![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gross Anatomy |
Gross Anatomy Seen with the naked eye / without magnification |
|
|
Histology |
Histology Microscopic anatomy of tissues. Determines functionality & attributes (eg. light, strong) |
|
|
Systemic Anatomy |
Systemic Anatomy organ systems |
|
|
Regional Anatomy |
Regional Anatomy body regions (eg. lower limb) |
|
|
Physiology |
Physiology Investigates functions of the body (often focused on cellular or molecular level) How does it operate? |
|
|
A molecule is made up of .... |
A cell is made up of ... Atoms |
|
|
An organelle is made up of .... |
An organelle is made up of ... Molecules |
|
|
A cell is made up of ... |
A cell is made up of ... - Different types and combinations of organic molecules. - Organelles (mitochondria, ER, golgi apparatus, nucleus) - Plasma membrane - Structural Supports (intermediate filaments, microtubules, microfilaments) - Cytosol |
|
|
Major classes of organic (carbon-containing) molecules found in humans? |
Major classes of organic molecules found in humans: - Lipids - Carbohydrates - Proteins - Nucleic acids |
|
|
Tissue is made up of ... |
Tissue is made up of ... Similar cell types |
|
|
Epithelial tissue |
Epithelial tissue - Forms lining (eg. epidermis, of open cavities of digestive & resp systems, organs of ventral cavity) - Covers glands |
|
|
Connective tissue |
Connective tissue Linking or supporting other body structures |
|
|
Muscle tissue |
Muscle tissue Generates movement |
|
|
Nervous tissue |
Nervous tissue Transmits & processes information |
|
|
Organs are made up of ... |
Organs are made up of ... Different types of tissues, each type performing a specific function |
|
|
An organ system is made up of ... |
An organ system is made up of ... Different organs, which together perform a specific collective function |
|
|
Anterior |
Anterior In front of ; towards the front |
|
|
Posterior |
Posterior Behind ; toward the back surface |
|
|
Dorsal |
Dorsal At the back side of the human body |
|
|
Ventral |
Ventral At the belly side of the human body |
|
|
Medial |
Medial Towards or at the midline of the body |
|
|
Lateral |
Lateral Away from the midline of the body |
|
|
Superior |
Superior Towards the head |
|
|
Inferior |
Inferior Towards the feet |
|
|
Proximal |
Proximal Closer to an origin |
|
|
Distal |
Distal Away from an origin |
|
|
Frontal / Coronal Plane |
Frontal / Coronal Plane Vertical plane, dividing the body into anterior & posterior sections |
|
|
Sagittal Plane |
Sagittal plane Vertical plane, dividing the body left from right |
|
|
Transverse Plane |
Transverse Plane Horizontal plane, dividing the body into superior & inferior sections |
|
|
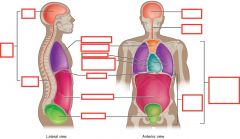
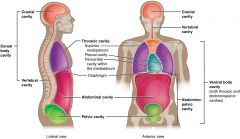
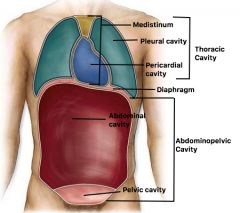
Dorsal Cavity |
Dorsal cavity Contains - Cranial - Vertebral cavities |
|
|
Ventral Cavity |
Ventral Cavity Contains - Thoracic - Abdominal - Pelvic cavities |
|
|
Posterior Cavities? |
Posterior cavities - Cranial (formed by cranium, holds brain) - Vertebral (formed by vertebrae, contains spinal cord) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
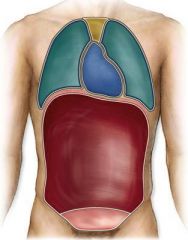
Serous Membranes |
Membranes in ventral cavity -AKA serosa -Lines organs in ventral cavity -Double-layered, -Suspends organ & allows movement -Outer Parietal layer, Inner Visceral layer -Lubricated by serous fluid between |
|
|
Cell membrane |
Cell membrane -Plasma membrane -Phospholipid bi-layer (50%), with embedded proteins (45%) and some carbs (5%) -Selectively permeable |
|
|
Cell membrane transport processes |
Cell membrane transport processes Active - using energy supplied by cell Passive - using no energy |
|
|
Passive Transport |
Passive transport - No energy required - Molecules move from high concentration to low - Simple diffusion (lipids) - Osmosis (water) - Ion channels - Facilitated diffusion (glucose) |
