![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
108 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Axillary Nerve Origin + Innervation |
-C5-C6, posterior cord
-Innervates the deltoid and the teres minor |
|
|
Spinal accessory nerve |
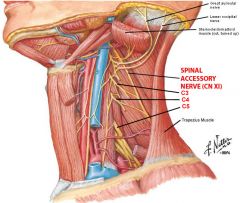
-Crosses the triangle within the layers of deep fascia investing the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscle -Innervates trapezius |
|
|
Suprascapular nerve |
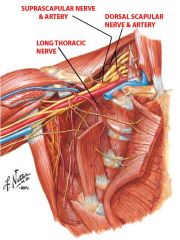
-C4, C5, C6 -Runs perpendicularly under clavicle close to acromion -Innervates the infraspinatus (C5, C6) and supraspinatus (C4, C5, C6) muscles |
|
|
Rotator cuff |
SITS: Supraspinatous Infraspinatous Teres Minor
"Cuff" because one muscle on the front of scapula, one on top, and two on the back
They stabilize the glenohumeral joint, meaning they are close to the pivot point! Don't participate in abduction or adduction
|
|
|
Triangle of auscultation |
Bordered by: Inferior portion of Trapezius Superior portion of Latissimus Dorsi Medial border of the scapula
-Lies over the 7th rib and 6th and 7th intercostal spaces -This is where breathing can be heard really well |
|
|
General info about brachial plexus |
-C5-C8 and T1, responsible for motor innervation of all muscles of the upper extremity except the trapezius and levator scapula
-Damage to the brachial plexus causes arm to lie medially |
|
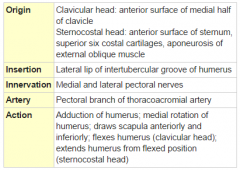
Pectoralis Major Muscle |
|
|
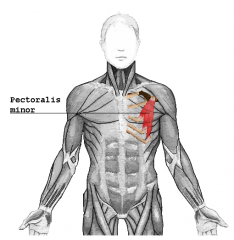
Pectoralis Minor Muscle |

|
|
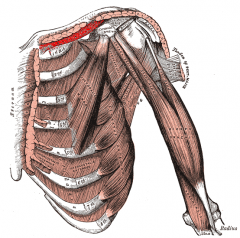
Subclavius Muscle |

|
|
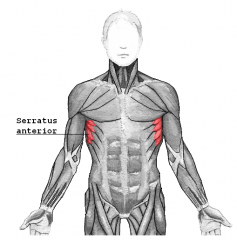
Serratus Anterior Muscle |
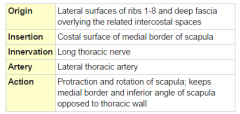
|
|
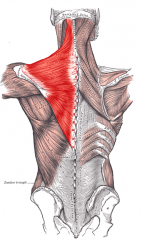
Trapezius Muscle |
|
|
Latissimus Dorsi |

|
|
Levator Scapulae Muscle |
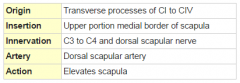
|
|
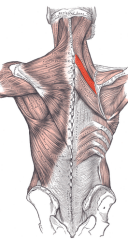
Rhomboid Minor Muscle |
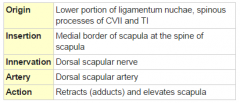
|
|
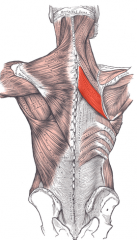
Rhomboid Major Muscle |

|
|
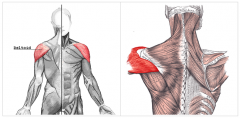
Deltoid Muscle |

(take off "adduction") |
|
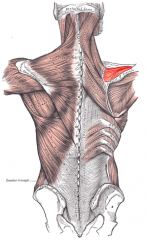
Supraspinatus Muscle |

