![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
simple squamous epithelium |
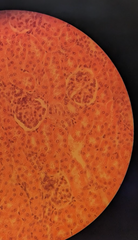
allows for rapid exchange location: lining lung air sacs |
|
|
simple cuboidal epithelium |

allows for absorption and secretion Location: kidney tubules |
|
|
simple columnar epithelium |
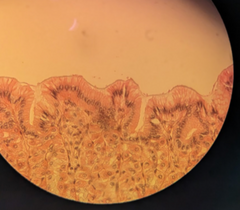
allows for absorption and secretion Locations: uterine tube(ciliated), anal canal(nonciliated), ect |
|
|
pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
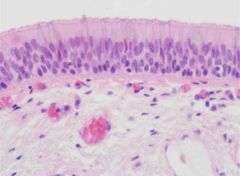
protection; ciliated form secretes mucin and moves mucus Location: respiratory tract lining |
|
|
stratified squamous epithelium |
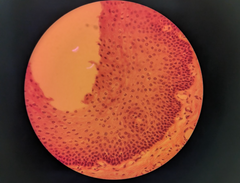
protection, can be keratinized Location: epidermis of skin(keratinized), esophagus(non keratinized) |
|
|
stratified cuboidal epithelium |
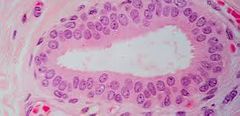
protection, secretion, support the walls of some ducts Location: lining of sweat glands |
|
|
stratified columnar epithelium
|
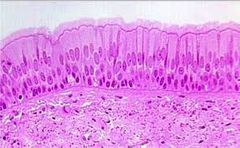
protection and secretion Location: ducts of some salivary glands |
|
|
transitional epithelium |
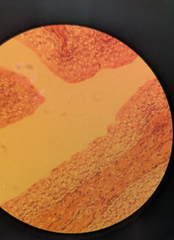
stretch and recoil Location: urinary tract |
|
|
cranial |

|
|
|
facial |

|
|
|
nuchal |

|
|
|
mental |

|
|
|
buccal |

|
|
|
frontal |

|
|
|
clavipectoral triangle |
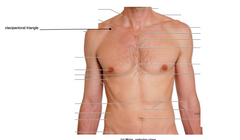
|
|
|
sternal angle |

|
|
|
linea alba |

|
|
|
umbilicus |

|
|
|
tendinous intersection |

|
|
|
costal margin |

|
|
|
left lower quadrant (LLQ) |

|
|
|
right lower quadrant (RLQ) |

|
|
|
right upper quadrant (RUQ) |

|
|
|
left upper quadrant (LUQ) |

|
|
|
umbilical region |

organs: stomach, pancreas, small intestines, transverse colon |
|
|
hypogastric region
|
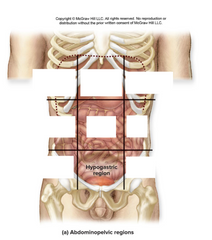
organs: small intestine, sigmoid colon, bladder |
|
|
epigastric region |

organs: stomach, liver, pancreas, right and left kidneys |
|
|
left hypochondriac region |
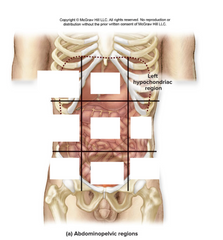
organs: stomach, liver, left kidney, spleen |
|
|
left lumbar region |

organs: small intestine, descending colon, left kidney |
|
|
left iliac region |

organs: small intestines, descending colon, left kidney |
|
|
right iliac region |
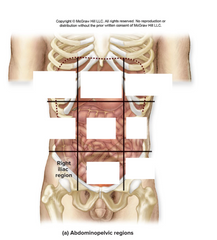
organs: small intestines, appendix, cecum and ascending colon |
|
|
right lumbar region |
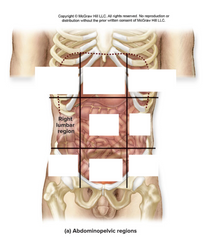
organs: liver, small intestines, ascending colon, right kidney |
|
|
right hypochondriac region |

organs: liver, gallbladder, right kidney 21
|
|
|
gluteal fold |
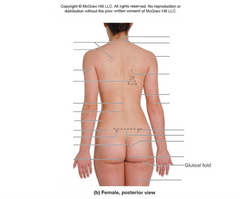
|
|
|
natal cleft |
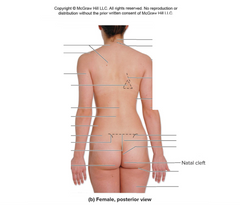
|
|
|
triangle of auscultation |

|
|
|
iliac crest |

|
|
|
median furrow |

|
|
|
loose areolar CT: mast cells |
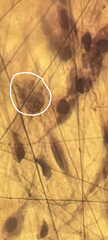
|
|
|
loose areolar CT: fibroblasts |

|
|
|
loose areolar CT: elastic fiber |
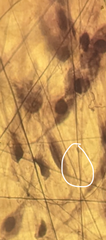
|
|
|
loose areolar CT: collagen fiber |
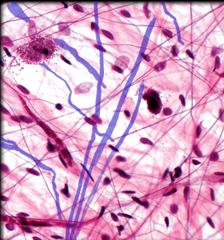
|
|
|
adipose CT: adipocytes
|

|
|
|
adipose CT: collagen fiber |

|
|
|
dense regular CT: fibroblasts |

|
|
|
dense regular CT: collagen fibers |

|
|
|
dense irregular CT: fibroblast |

|
|
|
dense irregular CT: collagen fibers
|

|
|
|
adheres junctions |
stabilize the apical surface |
|
|
desmosomes |
allows ET to stretch and recoil |
|
|
gap junctions |
stabilize the apical surface |
|
|
mast cells function |
secrete histamines and heparin |
|
|
collagen fiber |
most common protein in the body |
|
|
adipocytes function |
for energy storage and insulation |
|
|
plasma cells function |
secretes antibodies |
|
|
holocrine gland |
product is stored in a cell that disintegrates |
|
|
Sebaceous gland |
secretes sebum, directly into the hair follicle |
|
|
apocrine gland |
pinches off the apical potion storing product |
|
|
merocrine gland |
secretes products from vesicles via exocytosis |
|
|
areolar CT |
surrounds, protects, and connects epithelia to deeper tissue |
|
|
adipose CT |
stores energy and cushions organs |
|
|
reticular CT |
is the supportive framework for lymphatic organs, stroma |
|
|
dense regular CT |
avascular, parallel collagen fibers |
|
|
dense irregular CT |
randomly arranged collagen fibers, resin stress |
|
|
elastic CT |
allows stretch and recoil in large arteries
|
|
|
epithelial tissue |
highly mitotic, cannot contain sensory receptors |
|
|
histamine function |
vasodilator |
|
|
heparine |
anticoagulant |
|
|
anterior |
ventral, front |
|
|
posterior |
dorsal, back |
|
|
superior |
toward head |
|
|
inferior |
toward feet, away from head |
|
|
caudal |
toward tail |
|
|
cranial |
toward head |
|
|
rostral |
toward nose |
|
|
medial |
toward midline |
|
|
lateral |
away from midline |
|
|
deep |
internal, father away from surface |
|
|
superficial |
external, close to surface |
|
|
proximal |
toward trunk |
|
|
distal |
away from trunk |

