![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A malignancy involving the lateral breast would most likely metastasize FIRST to which of the following groups of nodes?
|
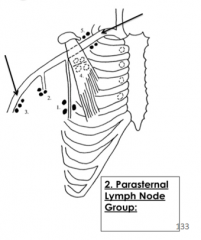
Axillary nodes-75% of lymph drains through this group
|
|
|
What are the boundaries of the axilla?
|
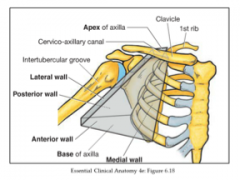
-Pec Major/minor
-Subscapularis/Lat Dorsi/Teres Major -Humerus -Lateral thoracic/Serratus Anterior -Apex (clavicle and first rib and scapula |
|
|
Which nerve innervates the serratus anterior?
|
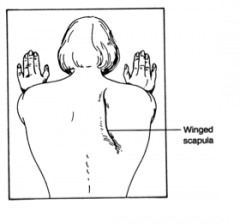
The long thoracic nerve
When injured this presents as a winged scapula |
|
|
What composes the axillary sheath?
|
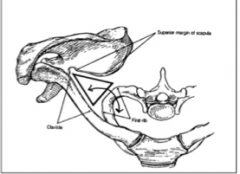
-Axillary artery (lateral border of the first rib to the inferior border of Teres Major
-Axillary vein -Brachial Plexus (C5-T1) -Lymph -Fat |
|
|
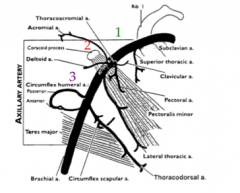
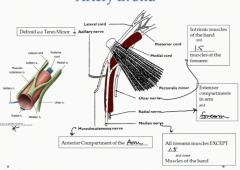
What are the boarders of the first portion of the axillary artery?
|
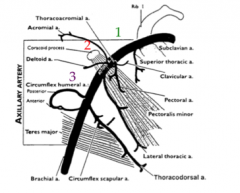
The lateral edge of the first rib to the medial boarder of pectoralis minor. This contains a branch to the superior thoracic artery that will go into the first rib space.
|
|
|
What are the boarders of the second portion of the axillary artery?
|
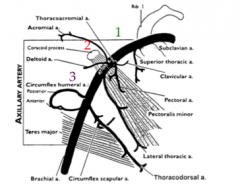
From the medial to the lateral boarder of pectoralis minor
This contains the lateral thoracic artery (supplies the serratus anterior) and the thoracoacromial artery/trunk (pectoral/deltoid/acromial/clavicular) |
|
|
What are the boarders of the third portion of the axillary artery?
|
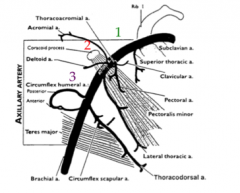
From the lateral boarder of pec minor to the inferior boarder of teres major this is where the brachial artery begins.
This contains the branches of the anterior humeral circumflex, the posterior humeral circumflex, and the subscapular arteries |
|
|
Which is larger? The anterior or posterior circumflex artery
|
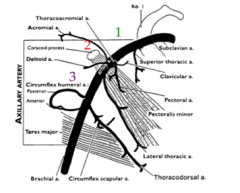
The posterior circumflex artery
|
|
|
What is the blood supply and innervation of the Latissimus Dorsi?
|
The thoracodorsal artery (branches from the subscapular artery) and thoracodorsal nerve
|
|
|
What is collateral circulation?
|
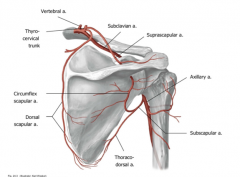
Vessels surrounding the same bone or joint area providing it with proper blood flow and alternative routes of flow in case of injury or ligation to the axillary artery
|
|
|
What are the two branches of the subclavian artery that supply the scapular arcade?
|
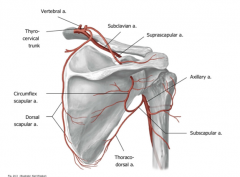
The dorsal scapular artery and suprascapular artery.
|
|
|
What are the two branches of the axillary artery that supply the scapular arcade?
|
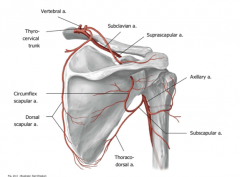
The circumflex artery and the thoracodorsal artery (coming from the subscapular artery
|
|
|
What spinal roots are included in the brachial plexus?
