![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
At the root of the penis, there are two ligaments. What are they and in what fascia are they located?
|
Fundiform Ligament is in the Superficial Fasica
Suspensory ligament is in the Deep Fascia |
|
|
What is the name of the fascia that covers the Corpra spongiosum and Corpra cavernosum?
|
Bucks fascia
|
|
|
What is the name of the sphincter that allows continence?
|
Internal Sphincter
|
|
|
Name the segments of the male urethra
|
P-PMS:
1. Pre-prostatic 2. prostatic 3. membranous 4. spongy |
|
|
Men often have a hard time urinating when BPH occurs. What does this stand for and in what zone does it occur?
|
Benign prosthetic hypertrophy occurs in the transitional zone.
|
|
|
Where do men typically have develop prostatitis? What structure exists here and what zone is it?
|
Ejaculatory ducts are here in the Central Zone.
|
|
|
Where do prostatic cancers tend to occur?
|
In the peripheral zone where glandular tissue occurs.
|
|
|
The anterior fibromuscular stroma is important for what?
|
Continence
|
|

Label
|
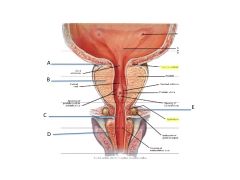
A. Intermeural portion
B. Prostatic portion C. Membranous portion D. Spongy portion E. Bulbourethral gland |
|
|
For females, "water under the bridge" refers to the way the ureter travels under the uterine artery. What's the equivalent in males?
|
How the ureter goes under the vas deferens
|
|

Label
|

A. Ureture
B. Vas deferens C. Seminal vesicles D. Prostatic vesicles (Neurovascular bundle) E. Prostate |
|
|
The testes are covered by a thick white structure called:
|
Tunica albuginea
|
|
|
What structure in the testes makes the sperm?
|
Semineferous tubules
|
|
|
The ducts between the semineferous tubules and epididymis is the:
|
rete testis or efferent ductules
|
|
|
What is the sperm-post-processing structure called?
|
Epididymis
|
|
|
Mature sperm is passed through what structure?
|
Vas deferens
|
|
|
What is the equivalent to the round ligament of the ovaries in males?
|
Gubernaculum testis.
|
|
|
Trace path of sperm
|
1. Semeniferous tubules
2. Rete testes 3. Efferent ductules 4. Head, body, tail of epididymis 5. Vas deferens |
|

label
|

1. Inferior vesicles
2. middle rectal 3. Internal pudendal a 4. Prostatic branches |
|
|
What are the penile blood vessels coming off the pudendal artery? (BP-DUD)
|
BP-DUD
1. Bulb of penis artery 2. Perineal artery 3. Deep artery of the penis (cavernosal a) 4. Urethral a 5. Dorsal artery of the penis |
|
|
What artery is important for maintaining and ending an erection?
|
Deep artery of the penis.
|
|
|
If a testicular cancer spreads, what is the first structure it spreads to?
|
Para-aortic lymph nodes (Caval/aortic)
|
|
|
If prostate cancer spreads, what structure will it spread to?
|
Internal iliac lymph nodes
|
|
|
If perineum cancer spreads, what structure will it spread to?
|
Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
|
|
|
If penis cancer spreads, what structure will it spread to?
|
Internal iliac inguinal nodes (proximal); deep inguinal nodes (distal)
|
|

Memorize?
|

?
|
|
|
What's the "point and shoot" thing Schelpheffer told us is helpful for remembering?
|
Parasympathetic is helpful for maintaining an erection.
Sympathetic is helpful for ejaculation. |
|
|
Beware that there was quite a bit more to Schelpheffer's lectures that seemed like too much detail. If you have time, go back to learn the para/sympathetic NS stuff re the male pelvis on the latter half of his lecture.
|
Beware that there was quite a bit more to Schelpheffer's lectures that seemed like too much detail. If you have time, go back to learn the para/sympathetic NS stuff re the male pelvis on the latter half of his lecture.
|

