![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Skull and its bones |
Frontal parietal (2) temporal (2) occipital ethmoid and sphenoid
|
|
|
Clavicle |
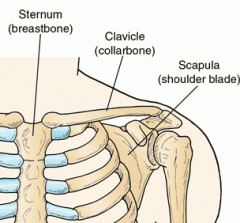
|
|
|
Sternum |
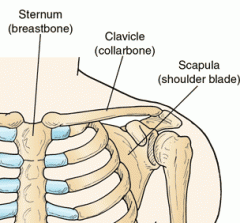
|
|
|
Sternoclavicular joint |
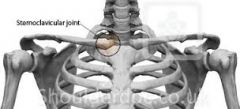
formed by clavicle and sternum
|
|
|
pectoral girdle |
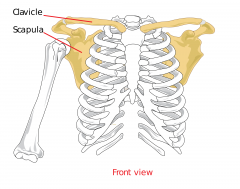
|
|
|
Scapula |
|
|
|
Acromion process |
|
|
|
acromioclavicular joint |
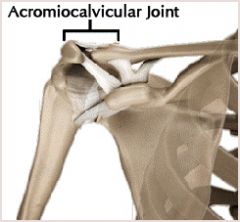
formed by acromion process and clavicle |
|
|
humerus |
|
|
|
glenoid fossa |
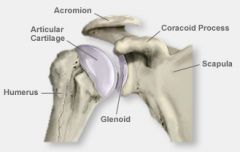
|
|
|
glenohumeral joint |
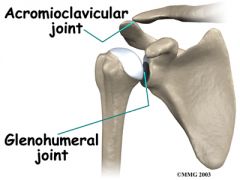
|
|
|
thoracic cavity |
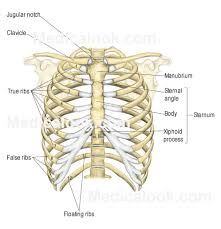
|
|
|
scapulothoracic joint |
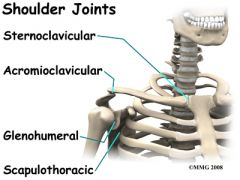
formed by thoracic cavity and scapula |
|
|
cervical vertebrae |
7 bones c1 - atlas c1 - axis c7 - most palpable |
|
|
thoracic vertebrae |
12 bones articulate with ribs have intervertebral discs |
|
|
true and false ribs |
12 are floating protect heart, lungs, liver |
|
|
lumbar vertebrae |
5 bones |
|
|
sacrum |
(5) |
|
|
coccyx |
(4 or more bones) |
|
|
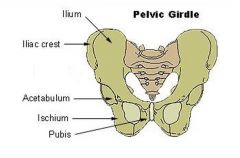
Pelvic girdle |
sacrum, coccyx, illium, ischium |
|
|
Sacroiliac joint |
sacrum and illium joint |
|
|
Illium and ischium |
|
|
|
Acetabulum joint |
hip joint formed by femur and pelvic girdle |
|
|
Glenoid fossa vs. acetabulum joint |
Acetabulum functions different than glenoid fossa
Glenoid fossa it's not deep because you need to raise your arms, rotate, to do overhead sports |
|
|
Greater trochanter |
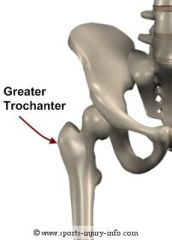
Below the pelvic girdle
The neck usually breaks when someone's hip is broken |
|
|
patella |
biggest sesamoid in the body |
|
|
tibia |
|
|
|
tibial tuberosity |
proximal end of the tibia |
|
|
oshgood schlatter |
protrusion of the tibial tuberosity |
|
|
Fibula |
holds 10% of body weight
|
|
|
Skull and its bones |
Frontal parietal (2) temporal (2) occipital ethmoid and sphenoid
|
|
|
Sternoclavicular joint |
formed by clavicle and sternum |
|
|
acromioclavicular joint |
formed by acromion process and clavicle |
|
|
glenohumeral joint |
articulation of the glenoid fossa and humerus |
|
|
scapulothoracic joint |
formed by the scapula and thoracic cavity |
|
|
Acetabulum joint |
hip joint formed by femur and pelvic girdle |
|
|
carpals |
"Sabine left the party to take Coates home"
Schapod, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform, Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, Hamate
|
|
|
Tarsals |
Calcaneus Talus Cuboid Cuneiform |
|
|
anatomical term for kneecap |
patella |
|
|
anatomical term for elbow |
olecranon process |
|
|
anatomical term for heel bone |
calcaneus |
|
|
anatomical term for funny bone |
ulnar nerve |
|
|
cervical spine |
7 bones |
|
|
thoracic spine |
12 bones |
|
|
lumbar spine |
5 bones |
|
|
melanocytes |
an individual with a dark skin color has more melanocytes than a fair-skinned person (false) |
|
|
hair matrix |
in order to permanently prevent growth of an unwanted hair, you must destroy the hair matrix (true) |
|
|
muscle tissues ? |
ch. 10 quiz |
|
|
homeostasis |
the ability of the body to maintain equilibrium by adjusting its physiological processes |
|
|
rectus femoris |
knee extensor, hip flexor |
|
|
gastrocnemius |
enables plantar and dorsiflexion |
|
|
forearm flexors |
flexor carpi radialis, flexoir pollicis longus, flexoir digitorum superficialis |
|
|
forearm extensors |
extensor carpi ulnarus, extensor digitorum, extensor carpi radialis brevis |
|
|
muscles in hamstrings |
semitendinosus, biceps femoris, semimembranosus |

