![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What will happen if the radial nerve is damaged?
How do you treat this? |
Will lose all of the extensors - hand will be flexed and deviated to ulna.
Tx: Will need to take a graft muscle and join it to a tendon on the damaged side. Must suit the graft to the main use of the hand/arm (ie suit function to the needs of the person) |
|
|
It is helpful to think of the hand as having opposing motor muscles, transmission through tendons and application through skin and pulp. Based on this, how could skin/soft tissue impinge on the functioning of a hand?
|
To allow joint to fold the skin must stretch and unfold. If however there is edema in the joint, the skin will be already stretched out and will thus prevent movement. Will need to "milk" fluid out of the joint in order to bend it.
|
|
|
How can problems in the tendons of the hand affect it's ability to function?
|
When the intrinsic muscles get paralyzed or there is rheumatory damage to tendons/joints, a clawhand will result. When a clawhand tried to grip something, the area of contact will be limited to the fingertips and the metacarpal heads. (= lots of pressure on a little area --> will become ischeamic and painful faster)
|
|
|
Sketch the collateral vessels that would provide blood supply to the arm should the brachial artery develop a slow occlusion.
|
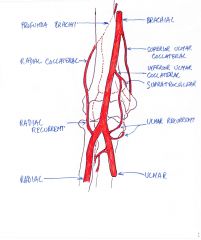
|
|
|
What is the commonest age and gender of people with supracondylar fractures?
What is a rare but v.serious complication? |
6.6years
2/3 boys : 1/3 girls Volkmann's contracture - flexion of the wrist and clawing of the hand that occurs when the brachial artery is occluded and there is ischemia. |
|
|
In what 3 ways can a supracondylar # impair the blood flow to the forearm?
Treatment? |
- Artery can get compressed by the injury itself (humerous will move anteriorly)
- Artery can get impaled when trying to reduce the # (sympathetics get stimulated and will constricte the surrounding vessels) - Compartment syndrome - bleeding/swelling increase the pressure --> arteries occluded --> muscles die = fibrosis & contractures Tx: remove the cast, disimpale the artery and use antagonists to block sympathetics |
|
|
What are 6 places where the radial N could be damaged?
|
1. Axilla (gunshot/stab) as it passes over subscapularis, T major and lat dorsi.
2. Spiral groove - btwn med and lat triceps 3. lateral epicondyle - humeral # 4. elbow joint - cubital fossa between bradialis & brachialis, (elbow dislocation) 5. Radial tunnel - as it pierces the firbrous bit of supinator 6. head of radius - from a # or a dislocation |
|
|
In what 3 places is the ulnar nerve susceptible to damage?
|
1. Direct injury/trauma to the elbow
2. Compression in the cubital tunnel, by a tight Flexor carpi ulnaris or valgus deformity (following a #) 3. Trauma to Guyon's Canal |
|
|
What is mallet finger? (cause, symptom tx?)
|
When the terminal portion of the extensor tendon is torn over the DIP joint. The DIP joint can no longer be extended and thus falls into flexion.
Tx: splint the finger and wait for the tendon to re-attach. |
|
|
What is a boutonniere deformity (cause, appearance?)
|
If you tear the central tendon then the the PIP joint will get flexed and the DIP joint will be extended. This happens because the lateral extensor tendons are tugging unopposed.
|
|
|
What holds the flexor digitorum tendons onto the bone? What is contained within these structures?
|
Long and short Vinculum tendons. They carry blood supply and nerves to the tendons. Nerves provide information about degree of tendon stretch and proprioception.
|
|
|
Why do you need to treat a pin prick injury carefully?
|
Because the synovial sheaths of the fingers are often continuous and can communicate. If infection gets in it can travel up and down filling the synovial cavity with pus.
This leads to a build up of pressure = vascular loss = destruction of tissue (will also be destroyed from bug's enzymes --> adhesions b/c of scarring) |
|
|
How would you test to see if flex dig superficialis was damaged?
|
Lay hand down with palm facing up. Hold fingers down and test only one at a time. (tethering the fingers like this will disable flex dig profundus b/c it has a single origin --> if one is held, they're all held). As pt to flex finger, expect no flexion at DIP joint, but good flexion at PIP joint. If there is no flexion at PIP flex dig superficialis likely injured (even if there's mcp flexion)
|
|
|
Carpal Tunnel:
- contents? - 4 cuases |
- all the flexor digitorum tendons and flexor pollicis longus
- extensive lumbercals (that begin in the tunnel); trauma (# lunate or dislocation); Endocrine (pregnancy/the pill); rheumatoid |
|
|
What's a colle's fracture? What does it look like and what should you watch out for?
|
Fracture in the distal 2cm of the radius. Produces the dinner fork deformity. Watch for median N damage!
|
|
|
A broken clavicle can be held in place by what?
|
The conoid and trapezoid portions of the coracoclavicular joint.
|

