![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Axilla (armpit) |
Pyramidal in shape, four sides, an apex and a base, serves as a passage for nerves and vessels of the upper limb. Contains: branches of the brachial plexus, axillary vessels, and axillary lymph nodes |
|
|
Cardiovascular system |
All we need to know: Arteries move blood away from heart and towards body structures Veins: carry blood towards heart and away from body structures. |
|
|
Pulmonary Ciculation |
Pulmonary arteries bring low O2 blood from heart to lungs Pulmonary veins bring high O2 blood from lungs to heart |
|
|
Systemic Circulation |
Systemic arteries bring high O2 blood from heart to body tissues Systemic veins bring low O2 blood from body tissues to heart |
|
|
Superficial viens |
Drain skin and subcutaneous tissue.
|
|
|
Cephalic Vein |
Begins on lateral side of hand, empties into subclavian vien |
|
|
Basilic Vein |
Begins on the medial side of hand, joins the brachial viens to form the axillary vein |
|
|
Median Cubital Vein |
Communication between the cephalic and basilic veins. |
|
|
Skin (integumentary system) |
Provides protection Regulate heat Transmits sensations |
|
|
Superficial Fascia (integumentary system) |
Location of cutaneous vessels and nerves Fat storage |
|
|
Deep Fascia (integumentary system) |
Holds structures in place Envelopes and separates muscles |
|
|
Arteries of the upper limb |
Aortic Arch---> (Brachiocephalic trunk on the right side)---> Subclavian A.---> Axillary A.---> Brachial A. |
|
|
Subclavian Artery- need to know |
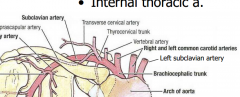
Need to know: Vertebral A. Thyrovervical trunk Internal thoracic A. |
|
|
Parts of Axillary Artery |
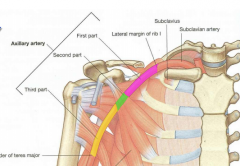
Part 1: b/w first rib and pec minor Part 2: lies posterior to pec minor Part 3: from pec minor to teres major |
|
|
Axillary A. need to know |
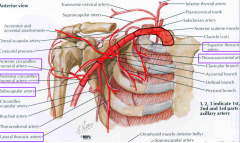
Superior thoracic A. Thoracoacromial A (trunk) Lateral Thoracic A. Subscapular A. Anterior and Posterior Circum. Hum A. |
|
|
Axillary Vein |
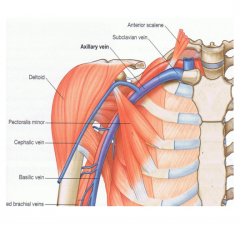
Continuation of brach. v, begins at inf teres major, ends at outer border of first rib. Then turns to subclavian v. Joined by the cep. & bas veins |
|
|
Brachial Artery |
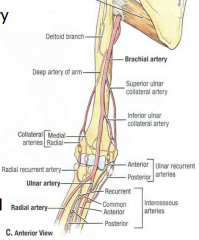
Begins at inf. teres major, ends at cubital fossa opposite the neck of radius. Divides into radial and ulnar arteries |
|
|
Collateral Arteries |
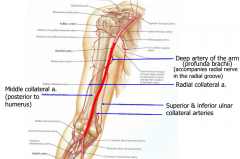
Anastomosis. Allows blood to reach forearm when brachial artery is blocked. Regardless of elbow flex. or exten. |

