![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Planes of the body |
- crsagittal - vertical cut - coronal/frontal - transverse - horizontal |
|
|
Body Cavities |
- dorsal - cranial & spinal - ventral - thoracic (mediastinum (pericardial), plueral) & abdominopelvic (abdonimal and pelvic) |
|
|
Junctions in epitheleal tissue |
- tight junction - form permeability barrier - gap junctions - allow cells to communicate - desmosomes - junctions made up of filaments betweens cells |
|
|
3 types of exocrine glands |
- merocrine - cells secrete substances (sweat gland) - apocrine - parts of cells break off (mammary) - merocrine - whole cells break off (subaceous) |
|
|
Types of loose CTP |
- loose, areolar - few loosely arranged collagen and elastin fibers, more ground substance. packing between tissues - loose, adipose - mostly fat cells, insulates, protects, energy storage - loose, reticular - like areolar but only reticular fibers, lymphatic tissue (filtration) |
|
|
Types of connective tissue proper |
- loose - dense |
|
|
Types of dense CTP |
- dense regular collagenous (white fibrous) - parallel collagen fibers w/ fibroblasts in between, poor vascularization. tendons and ligaments - dense irregular collagenous - random collage fiber arrangement - innermost layer of dermis, covering of some organs - elastic - high portion of elastic fibers - walls of arteries/lung airways |
|
|
how is cartilage named |
- by components of the matrix |
|
|
types of cartilage |
- hyaline - many collagen fibers - ribcage, joints, ends of long bones - fibrocartilage - more collagen fibers arranged in thick bundles, where lots of pressure located - knee, between vertebrae - more elastic fibers - rigid but elastic properties - ear lobes epiglottis |
|
|
2 cells types of nervous tissue |
- nuerons - generate and conduct impulses - nueroglia - supporting cells |
|
|
Epidermal strata |
- stratum basale - deepest, one layer of keratinocytes - high mitotic activity - stratum spinosum - prekeratin fibers - stratum granulosum - cells dies, flatten, fill w/ keratin - stratum lucidum - clear layer only found in palms and soles - stratum corneum - fully keratinized cells, shed when desmosomes break |
|
|
Types of skin cancers |
- basal cell carcinoma - least malignant, most common, shiny dome shaped growth from stratum basal - squamous cell carcinoma - keratinocytes in stratum spinosum, scaly red lesion, - melanoma - melanocyte cancer, ABCDE (asymetry, border, color, diameter, enlarging) |
|
|
types of burns |
- 1st degree - painful, dry - 2nd degree - painful, wet, dermis affected - 3rd degree, not painful, dry, subcutaneous tissue |
|
|
Eccrine vs apocrine glands |
- eccrine - open directly out of skin - apocrine - open into hair follicle |
|
|
Divisions of the nervous system |
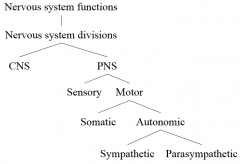
|
|
|
Nueroglia of PNS and CNS |
- CNS - astrocytes - anchor nuerons and blood vessels, microglia - specializes macrophage, ependymal cells - form choroid plexus, oligodendrocytes - PNS - schwann cells - wrap around axon, satellite cell - surround nuerons cell body in sensory ganglia |
|
|
Trigger zone |
- where APs generated, axon hillock (hold axon to cell body) & initial segment - begining of axon |
|
|
Vocab for CNS and PNS |
- CNS - Nuclei - cell bodies, nerve tracts - nerve proccess - PNS - Ganglia - cell bodies, Nerves - nerve proccess |
|
|
Multiple sclerosis & guillain-barre syndrome |
- MS - autoimmune disease of CNS, destroys oligodendrocytes - Guillain - Barre - autoimmune of the PNS, begins as infection of pathogen that resembles myelin -> body attacks it |
|
|
Function of types of nuerons |
- multipolar - motor and internuerons - bipolar - sensory organs in face - psuedo-unipolar - sensory receptors. |
|
|
What gates are involved in producing an AP |
- sodium potatssium pump (ATP) keeps outside positive and inside negative - voltage gated channels (Na open during AP, K close) |
|
|
Refractory period |
- Absolute - from beginning of the AP to the end of repolarization - Relative - requires stronger than usual stimulus because membrane is still more K permeable |
|
|
Continuous vs Saltatory conductions |
- continuous - unmyleinated axon, much slower - saltatory - myelinated, speed increases with increase in myelination and axon diameter |
|
|
4 major parts of the brain |
- brainstem - reflexes, cardiovascular, respiratory, motor - cerebrum - motor, decision making, some sensory, memory, evaulation of hearing and smell - cerebellum -controls posture, locomotion, eye movement - diencephalon - sensory relay, sleep cycle, mood, gland secretion, body temp, the ans, pleasure |
|
|
Parts and function of the brainstem |
- medulla oblongata - swallowing, vomiting, hiccuping, reflexes, cardiovascular & respiratory, pyramids control skeletal muscle - pons - intiates REM, respiratory - midbrain - visual reflex, hearing, motor, |
|
|
Parts of Diencephalon |
- Thalamus - sensory relay - hypothalamus - mood, emotion, pleasure, satiation, body temp, ans, horomone secretion, - epithalamus - regulate sleep cycle, |
