![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is histology? |
The study of structure and function of tissues. |
|
|
What are the 4 basic Tissue types? |
1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Muscular Tissue 3. Connective Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue |
|
|
Layer and Shap of Simple Squamous Epithelium? |
One cell layer and flat |
|
|
Layer and cell shape of simple cuboidal epithelium? |
One cell layer and cubed |
|
|
Layer and cell shape of simple columnar epithelium? |
One cell layer and like long columns. |
|
|
What is a location and function of simple squamous epithelium? |
Location: Lines blood vessels. Function: Gas Diffusion |
|
|
What is the location and function of simple cuboidal epithelium? |
Location:Kidney Tubules. Function: Secretion |
|
|
Location and Function of simple columnar epithelium? |
Location: Lining of stomach. Function:Absorption |
|
|
Location and Function of nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium? |
Location: Vagina. Function: Protection. |
|
|
Location and Function of Transitional Epithelium? |
Location: Urinary bladder. Function: Permits stretching |
|
|
Location and function of Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium? |
Location: Trachea, Function: Secretion and movement of mucus with cilia |
|
|
What is the abbreviation of Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium? |
P.C.C.E |
|
|
What is the purpose of connective tissue? |
Connective tissue protects and supports the body and its organs |
|
|
Location and function of areolar connective tissue? |
Location: Between Muscles. Function: Cushions organs. |
|
|
Location and Function of adipose tissue? |
Location: Buttock. Function: Protection and insulation |
|
|
Location and function of dense regular connective tissue? |
Location: Between skeletal muscles. Function:Provides firm attachment |
|
|
Location and function of dense irregular connective tissue? |
Location: Nerve and muscle sheaths. Function: Helps prevent overexpansion of organs. |
|
|
Location and function of hyaline cartilage? |
Location: Forms part of nasal septum. Function: Reduces friction. |
|
|
Function of Volkmann canal, haversian canal, lamella, lacuna, osteon, osteocyte, canaliculi? |
Central canal and volkmanns canal:N.A.V.L. Osteocyte:Maintain bone. Lacuna:House osteocytes. Osteon: thickest unit where stress is applied. functional unit of compact bone. Canaliculi: Exchange materials between blood vessels. Lamella: the thin plate in the matrix |
|
|
Function of RBC, WBCand platelets in blood ( Vascular connective tissue) |
Function of RBC:Transports oxygen. WBC: Immunity. Platelets: Clots blood |
|
|
Location and function of skeletal muscle? |
Location: Combined with connective tissue. Function :Stablizes postiion of skeleton. |
|
|
Location and function of cardiac muscle? |
Location: Walls of hollow organs. Function: Circulates blood |
|
|
Location and function of smooth muscle tissue? |
Location: Walls of blood vessels. FUnction: Moves food. |
|
|
What is the difference between microvilli and cilia? |
Microvilli: Absorbs and dont move. Cilia: Moves like it has a motor. |
|

What tissue is this? |
Simple squamous epithelium. |
|

What tissue is this? |
Simple cuboidal epithelium. |
|

What tissue is this? |
Simple Columnar epithelium |
|

What tissue is this?- Look at the flat cells near the surface! |
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
Location and function of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium? |
Location: Our entire body. Function: Reduce evaporation- make us waterproof. |
|

What tissue is this? |
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
|

What type of tissue is this? |
Transitional Epithelium |
|

What type of tissue is this? |
Transitional Epithelium- The cells on top are the same as the cells on the bottom. |
|
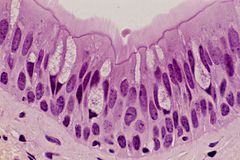
What tissue is this? |
P.C.C.E |
|

What tissue is this? Identify the thin and thick lines? |
Areolar connective tissue. Thin:Elastic Fibers. Thick: Collagen fibers. |
|
|
How to identify the chondrocyte and lacuna and perichondrium in the hyaline cartilage? |
Chondrocyte is the dark area. (like the nuclei) Lacuna is the outer area of the chondroctye. Perichondrium is the loose tissue that connects the tissue. |
|

What tissue is this?and what is the white bubble area? |
Adipose tissue, and adipocytes. |
|

What tissue is this? |
Dense regular connective tissue. |
|

What tissue is this? |
Dense irregular connective tissue. |
|

What tissue is this? |
Hyaline cartilage |
|

Identify Chondrocyte, Lacuna and perichondrium and their function. |
Lacuna: House of chondrocyte. Chondrocyte: Maintain Cartilage. Perichondrium: Surrounds hyaline cartilage |
|

What tissue is this? |
Blood- Vascular connective tissue. |
|

Locate WBC, RBC, Platelets and their function |
WBC- It has a nucleus- Immunity. RBC- No nucleus.- Transports oxygen. Platelets- Dark periods. - Blood clotting. |
|

What tissue is this? |
Skeletal muscle tissue |
|

What tissue is this? |
Skeletal muscle tissue |
|

Identify the nuclei |
Dark Spot- Nuclei is not compressed. |
|
|
Muscle tissue is classified into what three types? |
Skeletal muscle tissue, Cardiac muscle tissue and smooth muscle tissue. |
|

