![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the study of the causes, mechanisms and manifestations of developmental defects of a structural and/or functional nature is called...
|
teratology
|
|
|
Etiologies of developmental defects:
1. ________% are multifactorial in nature. 2. _______% are unknown in etiology. |
1. 20-25%
2. 50-60% |
|
|
Multifactorial etiologies causing developmental defects include __________ and ___________ causes.
|
environmental and genetic
|
|
|
an abnormal number of chromosomes other than an exact multiple of the haploid number is called ___________.
|
Aneuploidy
|
|
|
the absence of one member of a pair of chromosomes, either autosomes or sex chromosomes
|
monosomes
|
|
|
the addition of a third chromosome to a pair of chromosomes, either autosomes or sex chromosomes. fourth? fifth?
|
trisomy, tetrasomy, pentasomy
|
|
|
an abnormal number of chromosomes that is an exact multiple of the haploid number
|
polyploidy
|
|
|
Turner's syndrome is a ________________ of sex chromosomes.
|
monosomy
|
|
|
Broad chest with widely spaced nipples, webbed neck, absence of ovaries (gonadal dysgenesis) and absent sexual maturation, lymphedema of extremities and short stature are all characteristics of what disease?
|
Turner's
|
|
|
What is the only monosomy compatible with life?
|
Turner's
|
|
|
Trisomy 21, 18 and 13 are all trisomies of (autosomes/sex chromosomes).
|
autosomes
|
|
|
Atlantoaxial instability can be found in 15% of patients with ___________.
|
Down's syndrome
|
|
|
___% of embryos with down's syndrome are spontaneously aborted.
|
75%
|
|
|
The incidence of Down syndrome increases dramatically with maternal age due to an increased incidence of ________________.
|
meiotic nondisjunction
|
|
|
What disease?
Tall stature Broad hips Testicular atrophy with hyalinized seminiferous tubules Gynecomastia Possible mental retardation An incidence of 1:500 males |
Klinefelter syndrome
|
|
|
Klienfelter syndrome is a ____________ with a _____ karyotype.
|
-trisomy
-47,XXY |
|
|
The most common type of polyploidy is _________. This is mostly fatal.
|
triploidy (3 times the haploid number of chromosomes = 69 chromosomes).
|
|
|
In translocation, a piece of a chromosome is transferred onto a ___________.
|
nonhomologous chromosome
|
|
|
the transverse rather than longitudinal division of the centromere joining two chromatids is called...
|
isochromosome
|
|
|
In cri du chat syndrome, ____________ from chromosome 5 causes the symptoms of a catlike cry, microcephaly, mental retardation, and congenital heart disease.
|
-a partial deletion
|
|
|
If translocation between nonhomologous chromosomes is _____________, abnormal development may be avoided.
|
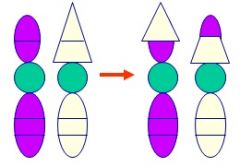
reciprocal
|
|
|
____________ usually does not lead to abnormal phenotype but is seen in some cases of hemophilia.
|
Inversion
|
|
|
about 15-20% of women with ____________ have isochromosomes
|
Turner syndrome
|
|
|
In _______________, the patient has two or more cell lines with different karyotypes resulting from a rare mitotic nondisjunction of chromosomes; either autosomes or sex chromosomes may be involved.
|
mosaicism
|
|
|
The antinauseant and sleeping pill ______________ causes total (amelia) or partial (meroamelia/phocomelia) developmental absence of limbs.
|
thalidomide
|
|
|
microcephaly, maxillary hypoplasia, short palpebral fissures, joint abnormalities, and cardiovascular defects are characteristics of...
|
fetal alcohol syndrome
|
|
|
___________, a folic acid antagonist used to treat leukemia, causes skeletal and central nervous system defects...including anencephaly (no head).
|
Aminopterin
|
|
|
___________, ( analogue of vitamin A) used for the oral treatment of severe acne can produce virtually any type of defect.
|
Isotretinoin
|
|
|
_______________ causes “fetal hydantoin syndrome,” which includes IUGR, microcephaly, ptosis, nail and/or distal phalangeal hypoplasia.
|
Phenytoin
|
|
|
Environmental chemicals such as _______________ can cause severe brain damage, mental retardation, and blindness (fetal Minamata disease).
|
methylmercury
|
|
|
_____________ may kill embryonic cells, damage chromosomes, and cause mutations; the CNS is especially vulnerable (microcephaly and spina bifida).
|
Ionizing radiation
|
|
|
Oligohydramnios, uterine malformations, fetal growth restraint, amniotic bands are all ___________________ factors that cause developmental defects.
|
mechanical
|
|
|
Oligohydramnios is ...
|
too little amniotic fluid
|
|
|
Name 3 infectious agents that can cause developmental anomalies.
|
1. Toxoplasma gondii
2. Rubella virus 3. Cytomegalovirus |
|
|
What is the most common viral infection of the human fetus?
|
Cytomegalovirus
|
|
|
What is the "TORCH" complex?
|
Embryos or fetuses infected in utero with
TOxoplasma, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, or Herpes simplex virus exhibit similar developmental defects (TORCH complex) |
|
|
_____________________ is usually acquired by eating raw or poorly cooked pork or lamb or by close contact with infected cats; results of infection may include HYDROCEPHALUS.
|
Toxoplasma gondii
|
|
|
____________ virus causes a syndrome that usually includes cataracts and may include glaucoma.
|
Rubella
|
|
|
Cytomegalovirus may result in __________________.
|
microphthalmia (an eye too small)
|
|
|
Most congenital malformations result from exposure during the ___________ period.
|
embryonic (weeks 3-8)
|