|
|
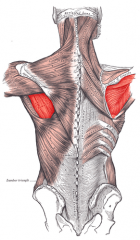
Infraspinatus Muscle |

|
|
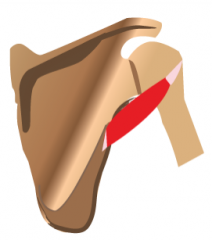
Teres Minor Muscle |

|
|

Teres Major Muscle |

|
|
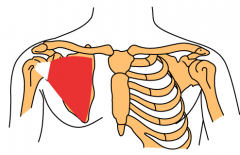
Subscapularis Muscle |

|
|
|
Triangular Space |
(Slightly more medial than the quadrangular space)
Borders: Teres major inferiorly, triceps brachii (long head) laterally, Teres minor superiorly
Contents: Circumflex scapular artery
|
|
|
Quadrangular Space |
Borders: Teres major inferiorly, humerus laterally, Teres minor superiorly, Triceps brachii (long head) medially
Contents: Axillary nerve, posterior humeral circumflex artery
(Slightly more lateral than the triangular space) |
|
|
Triangular Interval |
Borders: Teres major, Triceps brachii (long head), Humerus
Contents: Profunda brachii artery, Radial nerve |
|
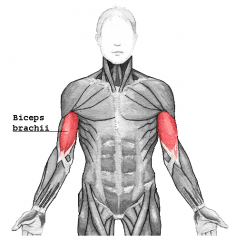
Biceps Brachii Muscle |
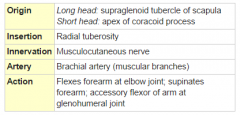
|
|
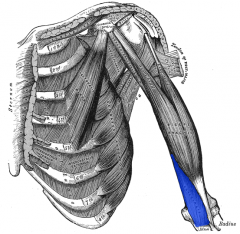
Brachialis Muscle |
|
|
Coracobrachialis Muscle |

|
|
Triceps Brachii Muscle |
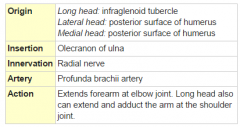
|
|
|
Musculocutaneous Nerve |
-Comes off of lateral cord of brachial plexus (C5-C7)
-Innervates coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, brachialis |
|
|
Medial Cutaneous Nerve of the Arm |
1. Comes from medial cord of brachial plexus |
|
|
Brachial Artery ****skip for now |
1. Continuation of the axillary artery after it crosses the inferior border of the teres major muscle |
|
|
Anterior Forearm Muscles (4-1-3) |
SUPERFICIAL LAYER Pronator teres muscle Flexor carpi radialis muscle Palmaris longus muscle Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle INTERMEDIATE LAYER Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle DEEP LAYER Flexor digitorum profundus muscle Flexor pollicis longus muscle Pronator quadratus muscle |
|
|
Posterior Forearm Muscles (6-3-3) |
SUPERFICIAL LAYER Brachioradialis muscle Extensor carpi radialis longus muscle Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle Extensor digitorum muscle Extensor digiti minimi muscle Extensor carpi ulnaris muscle DEEP LAYER Anconus Supinator muscle Extensor indicis muscle OUTCROPPING MUSCLES OF DEEP LAYER Abductor pollicis longus muscle Extensor pollicis longus muscle Extensor pollicis brevis muscle |
|
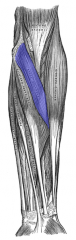
Pronator Teres Muscle |

Anterior arm, superficial layer |
|
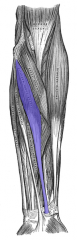
Flexor Carpi Radialis Muscle |

Anterior arm, superficial layer |
|
Palmaris Longus Muscle |

Anterior arm, superficial layer |
|
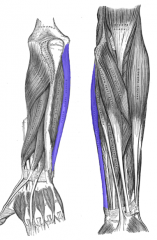
Flexor Carpi Ulinaris Muscle |
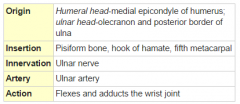
Anterior arm, superficial layer |
|
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Muscle |

Anterior arm, intermediate layer |
|

Flexor Digitorum Profundus Muscle |

Anterior arm, deep layer |
|

Flexor Pollicis Longus Muscle |

Anterior arm, deep layer |
|
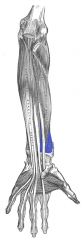
Pronator Quadratus Muscle |