|

The Ventral primary rami of C5, 6, 7, 8 and T1
|
|
|
What type of nerves are included in the VPR of the brachial plexus roots?
|

General Sensory Afferent and Efferent Nerves
(Sensory and Motor) |
|
|
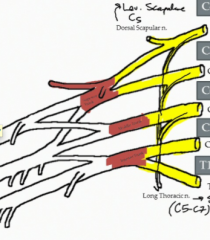
What muscles does the dorsal scapular nerve innervate and where does it branch from the brachial plexus?
|

The Rhomboids and Levator Scapulae. It contains nerve from the C5 VPR or the C5 root of the brachial plexus
|
|
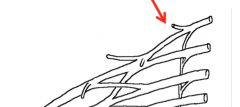
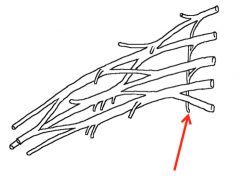
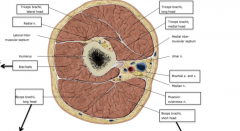
What is the nerve of the brachial plexus highlighted in the image?
|
Dorsal scapular nerve
|
|
|
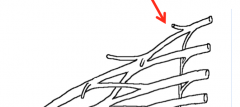
What muscle is innervated by the long thoracic nerve and where does it branch from the brachial plexus?
|
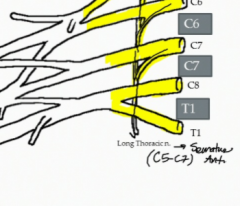
The Serratus Anterior and it branches from roots C 5, 6, and 7 traveling with the lateral thoracic artery
|
|
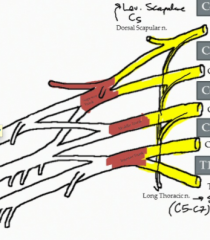
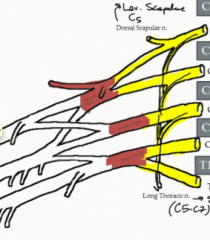
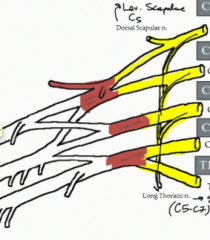
What is the nerve of the brachial plexus highlighted in the image?
|
Long thoracic nerve (C5-7)
|
|
|
The roots of the brachial plexus combine to form what?
|
The Superior, Middle, and Inferior trunks
|
|
|
Which roots combine to form the superior trunk of the brachial plexus?
|
C5 and C6
|
|
|
Which roots combine to form the superior trunk of the brachial plexus?
|
C7
|
|
|
Which roots combine to form the superior trunk of the brachial plexus?
|
C8 and T1
|
|
|
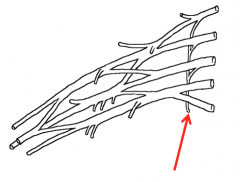
What are the branches from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus?
|
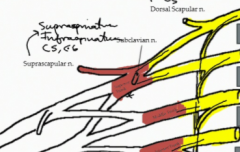
The Suprascapular (C5 and 6) and the subclavian nerve
|
|
What are the nerves highlighted in the image?
|
The suprascapular nerve (red) and the subclavian nerve (purple)
|
|
|
What muscles are innervated by the suprascapular nerve?
|
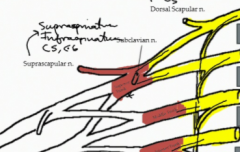
Supraspinatus and Infraspinatus. The nerve branches from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus and therefore contains nerve fibers from C5 and C6
|
|
|
Each trunk of the brachial plexus divides into how many divisions?
|

Two-The anterior and posterior
The anterior supplies the anterior or flexors of the arm and the posterior divisions supply the posterior or extensors of the arm |
|
|
Which divisions combine to form the lateral cord?
|

The anterior divisions of the superior and middle trunk
|
|
|
Which divisions combine to form the medial cord?
|

The anterior division of the inferior trunk
|
|
|
Which divisions combine to form the posterior cord?
|

The posterior divisions from all three trunks (superior, middle and inferior
|
|
|
What are the branches that come from the divisions of the brachial plexus?
|
None
|
|
|
How are the cords named?
|
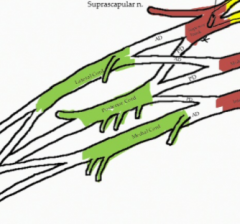
Due to their position with the axillary artery
|
|
|
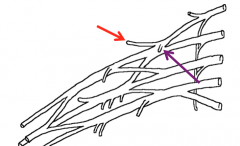
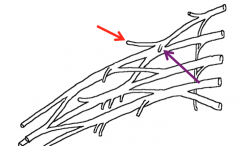
What are the branches from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus?
