![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
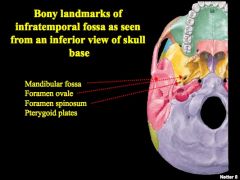
What are the boundaries for the infratemporal fossa?
|
Anterior: maxillary bone
Medial: Lateral pterygoid plate Lateral: Ramus of mandible Posterior: temporal bone |
|
|
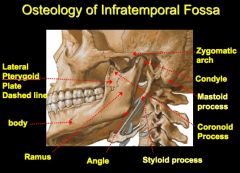
Name four structural components of the mandible.
|
Body
Ramus Condyle Coronoid process |
|
|
What type of movement of the TMJ will cause hinge like movements?
|
Elevation and depression
|
|
|
What type of movements of the TMJ will cause gliding movements?
|
Protraction and retraction
|
|
|
What two ligaments and connective tissue hold the TMJ together?
|
Sphenomandibular ligament
Stylomandibular ligament Joint capsule |
|
|
What covers the articular surface of the TMJ?
|
Hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
Dislocation of the TMJ will place the condyle into what area?
|
Infratemporal fossa
|
|
|
What direction does the head of the mandible move when the opens?
|
The head will glide anteriorly as it hinges open.
|
|
|
What structure is to prevent the dislocation of the condyle into the infratemporal fossa?
|
The articular tubercle
|
|
|
Describe the position of the condyle with respect to the articular tubercle when the jaw is closed, open, and dislocated.
|
Closed: Condyle is posterior
Open: Condyle is inferior Dislocated: Condyle is anterior |
|
|
Generally, which muscles, nerves and artery groups are found in the infratemporal fossa?
|
Muscles of mastication
Branches of the mandibular nerve Branches of the maxillary artery |
|
|
What nerve and type of nerve fiber innervates the teeth?
|
Inferior alveoli nerve
Somatosensory |
|
|
CN V carries two types of nerve fibers. What are they and what divisions carry them?
|
V1: General sense
V2: General sense V3: General sense and branchiomotor to muscles of mastication |
|
|
What type of sensory innervation does the tongue require?
|
General sensory
Special viscerosensory (Taste) |
|
|
What nerves innervate the glands of the head?
|
All innervated by CN VII except for parotid which is CN IX
|
|
|
What type of autonomic innervation do the glands of the head receive?
|
Parasympathetic
|
|
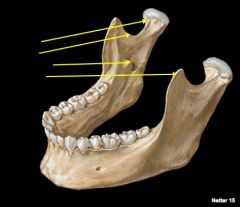
Identify structures
|
|
|
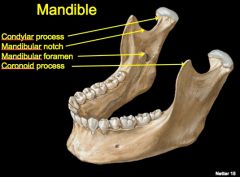
Identify structures
|
|
|
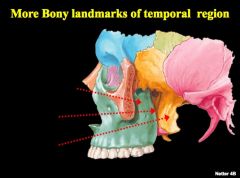
Identify structures
|
|
|
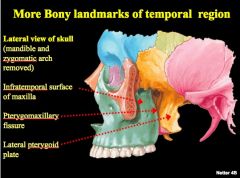
Identify structures
|
|
|
|
What is the action of the masseter? Which side will it deviate the jaw?
|
Elevator of the jaw
Sight deviation to the same side |
|
|
How are the fibers of the temporalis oriented?
|
Anterior fibers are vertical for elevation
Posterior fibers are horizontal for retraction |
|
|
What is the action of the temporalis?
|
Elevation and retraction
|
|
|
What is the point of insertion for the temporalis muscle?
|
The coronoid process
|
|
|
What CN supplies the muscles of mastication?
|
CN V3 (Mandibular division)
|
|
|
What muscle of mastication is used to open the jaw?
|
Lateral pterygoid muscle
(Pulls condyle forward) |
|
|
What two muscles of mastication form a sling (or "V") around the mandible?
|
Masseter and Medial pterygoid muscle
|
|
|
The lateral and medial pterygoid muscles arise from what boney structure?
|
Lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid
|
|
|
What muscles of mastication are elevators?
|
Masseter
Temporalis Medial pterygoid |
|
|
Which muscles of mastication are depressors?
|
Only lateral pterygoid
|
|
|
Which muscles of mastication are protractors?
|
Lateral pterygoid
Medial pterygoid (Masseter) |
|
|
Which muscles of mastication are retractors?
|
Only temporalis
|
|
|
Which muscles of mastication are rotators?
