are what type of antibody?
|
IgM
|
|
|
cellular respiration in the tissues that combines oxygen and glucose to produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP) energy for cellular process and
carbon dioxide as a by-product. what happens when there isn't enough oxygen in the muscles for ATP generation? |
When the demand for oxygen exceeds the supply
then anaerobic respiration can be used to generate ATP energy; lactic acid (lactic acid = lactate and H+ atoms) is the by-product. |
|
|
describe the flow of blood within the heart... there is a very thorough description for an answer fyi
|
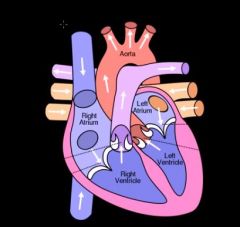
Deoxygenated blood from the venous system reaches the right atrium of the heart from
the body via the inferior and superior vena cava; it passes through the tricuspid valve (contains three cusps/flaps) into the right ventricle of the heart to be pumped out of the heart through the pulmonary valve (prevents backflow) via the pulmonary arteries (the only artery to carry de-oxygenated blood) to the lungs; oxygenated blood leaves the lungs via the pulmonary veins and reaches the left atrium of the heart, passing through the bicuspid (mitral) valve and into the left ventricle before being pumped out of the heart through the aortic valve into the aorta and to the body. |
|
|
heart beat is controlled by _____
|
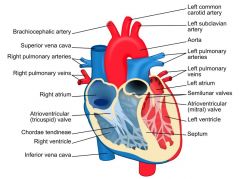
Heart beat: rate controlled by electrical impulses from the sinoatrial (SA) node
(pacemaker cells in the wall of the right atrium); atria contract first followed by the ventricles (impulses from the atrioventricular (AV) node, the bundle of His (AV bundle) and the Purkinje fibres); in other words, both atria contract together followed by both ventricles together a fraction of a second late |
|
|
blood pressure is ____
|
Blood pressure: systolic over diastolic (eg 120/70): systole (heart contracts) and
diastole (heart relaxes); systole + diastole = cardiac cycle (eg 75 cycles/min or one every 0.8 seconds). |
|
|
cardiac output is
|
Cardiac output (ml/min) = stroke volume (ml) × heart rate (beats per minute).
|
|
|
blood is composed of ____
|
Composition: 55% = plasma (of which 90% = water; 7% = proteins); 45% = cells
(99% = red; 1% = white). |
|
|
the functions of the blood are
|
transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, waste products and hormones and clotting factors (plasma);
regulates pH, temperature and osmotic pressure (plasma proteins); protects: leucocytes (white blood cells) fight infection; lymphocytes (two types): helper T-cells that mature in the thymus gland and B-cells that mature in the bone marrow and produce antibodies that respond to antigens (foreign bodies) |