|
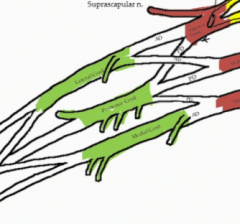
The Lateral pectoral nerve which innervates pec major
|
|
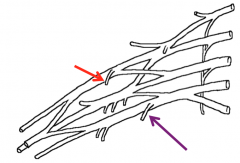
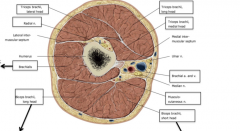
Name the nerves highlighted in the image
|
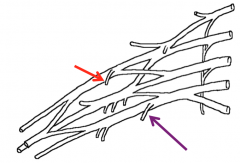
Lateral pectoral nerve (red)
Medial pectoral nerve (purple) |
|
|
What does the medial pectoral nerve innervate?
|
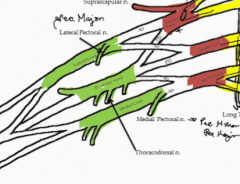
Pectoralis major and minor
|
|
|
What are the branches from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus?
|
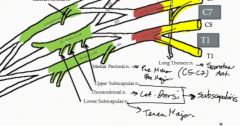
The thoracodorsal nerve which innervates the latissimus dorsi and the upper and lower subscapular nerves which in combination innervate the subscapularis muscle. The lower subscapular nerve also innervates teres major
|
|
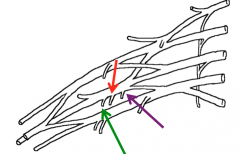
What are the nerves highlighted in the image above?
|
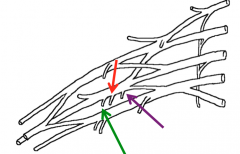
The branches of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus
Green-Lower Subscapular nerve Red-Thoracodorsal nerve Purple-Upper Subscapular nerve |
|
|
Which muscles are innervated by the branches from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus?
|
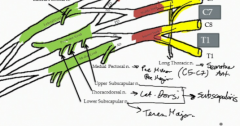
The latissimus dorsi is innervated by the thoracodorsal nerve
The subscapularis is innervated by the upper and lower subscapular nerve The teres major is innervated by the lower subscapular nerve |
|
|
What are the branches of the medial cord of the brachial plexus
|
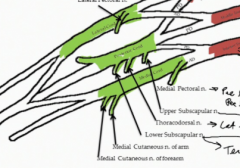
The medial pectoral nerve
The medial cutaneous nerve of the arm and the medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm |
|
|
What types of fibers are contained in the medial cutaneous nerves from the medial cord of the brachial plexus?
|
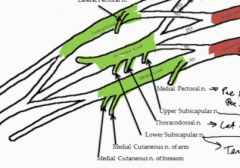
Only GSA General Sensory Afferent nerves
|
|
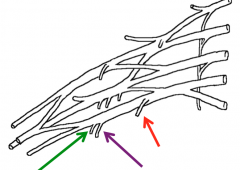
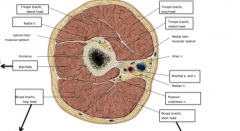
What are the nerves highlighted in the image?
|
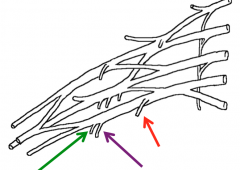
The branches of the medial cord of the brachial plexus
Green-Medial cutaneous nerves of the forearm Purple-Medial cutaneous nerves of the arm Red-Medial pectoral nerve |
|
|
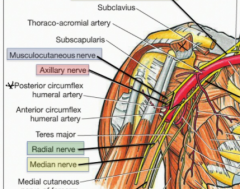
What are the terminal branches of the posterior cord?
|
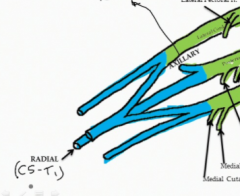
The Axillary nerve which contains nerve fibers from C5 and C6 roots and innervates the deltoid and the teres minor
The Radial nerve innervates muscles of the posterior compartment of the arm and forearm and contains nerve fibers from all roots of the brachial plexus (C5-T1) |
|
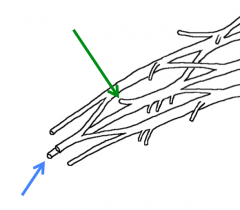
Name the nerves highlighted in the branches above?
