![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
True or False
The larynx serves to protect the lower airways, facilitates respiration, and plays a key role in phonation. In humans the protective and respiratory functions are compromised in favor of its phonatory function |
True
|
|
|
True or False
The protective function is entirely reflexive and involuntary, whereas the respiratory and phonatory functions are initiated voluntarily. |
False
The respiratory and phonatory functions are initiated voluntarily but regulated involuntarily. |
|
|
True or False
Sensory nerves to the larynx are derived from the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (eSLN) and the recurrent laryngeal nerves (RLNs); both are branches of the vagus nerve. The RLN and eSLN innervate the mucosa above and below the level of the true vocal cord, respectively. |
False
Sensory nerves to the larynx are derived from the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (iSLN) and the recurrent laryngeal nerves (RLNs); both are branches of the vagus nerve. The iSLN and RLN innervate the mucosa above and below the level of the true vocal cord, respectively. |
|
|
____ inhalation stimulation in partial upper airway obstruction activates ____ on the epiglottis and causes ____ slowing and increase in ____.
|
Water-aerosol
water chemoreceptors reflex respiratory slowing tidal volume |
|
|
The ___ innervates all intrinsic laryngeal muscles except the ___, which is innervated by the ___ division of the ___.
|
RLN
cricothyroid muscle external SLN |
|
|
Abduction of the vocal cords during respiration is brought about by the ___ muscle, whereas their adduction involves ___ muscles, particularly the ___ and ___ muscles.
|
posterior cricoarytenoid
all the intrinsic thyroarytenoid cricoarytenoid |
|
|
True or False
Reflexive glottic closure is achieved by simultaneous adduction of both vocal cords. Anesthesia and sedation preserve reflexive vocal cord closure and help prevent aspiration. |
False
Anesthesia and sedation impair reflexive vocal cord closure and predispose to aspiration. |
|
|
Do hypothermia, inspiratory phase, increased arterial pCO2, decreased arterial pO2, and positive intrathoracic pressure inhibit or facilitate reflexive glottal closure?
|
Inhibited
|
|
|
Do hyperthermia, expiratory phase, decreased pCO2, increased pO2, and negative intrathoracic pressure inhibit or facilitate reflexive glottal closure?
|
Facilitated
|
|
|
True or False
Laryngeal denervation leads to vocal dysfunction and aspiration during swallowing. |
True!
|
|
|
___ itself can lead to centrally mediated impaired reflexes and decannulation (adductor failure and vocal cord fusion).
|
Tracheostomy
|
|
|
____, even if denervated, resist air flow from the lower respiratory tract and serve expectorative function. The ____ resist air flow from outside and play a protective role in respiration, thus explaining the difficulty in overcoming laryngospasm by abrupt pressure peaks from above.
|
False Vocal Cords
True Vocal Cords |
|
|
True or False
By sharing a common passageway with the upper digestive system, the larynx is also compromised in its respiratory performance by resultant ventilatory turbulence and, therefore, resistance. |
True
|
|
|
True or False
The anatomic configuration in adult humans that benefits phonatory purposes of the larynx simultaneously serves its sphincteric and respiratory functions |
False
..simultaneously serves to compromise its sphincteric and respiratory functions |
|
|
This functional dilemma between respiration, swallowing and voicing is resolved at the laryngopharyngeal level by two important organic modifications: ____ and ____ among the three basic laryngeal functions as determined by precisely organized ____.
|
structural adaptation
delicate coordination brainstem reflexes |
|
|
True or False
Passive closure of the false cords alone appears essential to effective cough production (expectoration) |
True
|
|
|
It is generally agreed that the motor distribution to the intrinsic laryngeal musculature originates in the ____.
|
medullary nucleus ambiguus
|
|
|
The interarytenoid muscles receive ipsilateral/bilateral motor innervation from the ipsilateral/contralateral/both recurrent laryngeal nerve.s.
|
bilateral
both |
|
|
The muscle that widens the glottic chink, as takes place in respiration, is solely the _____ extending from the ____ to the ____
|
posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
posterior aspect of the cricoid plate muscular process of the arytenoid |
|
|
Posterior Cricoarytenoid
abducting the TVF |
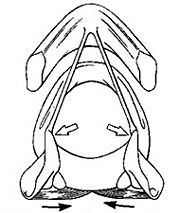
What is the muscle and what is it doing?
|
|
|
Thyroarytenoid
Helps adduct the TVF |
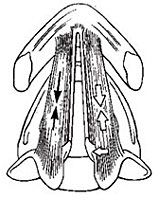
What is the muscle and what is it doing?
|
|
|
Lateral cricoarytenoid.
Adducting the TVF |
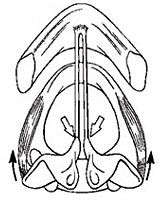
What is the muscle and what is it doing?
|
|
|
Interarytenoid
Adducting the TVF |
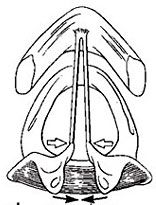
What is the muscle and what is it doing?
|
|
|
Cricothyroid
Adducting and tensing the TVF |
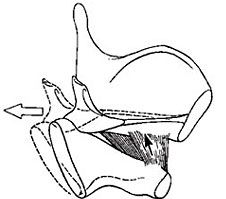
What's the muscle and what's it doing?
|
|
|
True or False
Each recurrent laryngeal nerve ipsilaterally innervates all muscles except the cricothyroid muscle, which receives its motor impulses from the external division of its contralateral superior laryngeal nerve. |
False
external division of its ipsilateral superior laryngeal nerve. |
|
|
True or False
The lateral cricoarytenoid, exerting a posterolateral pull on the arytenoid body rotates the vocal fold outward, effecting cord abduction on inspiration. |
False
The posterior cricoarytenoid |
|
|
Vocal fold adduction results from contraction of ____ other than the ____, major contributions arising from the action of ____ and ____ muscles
|
all intrinsic musculature
posterior cricoarytenoid thyroarytenoid lateral cricoarytenoid |
|
|
The ____ serve to close the posterior gap of the glottis, whereas the ____ adducts and tenses the vocal cord, passively lengthening it by ____.
|
interarytenoid muscles
cricothyroid muscle 30% |
|
|
True or False
When one cricothyroid muscle is denervated by sectioning the superior laryngeal nerve, the unopposed contraction of the contralateral cricothyroid muscle results in rotation of the posterior glottis toward the inactive side, with foreshortening of the cord on the side of denervation. |
True
|
|
|
True or False
unilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve injury results in the paramedian position of that cord because the unopposed action of the ipsilateral cricothyroid muscle, innervated by an intact superior laryngeal nerve, produces cord adduction on the uninjured side. |
False
produces adduction on the side of injury. |
|
|
True or False
Adductor motor components of recurrent laryngeal nerve are more resistant to injury than abductor fibers |
False!
|

