![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the two "modes" of secretion?
|
merocrine and holocrine
|
|
|
What is merocrine?
|
product is secreted by exocytosis (i.e contents are secreted directly out of the cell into the extracellular space)
|
|
|
What is holocrine?
|
The gland literally ruptures...and the product is secreted
|
|
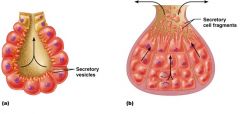
Image of merocrine and holocrine modes
|
Image of merocrine and holocrine modes
|
|
|
The second type of tissue we are learning about is connective tissue. Where can this be found?
|
connective tissue proper
cartilage bone blood |
|
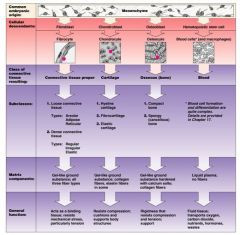
Connective tissue chart
|
Connective tissue chart
|
|
|
What are the 4 functions of connective tissue?
|
binding/support, protection, insulation and transportation
|
|
|
What is the common tissue of origin of connective tissue?
|
mesenchyme (a loose connective tissue)
|
|
|
Connective tissue has a nonliving extracellular matrix. This matrix consists of ______ ______ and ______
|
ground substance, fibers
|
|
|
What is "ground substance"?
|
unstructured material that fills the space between cells
|
|
|
What can the "fibers" be made of?
|
collagen, elastic or reticular
|
|
|
What is the function of "ground substance"?
|
serves as a molecular "sieve" through which nutrients diffuse between blood cpillaries and cells
|
|
|
Describe collagen fibers
|
tough, provides strength
|
|
|
Describe elastic fibers
|
long, thin, stretchy
|
|
|
Describe reticular fibers
|
branched, delicate networks
|
|
|
Name each connective tissue cell:
1. proper 2. cartilage 3. bone 4. blood |
1. fibroblasts
2. chondroblasts 3. osteoblasts 4. hematopoietic stem cells |
|
|
Connective tissue cells can also be ______ blood cells, ______ cells or _______
|
white
plasma macrophages |
|
|
Connective tissue proper (loose) includes ______, ______ and ______
|
areolar,
reticular adipose |
|
|
What gives rise to ALL other connective tissue and is found in the embryo?
|
mesenchyme: embryonic connective tissue
|
|
|
Describe characteristics of areolar connective tissue
|
1. gel-like matrix
2. wraps and cushions organs 3. all throughout the body |
|
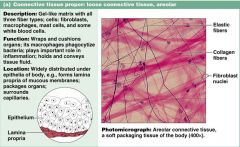
Connective tissue proper: loose
AREOLAR |
Connective tissue proper: loose
AREOLAR |
|
|
Describe characteristics of loose connective tissue proper: adipose
|
1. matrix has closely packed adipocytes
2. reserves food store, insulates 3. found under skin, around kidneys |
|
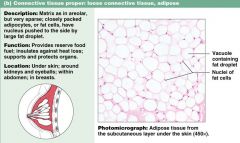
Connective tissue proper loose: ADIPOSE
|
Connective tissue proper loose: ADIPOSE
|
|
|
Describe characteristics of loose connective tissue proper RETICULAR
|
1. ground sub = reticular fibers
2. cells lie in a fiber network 3. soft internal skeleton, supports other cell types 4. found in bone marrow, spleen |
|
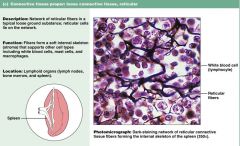
Connective tissue proper: loose RETICULAR
|
Connective tissue proper: loose RETICULAR
|
|
|
What are characteristics of loose connective tissue proper: DENSE REGULAR?
|
1. Parallel collagen fibers, few elastic
2. major cell type of fibroblasts 3. attaches muscle to bone, bone to bone 4. tendons, ligaments |
|
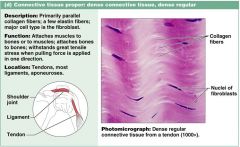
Connective tissue proper: loose DENSE REGULAR
|
Connective tissue proper: loose DENSE REGULAR
|
|
|
What are characteristics of loose connective tissue proper, DENSE IRREGULAR?
|
1. irregularly arranged collagen fibers
2. provides structural strength |
|
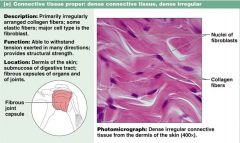
Connective tissue properl; loose DENSE IRREGULAR
|
Connective tissue properl; loose DENSE IRREGULAR
|