|
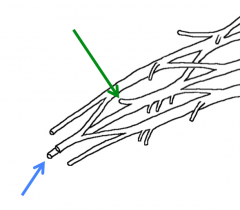
The terminal branches of the posterior cord
Green-Axillary nerve Blue-Radial nerve |
|
|
What are the terminal branches of the lateral cord?
|
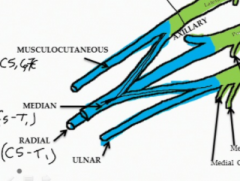
The musculocutaneous nerve innervates the anterior compartment of the arm (flexors) contains nerve fibers from C 5, 6, and 7
The median nerve contains fibers from C5-T1 and innervates the anterior muscles of the forearm (except for 1.5) |
|
|
What are the terminal branches of the medial cord?
|
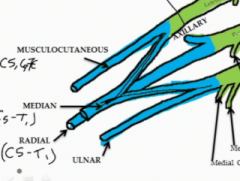
The ulnar nerve which contains fibers from C7-T1
|
|
|
What is the significance of "Read that damn cadaver book!"
|
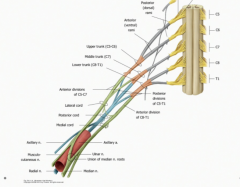
It helps show the progression of the brachial plexus:
Roots-Trunks-Divisions-Cords-Branches |
|
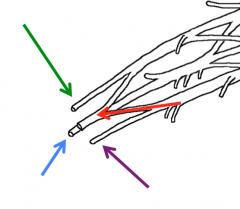
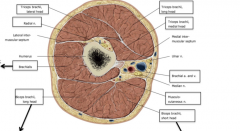
What nerves are highlighted in the image?
|
Green-Musculocutaneous
Blue-Radial Red-Median Purple-Ulnar |
|
|
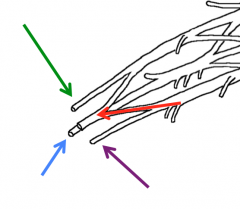
What does the musculocutaneous nerve innervate?
|
The anterior compartment of the arm
|
|
|
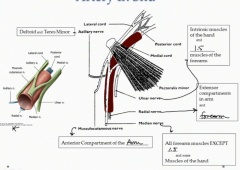
What does the medial nerve innervate?
|
All forearm muscles except 1.5 and some muscles of the hand
|
|
|
What does the ulnar nerve innervate?
|
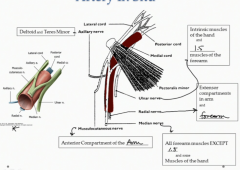
The intrinsic muscles of the hand and 1.5 muscles of the forearm
|
|
|
What does the radial nerve innervate?
|
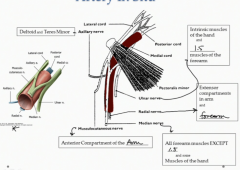
The extensor compartments in the arm and forearm
|
|
|
What does the axillary nerve innervate?
|
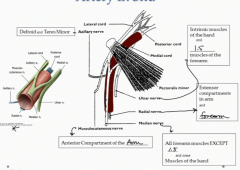
The deltoid and teres minor
|
|
|
What nerve innervates the coracobrachialis?
|
The musculocutaneous nerve
|
|
|
What is the scalene triangle?
|
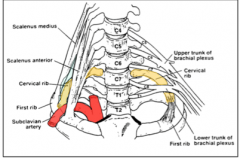
Outlet created by scalenus anterior and scalenus medius attaching to the first rib. Creates a triangle that the subclavian artery and brachial plexus exits from
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of abnormal cervical rib condition?
|
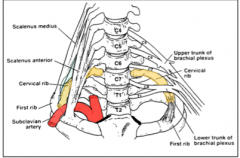
It compresses the lower trunk and the subclavian artery so vascular signs are cool skin, weak pulse, and white skin whereas nervous signs are paresthesia and pain.
|
|
|
What are the causes of an injury to the superior or upper part of the brachial plexus?
|

Increases the angle between the neck and shoulder including biking injuries and a dangerous delivery.