|
|
3 types of tracks in cerebral medulla |
- association fibers - connect areas in the same hemisphere - commussural fibers - connect one hemisphere to another - projection fibers - connect cerebrum to other parts of brain and spinal cord |
|
|
Alzheimers, concussions, contusions, hematona, hydrocephalus |
- alzheimers - loss nuerons from cerebral cortex - concussion - injury- temp loss of brain function - rest - contusion - bruising after injury - hospitalization - hemotoma - bleeding in brain - surgery - hydrocephalus - CFS trappe in ventricles - shunt |
|
|
CSF flow |
- formed by choroid plexus in ventricles - lateral ventrals -> intraventricular formation -> third ventricle -> cerebral aqueduct -> fourth ventricle -> apertures or central canal - reobsorbed by arachnoid granulations |
|
|
Cranial Nerves |
I Olfactory Sensory II Optic Sensory III Oculomotor Motor IV Trochlear Motor V Trigeminal Both VI Abducens Motor VII Facial Both VIII Vestibulocochlear Sensory IX Glossopharyngeal Both X Vagus Both XI Accessory Motor XII Hypoglossal Motor |
|
|
Structure of spinal cord |
- Cervical & lumbar englargement - Cauda equina - conus medullaris - end at l2 |
|
|
Meninges |
- pia matter - subarachnoid space - arachnoid matter - subdural space - dura matter -epidural space - bone |
|
|
Connective tissue of spinal nerves |
- endoneurium - surrounds individual nerves - perineurium - surround fasicles - epineurium - surrounds who nerve |
|
|
Spinal nerve pairs |
- 8 cervical - 12 thoracic - 5 lumbar - 5 sacral - 1 coccygeal |
|
|
dermatome |
- map showing skin area supplied by sensory innervation by spinal nerve. neccessary to determine level of spinal nerve damage |
|
|
spinothalamic tract and dorsal column/medial lemniscal tract |
- spinothalamic - convey pain and temperature - immediately decussate to opposite side of spinal cord to thalamus then somatic sensory cortex - contralateral - dorsal column/medial lemniscal - 2 pt descrimination & proprioception - crosses over in the medulla oblongata - ipsilateral |
|
|
direct pathway vs indirect pathway |
- direct - conscious control of movement - decussate in pyramids, - indirect - unconscious control of movement, muscle tone |
|
|
Contrast somatic vs autonomic nervous system |
- somatic - one synapse, stimulation only, Ach, receptor molecules: nicotinic - autonomic - two synapse, stimulation or inhibition, ACh or norepinephrine, receptor varies with synapse and nuerotransmitter |
|
|
Parasympathetic vs sympathetic |
- parasympathetic: pre ganglionic cell bodies in brainstem or lateral horns of SC S2-S4, autonomic ganglia are terminal ganglia - sympathetic: pre ganglionic cell bodies in lateral horns between T1 and L2, autonomic ganglia are chain ganglia and collateral ganglia |
|
|
Componenents of extracellular bone matrix |
- collagen - organic - allows bendiness - hydroxyapatite - inorganic - rigidness |
|
|
Bone cells |
- osteoblasts - build bone - osteocytes - maintain - osteoclasts - breakdown |
|
|
lacunae vs canaliculi |
- lacunae - space where osteocyte is - canaliculi - space where osteocyte proccesses are |
|
|
intramembranous ossification vs endochondral ossficiation |
- intramembranous - connective tissue - forms skull and clavicle - osteochondral progenitor cells -> osteoblasts -> spongybone -> spongybone just inside periosteum become compact bone - endochodral - cartilage - all other bones - blood vessels bring osteoblasts, form bone collar, secondary ossification centers in epiphysis |
|
|
Abnormal curvatures of spine |
- scoliosis - lateral curve + kyphosis - kyphosis - exaggeration of thoracic curve - lordosis - lumbar curvature |
|
|
Cervical vs thoracic vs lumbar vertebrae |
- cervical - atlas + axis, bifid proccess, transverse foramina blood vessels, traingular - thoracic - long, thin proccesses, round shape - lumbar - large, thick body, thick lamina, rectangular shape |
|
|
Structure of ribs |
- Vertebrosternal (true ribs) - 7 pair - attach to sternal via costal cartilage - vertebralchondral (false ribs) - 3 pair - attached indirectly to sternum - vertebral/floating ribs - 2 pair - do not attach to sternum |
|
|
types of joints |
- fibrous - fibrous connective tissue, no cavity, no movement - cartilaginous - cartilage, no cavity, slight movement - synovial - joint cavity, move freely |
|
|
fibrous joint types |
- sutures - skull - syndesmoses - bones joined by ligaments - radioulnar - gomphoses - peg and socket - teeth |
|
|
Elbow joint bones, ligaments and functions |
- humeroulnar joint, humeroradial, proximal radioulnar - ulnar collateral ligament - reinforces humeroulnar joint - radial collateral ligament - reinforces humeroradial joint - radial annular ligament - reinforces proximal radiounar joint |
|
|
knee joint ligaments |
- Anterior cruciate ligament - prevents anterior displacement - posterior cruciate ligament - prevents posterior displacement - fibular and tibial ligaments - stabilize joint |