Anterior arm, deep layer |
|

Brachioradialis Muscle |
Posterior arm, superficial layer |
|
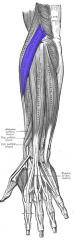
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Muscle |

Posterior arm, superficial layer |
|
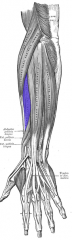
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Muscle |

Posterior arm, superficial layer |
|

Extensor Digitorum Muscle |

Posterior arm, superficial layer |
|
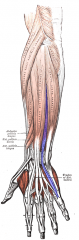
Extensor Digiti Minimi Muscle |

Posterior arm, superficial layer |
|
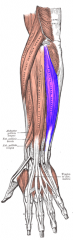
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Muscle |

Posterior arm, superficial layer |
|
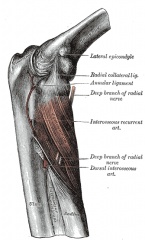
Supinator Muscle |

Posterior arm, deep layer |
|
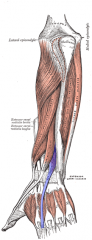
Extensor Indicis Muscle |

Posterior arm, deep layer |
|
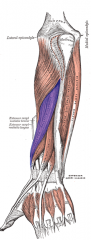
Abductor Pollicis Longus Muscle |

Posterior arm, deep layer |
|
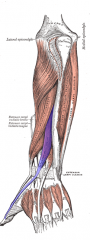
Extensor Pollicis Longus Muscle |
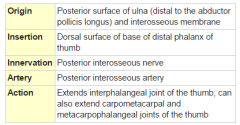
Posterior arm, deep layer |
|
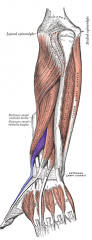
Extensor Pollicis Brevis Muscle |
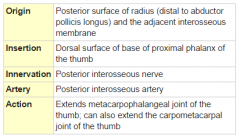
Posterior arm, deep layer |
|
|
Median Nerve Origin + Pathway |
-Comes from lateral (C5, C6, C7) and medial cord (C8, T1) 1. Travels through cubital fossa → passes under bicipital aponeurosis and between two heads of pronator teres muscle → enters anterior compartment of forearm 4. The rest of the median nerve is now called the anterior interosseus branch of median nerve |
|
|
Ulnar Nerve *****skip for now |
1. Runs posterior to medial epicondyle of humerus |
|
|
Path of Radial Nerve |
-Comes from posterior cord of brachial plexus (C5, C6, C7, T1) -Enters radial groove of humerus along with profunda brachial artery, between the lateral and medial head of triceps -Goes into cubital fossa by piercing intermuscular septum between brachialis and brachioradialis -Passes anterior to lateral epicondyle of humerus, and divides into Superficial Branch and Deep Branch (which turns into Posterior Interosseus Nerve) |
|
|
Medial Cutaneous Nerve of the Forearm (Medial Antebrachial Cutaneous Nerve) |
1. Comes off the medial cord
2. Provides cutaneous innervation of medial part of forearm |
|
|
Long Thoracic Nerve |
-Arises from the C5, C6, and C6 roots -Emerges from the middle scalene muscle and runs far down below the brachial plexus -Supplies the serratus anterior |
|
|
Dorsal Scapular Nerve |
-Arises from C5 root and goes through the middle scalene muscle -Supplies rhomboid minor and rhomboid major muscles |
|
|
5 Branches of the Posterior Cord of the Brachial Plexus |
1. Axillary nerve: goes around the neck of the humerus along with the humeral circumflex artery; supplies deltoid and teres minor 2./3. Subscapular nerves (upper/lower); supply subscapularis and teres major 4. Thoracodorsal nerve; supplies the latissimus dorsi 5. Radial nerve: Passes anterior to lateral epicondyle of humerus to innervate the posterior of the arm with some exceptions |
|
|
Lateral Cord of the Brachial Plexus |
1. Lateral pectoral nerve (C5-C7), which pairs with medial pectoral nerve to innervate the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor 2. Musculocutaneous nerve (C5-C7); innervates three upper arm muscles (coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, and brachialis) |
|
|
Medial Cord of the Brachial Plexus |
Gives rise to medial pectoral nerve, which pairs with lateral pectoral nerve to innervate the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor |
|
|
2 Pronator Muscles
2 Supinator Muscles |
Pronators: 1. Pronator Teres 2. Pronator Quadratus
Supinators: 1. Biceps brachii 2. Supinator
|
|
|
Most common rotator cuff injury |
Falling with your arm out First to get injured is usually the supraspinatous Any of the tendons ripping can go through the joint capsule and tear the whole cuff |
