![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
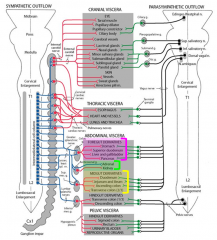
The wall of the GI tract contains __________________ that form the enteric nervous system (ENS)
|
intrinsic ganglia & nerve plexuses
|
|
|
T/F
The ENS requires ANS influence to function |
FALSE
ENS is capable of independently maintaining function--> however, sympathetic & parasympathetic nervous systems do influence activity |
|
|
What are the 2 main intrinstic nerve plexuses that form the ENS?
|
1. Meissner's/Submucous Plexus
(w/i submucosa) 2. Auerbach's/Myenteric Plexus (w/i muscularis externa) |
|
|
What do nerve fibers (sympathetic & parasympathetic) travel along to reach organs?
|
they travel along blood vessels to innervate the abdominal organ in which the vessels supply
|
|
|
The sympathetic nervous innervation of abdominal organs consists of preganglionic nerve fibers that reach prevertebral ganglia through _________________
|
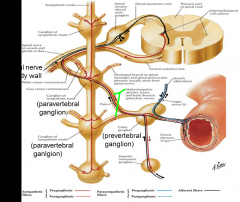
abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves
|
|
|
Sympathetic postganglionic nerve fibers from nerve cell bodies within ______________ follow arteries to organs
|
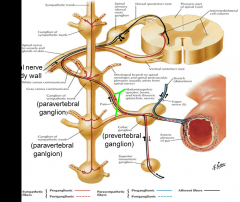
cell bodies within prevertebral ganglia
|
|
|
Prevertebral ganglia, which are collections of postganglionic sympathetic neuron cell bodies are located where?
|
along the abdominal aorta at the origins of the celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, inferior mesenteric artery, & renal arteries
|
|
|
What ganglia is located at the following origins:
celiac trunk superior mesenteric artery inferior mesenteric artery renal artery |
celiac trunk- celiac ganglia
superior mesenteric artery- superior mesenteric ganglion inferior mesenteric artery- inferior mesenteric ganglion renal artery- aorticorenal ganglia |
|
|
Abdominopelvice splanchnic nerves, that carry preganglionic sympathetic nerve fibers to prevertebral ganglia, have cell bodies where?
|
cell bodies w/i the intermediolateral cell column (IMLCC)
|
|
|
What are the abdominaopelvic splanchnic nerves?
|
-Thoracic splanchnic nerves, subdivided into;
Greater splanchnic (T5-9) Lesser splanchnic (T10-11) Least splanchnic (T12) -Lumbar splanchnic nerves (L1-2, sometimes L3) |
|
|
What do the Throacic & Lumbar (preganglionic) nerves generally supply?
|
Thoracic- foregut (celiac trunk) & midgut (superior mesenteric artery)
Lumbar- hindgut (inferior mesenteric artery) |
|
|
What do the following supply?
celiac ganglia nerve fibers (w/ celiac trunk)- |
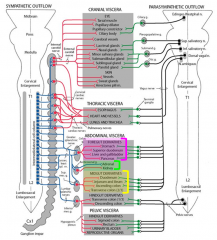
celiac ganglia nerve fibers (w/ celiac trunk)-
forgut= stomach, proximal duodenum, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen |
|
|
What do the following supply?
superior mesenteric ganglia fibers (w/ superior mesenteric artery)- |
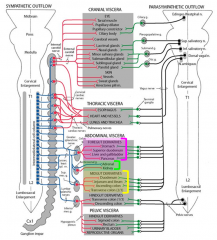
superior mesenteric ganglia fibers (w/ superior mesenteric artery)-
midgut= distal duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, appendix, ascending & transverse colong |
|
|
What do the following supply?
inferior mesenteric ganglia fibers (w/ inferior mesenteric artery)- |
inferior mesenteric ganglia fibers (w/ inferior mesenteric artery)-
hindgut= descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, & upper anal canal |
|
|
Sympathetic effects on GI
|
-vasoconstriction in blood vessels of viscera
-reduced glandular secretion -reduced peristalsis |
|
|
Parasympathetic effects on GI
|
-increased glandular secretion
-increase peristalsis -inhibit pyloric sphincter |
|
|
What are the 2 sources of preganglionic parasympathetic innervation?
|
1. Vagus nerves (CN X)--> forgut & midgut
2. Pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2-4)--> hingut |
|
|
Vagus nerve fibers enter the abdomen through the esophageal hiatus of the diaphram as what?
|
anterior & posterior vagal trunks formed from the esophageal plexus
|
|
|
What do the vagal trunks supply?
|
preganglionic parasympathetic input to ganglion cells near or w/i the walls of visceral structures (forgut & midgut):
distal esophagus stomach liver & gallbladder pancreas duodenum, jejunum, & ileum ascending & transverse colon |
|
|
Pelvic splanchnic nerves leave the sacral spinal cord through the anterior rami of S2-4, what do they supply?
|
preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to hindgut derivatives:
descending colon sigmoid colon rectum upper anal canal |
|
|
T/F
Pelvic splanchnic nerves, like the rest of the splanchnic nerves carry only sympathetic fibers |
FALSE
Pelvic splanchnic nerves are the ONLY splanchnic nerves that carry parasympathetic nerves |
|
|
_________________ accompany sympathetic nerves and carry pain from abdominal viscera to spinal cord. What is this "pain" stimulated by?
|
Visceral afferent fibers
stimulated by: tissue injury sudden distention muscle spasms |
|
|
Where do the following refer pain?
foregut derivatives midgut derivatives hindgut derivatives |
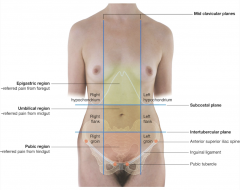
foregut derivatives- epigastric region
midgut derivatives- umbilical region hindgut derivatives- pubic (hypogastric) region |
|
|
Irritation of the phrenic nerve may cause referred pain to the (ipsilateral/contralateral) shoulder.
Why does this occur? |
ispilateral shoulder
the phrenic nerve (C3-5) & supraclavicular nerves (C3-4) which supplies the cutaneous innervation of the shoulder enter the same spinal cord segments |

