![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
front face and arms/palms out |
Anatomical Position |
|
|
top of head of the body |
Superior |
|
|
the bottom of your feet of your body |
Inferior |
|
|
near to the center |
Proxmial |
|
|
Distant to the center |
Distal |
|
|
inside toward midline (inside of knees) |
medial |
|
|
outside of midline (outside of knees) |
lateral |
|
|
towards front |
anterior |
|
|
towards the back |
Posterior |
|
|
towards the stomach (non-human) |
Ventral |
|
|
towards the back (non-human) |
Dorsal |
|
|
Frontal, Orbital, Nasal, Buccal (cheek), Oral |
Cephealic (head) |
|
|
throat |
Cerrical |
|
|
Sternal, axillary |
Thoracic |
|
|
Abdonminal |
umbillical |
|
|
genital |
pubic |
|
|
Coal, Femoral, Patellar, Pupliteal, Crual, sural, fibular |
Lower Limb |
|
|
tarsal, calcaneal, digital, plantar |
Pedal |
|
|
Hip |
Coxal |
|
|
thigh |
femoral |
|
|
Patellar |
knee |
|
|
pupliteal |
back of knee |
|
|
crual |
shin |
|
|
sural |
calf |
|
|
fibular |
splinter bone |
|
|
tarsal |
ankle |
|
|
calcaneal |
heel |
|
|
digital |
fingers and toes |
|
|
plantar |
ball of foot |
|
|
vertical plane that divides the body into right and left |
Sagittal |
|
|
directly through midline |
Midsagittal |
|
|
parallel to the midline |
Parasagittal |
|
|
vertical plane that divides body into anterior and posterior parts |
Frontal |
|
|
horizontal plane that divides into inferior and superior parts |
Transverse |
|
|
not straight across (diagonal) |
Oblique Section |
|
|
Abdominal Cavity Quadrants |
Right upper quadrant Left upper quadrant Right lower quadrant Left lower quadrant |
|
|
gastric |
stomach |
|
|
hypogastric |
lower than stomach |
|
|
epigastic |
above or on top of stomach |
|
|
ilac |
hip |
|
|
inguinal |
private regions |
|
|
contains brain |
cranial cavity (Dorsal Body) |
|
|
contains spinal cord |
Vertebral Cavity (Dorsal Body) |
|
|
Thoracic Cavity |
contains heart and lungs (Ventral Body) |
|
|
Abdominal cavity (Ventral Body) |
contains digestive viscera |
|
|
contains urinal bladder reproductive organs and rectum |
pelvic cavity (Ventral body) |
|
|
cover organs of ventral doby cavity |
Serous membrane |
|
|
covers organs |
Visceral layer |
|
|
attaches to and covers ventral wall |
Parietal layer |
|
|
lubricates the space between the two layers (Visceral & Parietal) |
Serous fluid |
|
|
membrane covering lungs |
Pluera |
|
|
membrane covering the heart |
Pericardium |
|
|
membrane covering the abdominal organs |
Peritoneum |
|
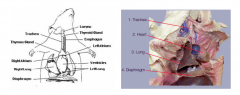
|
know |
|
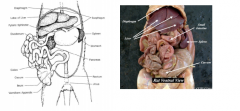
|
know |
|
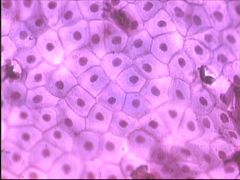
Name and Location?