What tissue is this? |
Smooth muscle tissue |
|

What tissue is this? |
Smooth muscle tissue |
|

What tissue is this? |
smooth muscle Tissue |
|

What tissue is this? |
Cardiac muscle tissue |
|

What are the small breaks called |
Intercalated discs |
|
|
What does the nervous tissue do? |
Inititates, Trasmits and interprets nerve impulses that coordinate the body. |
|

What tissue is this? Also name 5 sections. |
This is nervous tissue: Neuron. Neuron, dendrite, nucleus of neuron, soma, neuroglia. |
|
|
Function of neuron, dendrite, nucleus of neuron, soma, neuroglia? |
Neuron: Conduct impulses. Dendrite: Conduct towards the cell. Neuroglia: Support the nerves. Soma: Houses the neuron. |
|

What tissue is this? |
Bone Tissue ( Osseous connective tissue) |
|

Label this tissue and what tissue is it? |

Bone Tissue( Osseous connective tissue) |
|
|
Describe Tissue membrane? |
Tissue membrane form physical bariers that line or cover the bodies surfaces. |
|
|
What are tissue membranes composed of? |
Each Tissue membrane is composed of an epithelium supported by connective tissue. |
|
|
List the four types of tissue membranes found in the body? |
Mucous membranes, Serous membranes, Cutaneous Membrane, Synovial Membranes. |
|
|
Type of tissue membrane each epithelium is found in? |
Mucous membrane: Simple Columnar epithelium Serous Membrane: Mesothelium Cutaneous membrane: Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium Synovial Membrane: Does not contain epithelium |
|
|
What type of connective tissue are found in the tissue membranes? |
Mucous Membranes: Areolar connective tissue. Serous Membranes: Areolar Connective Tissue Cutaneous Membrane: Areolar Connective Tissue and Dense Irregular connective Tissue Synovial Membrane: Areolar Connective Tissue |
|
|
4 cells and function found in connective tissue proper. ( Areolar) |
Fibroblasts: Secretes proteins that assemble to form large extracellular fibers. FIbrocytes: maintain the connective tissue fibers. Lymphocytes: Produce antibiodies ( Proteins) defend the body against disease. Macrophages:Engulf damaged cells or pathogens that enter the tissue. |
|
|
What type of tissue is the EPIDERMIS |
Keratinized stratified Squamous Epithelium |
|
|
What type of tissue is the DERMIS |
Dense Irregular connective tissue |
|
|
What type of tissue is the HYPODERMIS |
Loose connective tissue |
|
|
What type of tissue the Dermal Papilla? |
Areolar Connective Tissue |
|
|
Location and Function of Stratum Corneum? |
Location: Whole Body. Function: Forms barrier to protect underlying tissue from infection. |
|
|
Location and Function of Stratum corneum? |
Location: Soles of feet. (ONLY IN THICK SKIN). Function: Protects most common area of damage. |
|
|
Location and function of Merocrine sweat gland? |
Location: Groin. Function. Produce Sweat. |
|
|
Location and Function of Stratum Granulosum? |
Location: Under stratum corneum. Function: Prevents waterloss. |
|
|
Location and Function of Lamellated Corpuscle? |
Location: Hands. Function: Nerve ending for sensitivity. |
|
|
Location and function fo stratum spinosum? |
Location: Near Stratum basale. Function:Strength and flexibility of skin. |
|
|
Location and function of Tactile Corpuscle? |
Location:Upper Dermis. Function:Responds to touch and pressure. |
|
|
Location and function of Statrum Basale: |
Location: Everywhere there is skin. Function: Produces new cells. Contains melanocytes. |
|
|
Location and function of Dermal Papilla? |
Location:Dermis. Function: Brings nutrients and Oxygen to lower epidermis cells. |
|
|
Location and function of Apocrine sweat gland? |
Location:Armpits. Function:Secrete a fatty secretion- Scented |
|
|
Function of hypodermis? |
Storage of body fat. |
|
|
Location and function of Sebaceous glands? |
Location:Hair. Function: Oil- Sebum |
|
|
Function of Dermis? |
Supports Epidermis |
|
|
Location and function of Arrector Pilli? |
Location: Attach to hair. Function: Contract to generate heat- Makes hair stand up |
|
|
Location and function of Epidermis? |
Location: Outmost layer of skin. Function: Barrier to infection from environment. |
|
|
Location and function of nonKeratinized stratifed squamous epithelium? |
Location: Inner cheek. Function: Protect against abrasion. |
|

What type of tissue is this ( Thick or thin) and in what order are the layers? |
THICK SKIN Epidermis Stratum Corneum Stratum Lucidum Stratum Granulosum Stratum Spinosum Stratum Basale Dermis |
|

What type of tissue is this ( THICK OR THIN) what order are the layers? |
THIN SKIN Epidermis Stratum Corneum Stratum Granulosum Stratum Spinosum Stratum Basal Dermis |
|

This is just to look at |
Just memorize the order and identify them. |
|

What tissue is this?and identify three sections of it? |
Blood- Connective Tissue. Platelets. RBC and WBC |
|

What tissue is this? Identify structures on this picture? |
Neuron- Nervous Tissue. Neuroglia- Dendrite- Axon- Soma- nucleus |