|
|
Osmosis |
Osmosis - Passive transport - Movement of water through globular protein channels of membrane from high concentration to low |
|
|
Simple Diffusion |
Simple diffusion - Passive transport - Molecules move through phospolipid portion of membrane from high concentration to low |
|
|
Ion/Membrane Channels |
Ion/Membrane channels - Passive transport - Specific molecules allowed to move through proteins in cell membrane, from high concentration to low - eg. Salt |
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion |
Facilitated diffusion - Passive transport - Specific molecules move through specific protein channels, from high concentration to low - Protein channel changes shape to assist movement |
|
|
Active Transport |
Active transport - Cell supplies energy (usually ATP) - Molecules moved against concentration or electrochemical gradient |
|
|
Sodium Potassium Pump |
Sodium Potassium Pump - Active Transport - 3x Sodium ions pumped out of cell, 2x Potassium ions pumped into cell - Using membrane protein ATPase - Essential for nerve and muscle function - Creates chemical concentration gradient (potential energy) |
|
|
Chemical Concentration Gradient |
Chemical concentration gradient - potential energy - harnessed by opening membrane channels and allowing diffusion = electrical current |
|
|
Cytosol |
Cytosol - Semi-fluid portion of cell (organelles sit in) - 75-90% water - Proteins, carbs & lipids - Minerals (sodium & chloride) - Has low sodium, low chloride & high potassium |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
Cytoplasm = Cytosol + organelles |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Cytoskeleton - Filamentous proteins in cytoplasm - Microtubules - Intermediate filaments - Microfilaments |
|
|
Microtubules |
Microtubules - Determine shape of cell & distribution of organelles - Mitochondria, lysosomes & secretory vesicles are continually moved & repositioned along them - Can join to form centrioles, cilia & flagella |
|
|
Microfilaments |
Microfilaments - Thinnest strands that 'web' through cell - Based on protein actin - Resists compression - Involved in cell motility or changes in cell shape |
|
|
Intermediate Filaments |
Intermediate filaments - Protein fibers resembling rope - Most stable & permanent - Resist forces exerted on the cell - eg. Keratin |
|
|
Cilia |
Cilia - Made of microtubules in 9+2 arrangement - Extensions on surface of cells - Move substances (eg. mucous) in one direction across cell surfaces |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Mitchondria - Enzymes synthesise ATP - Double membrane - Inner membrane folded - Folds = cristae - Spaces between folds = matrix - Has own DNA, RNA & ribosomes |
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Endoplasmic Reticulum - Involved in production of proteins - Involved in synthesis & metabolism of lipids - Continuous with outer nuclear membrane - Rough ER = makes proteins & phospholipids - Smooth ER = makes lipids, steroid hormones & carbs; calcium storage |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
Golgi apparatus - Stacked & flattened membranous sacs - modifies, concentrates & packages the proteins & lipids made in Rough ER - Has secretory vesicles which transport this to cell membrane, or other location in cell |
|
|
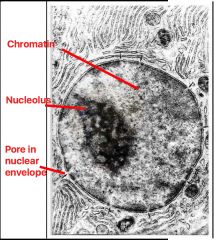
Nucleus |
Nucleus - Contains chromatin & nucleolus - Bound by nuclear envelope |
|
|
Nuclear envelope |
Nuclear envelope - Double membrane separated by fluid-filled space - Ribosomes on outer surface (continuous with Rough ER) - Has nuclear pores |
|
|
Chromatin |
Chromatin - Located in nucleus - DNA + histone proteins + RNA chains - packages DNA |
|
|
Nucleolus |
Nucleolus - Makes ribosomal RNA's - Adds to proteins to form ribosomal subunits - Exported to cytosol via nuclear pores |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Ribosomes Make proteins |
|
|
|