|
Simple Squamous Epithelium
-kidney, alveoli in lungs, blood vessel |
|
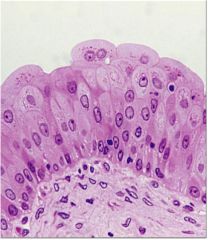
Name and Location? |
Transitional Epithelium
-lines the ureters, urinary bladder, and part of the urethra |
|
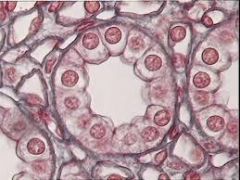
Name and Location? |
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
-Kidney tubules; ducts and secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface |
|
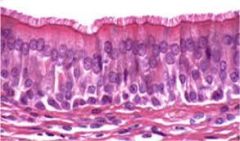
Name and Location? |
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
-nonciliated type in male's sperm-carrying ducts and ducts of large glands; ciliated variety lines the trachea, most of the upper respiratory tract |
|

Name and Location? |
Connective Tissue: Areolar Tissue
-widely distributed under epithelia of body |
|
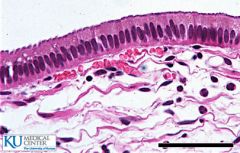
Name and Location? |
Simple columnar epithelium
-nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract (stomach to anal canal), gallbladder and excretory ducts of some glands; ciliated variety lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus. |
|
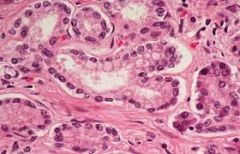
Name and Location? |
Stratified squamous epithelium
-nonkeratinized type forms the moist lining of the esophagus, mouth, and vagina; keratinized type forms the epidermis of the skin, a dry membrane |
|
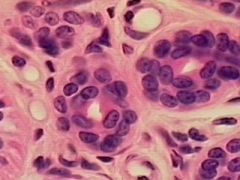
Name and Location? |
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
-Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands. |
|
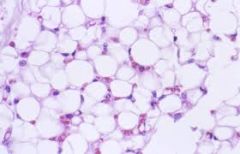
Name and Location? |
Adipose tissue
-under skin, around kidneys and eyeballs, within abdomen, in breasts. |
|
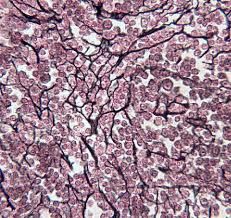
Name and Location? |
Reticular connective fibers
-lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen) |
|
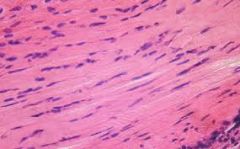
Name and Location? |
Dense regular connective tissue
-tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses |
|

Name and Location? |
Elastic Connective tissue
-walls of large arteries; within certain ligaments associated with vertebral column, within the walls of the bronchial tubes |
|
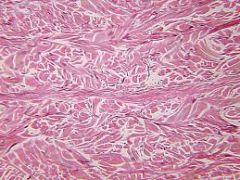
Name and Location? |
Dense irregular connective tissue
- fibrous capsules of organs and joints; dermis of the skin; submucosa of digestive tract |
|
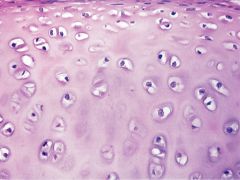
Name and Location? |
Hyaline cartilage
-forms most of the embryonic skeleton; covers the ends of long bones in joint cavities; forms the costal cartilages of the ribs, cartilages of the nose, trachea, and larynx |
|
|
What is Histology? |
the study of tissues |
|
|
What is osmosis? |
a process by which molecules of a solvent tend to pass through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one, thus equalizing the concentrations on each side of the membrane |
|
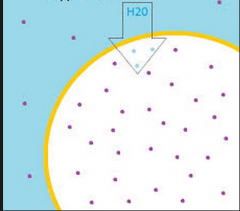
|
Hypotonic |
|
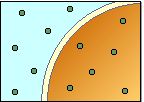
|
Isotonic |
|
|
hypertonic |
|
|
What is the tendency of molecules to spread into an available space? |
Diffusion |
|
|
what is the separation of particles in a liquid on the basis of differences in their ability to pass through a membrane? |
Dialysis |
|
|
What is the movement of water and solutes across the cell membrane due to hydrostatic pressure from the cardiovascular system? |
Filtration |
|
|
what is a red protein responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood of vertebrates. Its molecule comprises four subunits, each containing an iron atom bound to a heme group? |
Hemoglobin |
|
|
How is Hemoglobin tested? |
color scale |
|
|
what is the ratio of the volume of red blood cells to the total volume of blood? |
Hematocrit |
|
|
How is hematocrit tested? |
taking blood and placing in to a capillary and placed into a centrifuge |
|
|
antigens have oposite antibodies: A- B- AB- O- |
B A NO ANTIBODIES NOT ANTIGENS |
|
|
My blood is A+ can receive? can give to? |
receive: O-, O+, A-, A+ give: A+, AB+ |
|
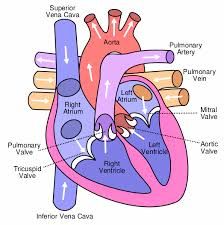
|
know
|
|
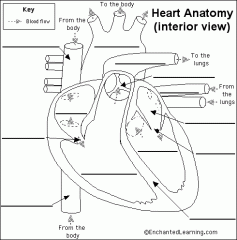
|
know
|
|
|
TV |
Tidal volume -inspire normally then expire normally into the spriometer |
|
|
IRV |
Inspiratory reserve volume -inspire maximally and expire into the spirometer normally |
|
|
ERV |
Expiratory reserve volume -inspire normally, expire forefully and completely |
|
|
VC |
Vital capacity -inspire and expire maximally and forcebility |
|
|
know |