|
|
Flexion of the arm (2 major muscles, 2 helpers) |
MAJOR 1. Deltoid (anterior chords) 2. Pectoralis major
-Engaged if you're flexing with a force ex when bowling 1. Coracobrachialis 2. Biceps brachii
-can only help if the insertion is more anterior than the arm (so if arm is coplanar, useless)
|
|
|
Extension of the arm (4 major muscles, 2 helpers) |
MAJOR 1. Deltoid (posterior chords) 2. Pectoralis Major 3. Latissimus Dorsi 4. Teres Major
HELPERS 1. triceps (long head) 2. coracobrachialis, barely barely |
|
|
Abduction of the arm (2 major muscles) |
1. Deltoid (mostly lateral part/middle head, though anterior and posterior heads can help) 2. Supraspinatus, need it for first 15 degrees of movement |
|
|
Adduction of the arm (5 major muscles) |
1. Pectoralis major 2. Latissimus dorsi 3. Teres major 4. Coracobrachialis 5. Triceps (long head)
The latter two are useful when arm is fully abducted but almost useless when arm close to body |
|
|
Medial rotation of the arm (5 major muscles) |
1. Pectoralis major 2. Latissimus dorsi 3. Teres major 4. Subscapularis 5. Deltoid (anterior part)
Basically if origin is medial to humerus and insertion is somewhere on anteromedial side5tf |
|
|
The Lady Between Two Majors |
"The lady between two majors": |
|
|
Lateral Rotation (3 major muscles) |
1. Deltoid (posterior) 2. Infraspinatus 3. Teres minor |
|
|
Flexion of the Elbow (3 major muscles) |
1. Biceps brachii 2. Brachialis 3. Brachioradialis |
|
|
Which two nerves have to get destroyed to abolish flexion at the elbow? |
1. Musculocutaneous nerve (innervates biceps and brachialis) 2. Radial nerve (innervates brachioradialis) |
|
|
Extension of the Elbow (1 major muscle, 1 helper); Which nerve would you have to knock out to compromise extension at the elbow? |
Major: triceps Helper: anconeus Radial Nerve, for ex via a midshaft humerus fracture |
|
|
Pronation of the forearm (2 major muscles); Which nerve would you have to knock out to compromise pronation? |
1. Pronator Teres 2. Pronator Quadratus Median Nerve |
|
|
Supination of the forearm (2 major muscles); Which nerves would you have to knock out to compromise supination? |
1. Supinator Muscle, innervated by Radial nerve 2. Biceps Brachii, innervated by Musculocutaneous Nerve |
|
|
Path of Axillary Nerve |
-Comes from posterior cord of brachial plexus (C5, C6) -Passes through quadrangular space along with posterior circumflex humeral artery, to posterior aspect of arm; innervates deltoid and teres minor -Winds around surgical neck of humerus -Gives rise to Lateral Brachial Cutaneous Nerve |
|
|
Path of Musculocutaneous Nerve |
-Comes from lateral cord of brachial plexus (C5, C6, C7) -Pierces and innervates coracobrachialis muscle |
|
|
Superficial Branch of Radial Nerve - Pathway and Innervation |
-Superficial radial nerve travels under brachioradialis muscle along with radial artery -Enters anatomical snuffbox, and provides cutaneous innervation to dorsal thumb, index, and half of middle finger up until the distal phalanges (which are innervated by the median nerve |
|
|
Radial Nerve Origin + Innervations of Radial Nerve Proper |
-Posterior cord of Brachial Plexus, C5, C6, C7, T1 -Radial nerve proper innervates Brachioradialis, Anconeus, and Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus |
|
|
Innervations of Superficial Branch of Radial Nerve |
-Deep branch dives through two heads of supinator muscle + innervates it → becomes posterior interosseous nerve → innervates all of the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm |
|
|
Thenar Compartment of Hand (3) |
1. Abductor Pollicis Brevis 2. Flexor Pollicis Brevis 3. Opponens Pollicis Muscle |
|
|
Hypothenar Compartment of Hand (3) |
1. Abductor Digiti Minimi 2. Flexor Digiti Minimi 3. Opponens Digiti Minimi |
|
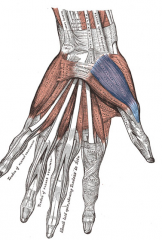
Abductor Pollicis Brevis Muscle |