The signs are Erb's Palsy which cause paralysis of the muscles of the shoulder and arm supplied by the nerves of C5 and C6 |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Erb's Palsy
|
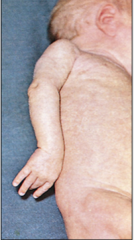
The waiters tip position caused because the nerves of C5 and C6 are paralyzed
1. Arm medially rotated (lost lateral rotators infraspinatus, teres minor, deltoid) 2. Adducted shoulder (lost supraspinatus and deltoid) 3. Extended elbow 4. Flexion at the wrist (loss of extensors) |
|
|
What are the causes of an injury to the inferior or lower part of the brachial plexus?
|
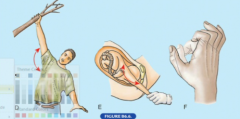
When the upper limb is hyperabducted such to break a fall or when a baby is pulled excessively during delivery
|
|
|
What is the presentation of a injury to the inferior parts of the brachial plexus?
|
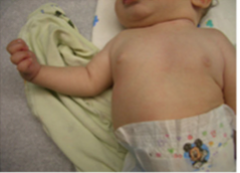
Klumpke's Paralysis
The extensors of the digits are affected leaving a claw hand presentation because the ulnar fibers have been injured. |
|
|
What are the three potential sites of neruovascular compression in the axillary area?
|
1. Interscalene triangle
2. Subcoracoid region 3. Costoclavicular space |
|
|
What are the flexors of the arm (anterior compartment)?
|
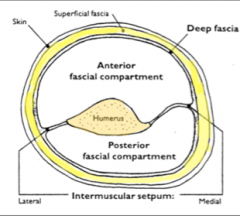
Biceps Brachii
-Long head -Short Head Brachialis Coracobracialis |
|
|
What is the nerve supply of the anterior compartment of the arm?
|
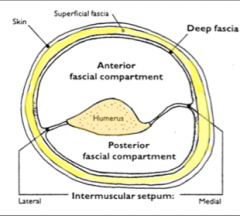
The musculocutaneous nerve
|
|
|
What are the extensors of the arm (posterior compartment)?
|
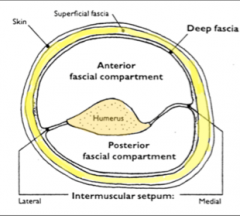
The triceps brachii
-Long head -Lateral head -Medial head |
|
|
What is the nerve supply of the posterior compartment of the arm?
|
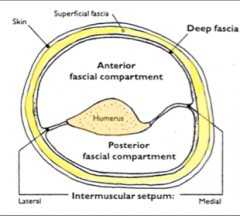
The radial nerve
|
|
|
Which muscles originate on the coracoid process?
|
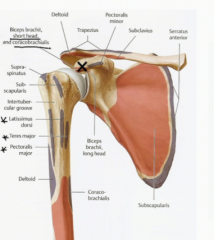
The short head of the biceps brachii
Pectoralis minor Coracobrachialis |
|
|
What is the distal insertion of the coracobrachialis?
|
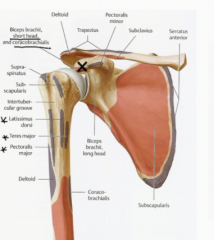
The mid part of the humerus (anterior side)
|
|
|
Which is more medial: radius or ulna?
|
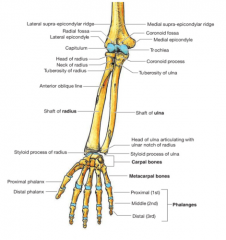
The ulna
|
|
|
What is the lateral epicondyle?
|
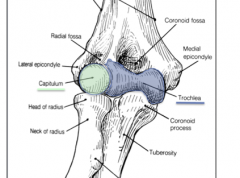
A bony projection of the distal humerus commonly referred to as the common extensor tendon which is injured from a tennis backhand or tennis elbow
|
|
|
What is the medial epicondyle?
|
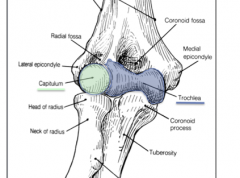
A bony projection of the distal humerus and a insertion point for many posterior extensor muscles also known as the common flexor tendon. When injured this is known as golfer's elbow
|
|
|
What are the two condyles of the distal humerus?
|
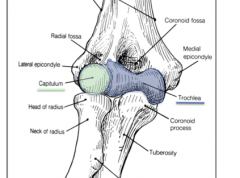
The lateral Capitulum (articulates with the radius) and the medial Trochlea (articulates with the head of the ulna)
|
|
|
What is the significance of the radial tuberosity?
|
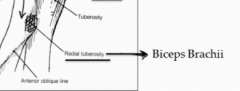
This is the insertion point of the biceps brachii which can then act as a powerful supinator (why screws should always be screwed in with the right hand
|
|
|
What is the insertion of the brachialis?
