![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The type of energy in the food we eat is ___ ___
|
chemical potential
|
|
|
When we turn the energy of food into motion, we call that energy of motion ___ ___
|
kinetic energy
|
|
|
The type of energy that is utilized in our home wiring or our nervous system is ....
|
electrical energy
|
|
|
The type of energy that UVA, B, & C is that does damage to our skin is ___ energy
|
light or radiant or electromagnetic
|
|
|
The universal solvent is ....
|
water
|
|
|
Water has a high heat of vaporization, meaning that it takes _____ energy to evaporate water from your skin.
|
a lot of
|
|
|
Water has a high heat capacity, meaning that it takes _____ energy to change the temperature of water.
|
a lot of
|
|
|
Water is a major ______ regulator and l____.
|
temperature
lubricant |
|
|
About ___ % of our body is water (depending on how hydrated you are).
|
50-75%
|
|
|
Muscle contains about ____% water
|
75
|
|
|
The brain contains of about ____% water.
|
90
|
|
|
Bone consists of about ____% water.
|
22
|
|
|
Blood consists of about ___% water.
|
83
|
|
|
If you get dehydrated, you can expect what kinds of symptoms? name a few
|
tiredness, migraine, constipation, muscle cramps,
irregular blood pressure, kidney problems, dry skin |
|
|
When you become 20% dehydrated, you risk....
|
death
|
|
|
Most chemical reactions do not occur spontaneously because they require ____ to activate them.
|
energy
|
|
|
The amount of energy needed to get a reaction going is called ____ energy.
|
activation
|
|
|
In your body, proteins that speed up chemical reactions, such as in the removal of toxins, are called....
|
enzymes
|
|
|
An enzyme that removes hydrogen peroxide is called....
|
catalase
|
|
|
The body has _____s (#) of cells.
|
trillions
|
|
|
Cells provide physical ____, regulation of ____ with the environment, s____, and s____ support.
|
isolation, exchange,
sensitivity, structural |
|
|
The DNA of cells is found where?
|
in the nucleus
|
|
|
The DNA is responsible for....
|
providing instructions for how to build a cell or organism
|
|
|
Chemicals in your body that are fatty are...
|
lipids
|
|
|
Cells make lots of different p____, each of which contain a different combination of a__ a___
|
proteins
amino acids |
|
|
The main energy source for your body comes from....
|
carbohydrates
|
|
|
Carbohydrates contain the elements ___ ___ & ___
|
C, H, O
|
|
|
Cells that are capable of differentiating into any type of cell are called....
|
stem cells
|
|
|
Why do cells need to be numerous before differentiation can occur?
|
So there are enough to have all necessary parts.
|
|
|
Cancer is ....
|
abnormal cell growth
|
|
|
Some things that cause cancer are....
|
genetic predisposition, radiation,
pollution, toxins, sun |
|
|
Cancer that remains together in a connective tissue and doesn't spread is....
|
benign cancer
|
|
|
Cancer that does spread throughout the body is ....
|
malignant cancer
|
|
|
When malignant cancer spreads, we say it is...
|
metastasizing (undergoing metastasis)
|
|
|
The type of cancer that is not usually life threatening is ___ cancer, while ____ cancer is usually fatal.
|
benign
malignant |
|
|
Breast cancer that metastasizes to the bones is considered to be .....
|
breast cancer
|
|
|
Cancer can spread to adjacent ____, through the ____ system, or through the ____ to distant locations.
|
tissue
lymph blood |
|
|
A malignant cancer that metastasizes to another location and making a tumor there is called a .....
|
secondary tumor
|
|
|
Comprising about 12% of our body weight and about twice as much energy as an equal quantity of carbohydrates are.....
|
lipids
|
|
|
Making up about 20% of our body weight, these chemicals do a lot of jobs, such as support, buffering, transport, defense, movement, metabolic regulation. What are they?
|
proteins
|
|
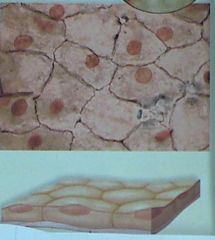
This somewhat flattened-out cell is ....
|
simple squamous
|
|
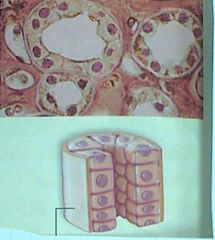
These cells are...
|
simple cuboidal
|
|
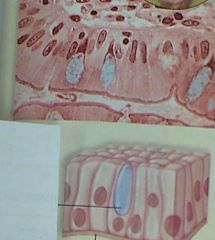
These cells (with a goblet cell also) are....
|
simple columnar
|
|
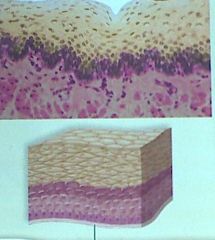
These cells that are layers of flattened cells are....
|
stratified squamous
|
|
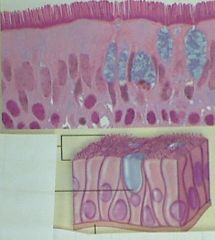
This set of cells has "little hairs" on the top of it. It is _____ ______ ____
|
pseudostratified ciliated columnar
|