Part of Thenar Compartment |
|
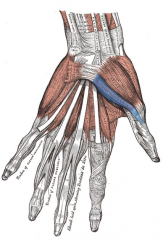
Flexor Pollicis Brevis Muscle |

Part of Thenar Compartment |
|
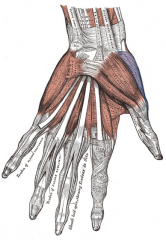
Opponens Pollicis Muscle |

Part of Thenar Compartment |
|
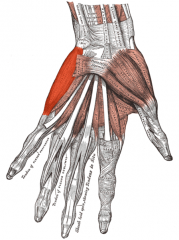
Abductor Digiti Minimi Muscle |

Part of Hypothenar Compartment |
|
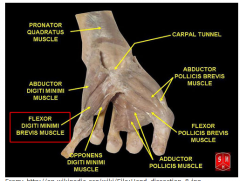
Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis Muscle |

Part of Hypothenar Compartment |
|
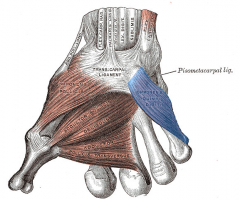
Opponens Digiti Minimi Muscle |
Part of Hypothenar Compartment |
|
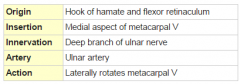
Lumbricals |

4 of them |
|
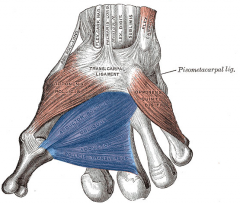
Adductor Policis Muscle |
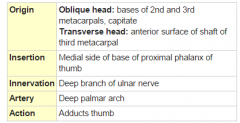
|
|
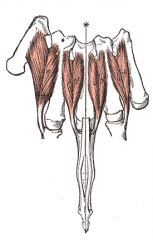
Dorsal Interossei Muscles |
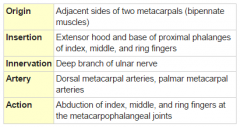
4 of them total, 2 for middle finger |
|
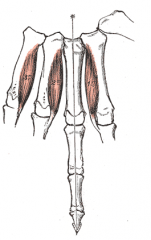
Palmar Interossei Muscles |