|
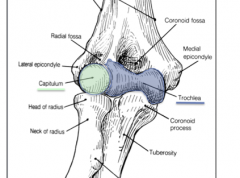
The tuberosity of the ulna
|
|
|
What are the two major points of articulation of the elbow joint?
|
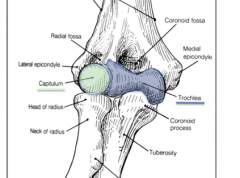
-The speroidal capitulum of the humerus with the slightly concave head of the radius
-Spool shaped trochlea of the humerus with the trochlear notch of the ulna (above the coranoid process) |
|
|
What is the insertion of all triceps heads?
|
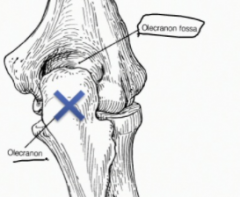
The olecranon
|
|
|
What does the olecranon of the ulna fit into? What does this prevent?
|
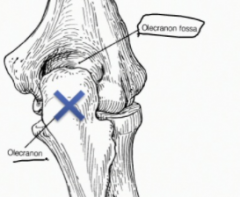
The olecranon fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus which prevents hyperextension
|
|
|
What does hitting your funny bone cause?
|
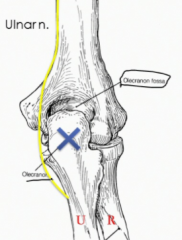
Tingling or paresthesis of the medial 1.5 digits
|
|
|
Why would a radial nerve injury midway down the humerus not affect the triceps which are innervated by the radial nerve?
|
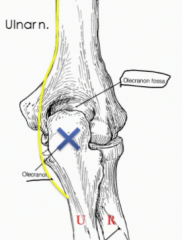
This is because they innervate the triceps near their origin so extension will not be affected. More down stream the flexors of the wrist will be affected so this may cause wrist drop.
|
|
|
What movements are possible at the elbow joint?
|
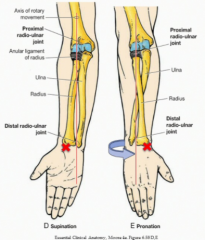
The flexion/extension of the hinge joint and the pronation/supination of the pivot joint
|
|
|
What is the most common dislocation for children under ten?
|
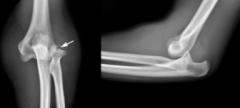
An elbow dislocation
|
|
|
What are the attachments of the small head of the biceps brachii?
|
The coracoid process of the scapula and the radial tuberosity of the humerus-this supinates and flexes the forearm
|
|
|
What are the attachments of the long head of biceps brachii?
|
The supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula and the distal attachment of the radial tuberosity-this supinates and flexes the arm
|
|
|
What are the insertions of the brachialis muscle?
|
The midline of the humerus to the ulna tuberosity on the anterior portion therefore is a strong flexor.
|
|
|
What will the musculocutaneous nerve innervate?
|
The anterior portion of the arm mainly the biceps and the brachialis
|
|
|
Where is the insertion point of the triceps?
|
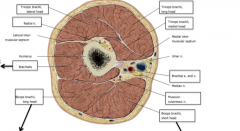
The long head inserts on the infraglenoid process of the scapula therefore the triceps brachii act on both the shoulder and the elbow joint. Innervated by the radial nerve.
|
|
|
Tell the story of the axillary nerve.
|
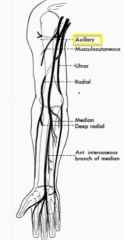
A terminal branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. This travels posteriorly around the surgical neck of the humerus to innervate the deltoid and teres minor (C5/6)
|
|
|
Tell the story of the musculocutaneous nerve.
|
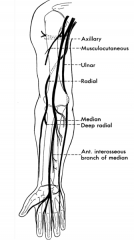
The terminal branch of the lateral cord it dives deep into the coracobrachialis muscle. This contains GSA and GSE fibers. After emerging from the coracobracialis this travels superficial to the brachialis and deep to the biceps. After the elbow joint it becomes the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm and is only afferent.
|
|
|
Tell the story of the radial nerve.
|
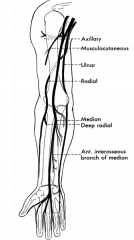
A terminal branch of the posterior cord that dives deep innervating the triceps brachii then going through the spiral groove to innervate the brachiradialis muscle and superficial of the brachialis. This branches into the morot deep radial nerve and the superficial radial nerve (sensory)
|