|
Temporalis
Lateral pterygoid Medial pterygoid |
|
|
What type of membrane covers the non-weight bearing surfaces of the TMJ?
|
Synovial membrane
|
|
|
What nerves course in between the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles?
|
Inferior alveolar nerve and the lingual nerve
|
|
|
Which muscles of mastication are in the infratemporal fossa?
|
Medial and lateral pterygoids
|
|
|
What are the branches of the Maxillary artery that can be found deep in the infratemporal fossa?
|
(MIMS)
Middle meningeal Inferior alveolar Muscular branches Sphenopalatine |
|
|
What are the branches of the Maxillary artery?
|
Middle Meningeal
Inferior alveolar Muscular branches Deep temporal Sphenopalatine |
|
|
Through what area does the deep temporal artery pass?
|
pterygomaxillary fissure
|
|
|
What does the middle meningeal artery supply?
|
The dura of the neurocranium
|
|
|
What are the branches of the CN V3?
|
Main Trunk:
Meningeal Medial pterygoid Tensor veli palatini Tensor tympani Anterior Division: Buccal (S) Lateral pterygoid (M) Masseter (M) Anterior deep temporal (M) Posterior deep temporal (M) Posterior Division: Auriculotemporal (S) Lingual (S) Inferior alveolar (S) (M branch--mylohyoid) |
|
|
What the anterior branches of CN V3?
|
Anterior Division:
Buccal (S) Lateral pterygoid (M) Masseter (M) Anterior deep temporal (M) Posterior deep temporal (M) |
|
|
What are the posterior branches of CN V3?
|
Posterior Division:
Auriculotemporal (S) Lingual (S) Inferior alveolar (S) (M branch--mylohyoid) |
|
|
What main truck branches of CN V3?
|
Meningeal
Medial pterygoid Tensor veli palatini Tensor tympani |
|
|
Parasympathetics for the head will leave the brainstem on what CNs?
|
III (pupils)
VII (glands) IX (parotid) |
|
|
What cranial nerves have parasympathetic fibers?
|
III, VII, IX, X
|
|
|
How do parasympathetics reach their targets in the head?
|
On cranial nerve V
|
|
|
Where are the sensory cell bodies of CN V?
|
Trigeminal ganglion
|
|
|
Parasympathetics of CN VII jump on what nerve to supply the sublingual gland?
|
Lingual (CN V3)
|
|
|
What ganglion do parasympathetics from VII synapse on to reach the submandibular and sublingual glands?
|
Submandibular ganglion
|
|
|
How do taste fibers reach the anterior 2/3 of the tongue?
|
Special viscerosensory from CN VII travels Chorda tympani to the lingual nerve to reach the tongue.
|
|
|
Through what opening does the chorda tympani pass?
|
petrotympanic fissure
|
|
|
What CN innervates the stylohyoid and posterior digastric?
|
Branchiomotor fibers of CN VII
|
|
|
Describe the path of parasympathetics to the parotid gland.
|
Parasympathetics from IX travel on the lesser petrosal and synapse on the otic ganglion and reach the parotid gland on the auriculotemporal nerve of CN V3.
|
|
|
What structures pass through the foramina of the cribriform plate?
|
Olfactory nerve bundle
|
|
|
What structures pass through the optic canal?
|
Optic nerve (CN II)
Ophthalmic artery |
|
|
What structures pass through the superior orbital fissure?
|
CN III
CN IV CN V1 (parts) CN VI Superior ophthalmic vein |
|
|
What structures pass through the foramen rotundum?
|
CN V2
|
|
|
What structures pass through the foramen ovale?
|
CN V3
Accessory meningeal artery Lesser petrosal nerve |
|
|
What structures pass through foramen spinosum?
|
Middle meningeal artery and vein
Middle meningeal branch of mandibular nerve [CN V3] |
|
|
What structures pass through the carotid canal?
|
Internal carotid artery
Internal carotid nerve plexus |
|
|
What structures pass through the internal auditory meatus?
|
Facial [CN VII]
Vestibulocochlear [CN VIII] Labyrinthine artery |
|
|
What structures pass through the jugular foramen?
|
Glossopharyngeal nerve [CN IX]
Vagus [CN X] Inferior petrosal sinus Sigmoid sinus Posterior meningeal artery |
|
|
What structures pass though the hypoglossal canal?
|
Hypoglossal nerve [CN XII]
|
|
|
What structures pass through the foramen magnum?
|
Medulla oblongata
Meninges Vertebral artery Spinal roots of accessory nerves |