3 of them, middle finger doesn't need one |
|
|
Median Nerve Motor Innervation in the Hand |
1/2 LOAF 1/2
-1/2 lumbricles (2+3) -opponens pollicis -abductor pollicis brevis -1/2 flexor pollicis brevis (superficial head)
|
|
|
Ulnar Nerve Motor Innervation in the Hand (8) |
-1/2 lumbricles (4+5) -opponens digiti minimi -abductor digiti minimi -flexor digiti minimi -1/2 flexor pollicis brevis (deep head) -all 4 palmar interossei -all 4 dorsal interossei -adductor pollicis |
|
|
Anterior Forearm Innervation + Exceptions |
-All the layers are innervated by the Median nerve except for Flexor Carpi Ulinaris and Flexor Digitorum Profundus (which is 1/2 and 1/2) -These are innervated by the Ulnar nerve, which is sandwiched between them |
|
|
Cutaneous Innervation of the Hand |
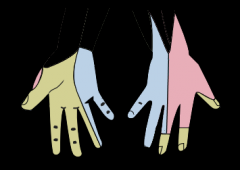
-Palmar branch of Median Nerve: cutaneous innervation to 1/2 thenar, 2 1/2 fingers on the palmar side + their tips on the dorsal side -Superficial Branch of Radial Nerve: 1/2 thenar, dorsal index + 1/2 middle -Ulnar Nerve: 2 1/2 on dorsal ulnar side, 1 1/2 on palmar ulnar side
|
|
|
Branches of the Median Nerve |
-Recurrent branch of median nerve (to thenar compartment) -Anterior interosseus branch of median nerve does the deep layer of the forearm (1/2 Flexor Digitorum Profundus, Flexor Pollicis Longus, Pronator Quadratus) |
|
|
Order of the Superficial Layer of Anterior Forearm |
Pass Fail Pass Fail, in order from lateral to medial
Pronator Teres Flexor Carpi Radialis Palmaris Longus Flexor Carpi Ulinaris |
|
|
Order of the Superficial Layer of Posterior Forearm |
From radial to ulnar: 1. Brachioradialis 2. Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus (to shorter finger) 3. Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis (to longer finger) 4. Extensor Digitorum (4 of them) 5. Extensor Digiti Minimi 6. Extensor Carpi Ulinaris |
|
|
Order of the Deep Layer of Posterior Forearm |
From elbow to hand: 1. Anconeus 2. Supinator 3. Abductor Pollicis Longus 4. Extensor Pollicis Brevis 5. Extensor Pollicis Longus 6. Extensor Indicis |
|
|
Flexion of the Wrist (3 major) + which nerve(s) would need to get knocked out? |
1. Flexor Carpi Radialis (Median Nerve) 2. Flexor Carpi Ulinaris (Ulnar Nerve) 3. Palmaris Longus (Ulnar Nerve) |
|
|
Extension of the Wrist (3 major) + which nerve(s) would need to get knocked out? |
1. Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus 2. Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis 3. Extensor Carpi Ulinaris
Radial nerve for all of them |
|
|
Radial Abduction of Wrist (3 major) + which nerve(s) would need to get knocked out? |
1. Flexor Carpi Radialis 2. Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus 3. Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
They all work simultaneously, so you would need to knock out both Median (for the Flexor Carpi Radialis) and Radial nerve (for the other two) |
|
|
Ulnar Abduction of Wrist (2 major) + which nerve(s) would need to get knocked out? |
1. Flexor Carpi Ulinaris 2. Extensor Carpi Ulinaris
Ulnar Nerve (for Flexor Carpi Ulinaris) and Median Nerve (for Extensor Carpi Ulinaris) |
|
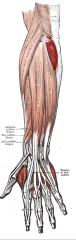
Anconeus |
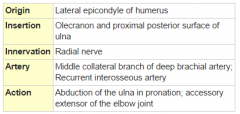
Posterior arm, deep layer |
|
|
Anatomical Snuffbox + Contents |
-Scaphoid carpal bone forms the floor -Extensor Pollicis Brevis tendon forms the lateral/radial border -Extensor Pollicis Longus tendon forms the medial/ulnar border
-Radial artery and dorsal cutaneous branch of radial nerve pass through it |
|
|
Carpal Tunnel + Contents |
-Formed by flexor retinaculum on top, carpal bones at the bottom -Contents: median nerve and the tendons of flexor pollicis longus, flexor digitorum superficialis, and flexor digitorum profundus |
|
|
Guyon's Canal + Contents |
-Formed by flexor retinaculum and transverse carpal ligament overlying the depression between the pisiform and hamate -Contents: ulnar nerve + artery |

