![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Consists of a group of glands that produces regulatory chemicals called hormones
|
Endocrine system
|
|
|
These two systems work together to control and coordinate all the systems of the body
|
Endocrine system
Nervous system |
|
|
Chemical messengers that have specific regulatory effects on certain cells or organs
|
Hormones
|
|
|
Hormones that affect many tissues
|
Growth hormone
Thyroid hormone Insulin |
|
|
Hormones that affect only specific tissues
|
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) |
|
|
Hormone that acts only on the thyroid gland
|
TSH
|
|
|
Hormone that stimulates only the outer portion of the adrenal gland
|
ACTH
|
|
|
The specific tissue acted on by each hormone
|
target tissue
|
|
|
These hormones are proteins or related compounds also made of amino acids
|
Amino acid compounds
|
|
|
Hormones fall into these two categories
|
Amino acid compounds
Steroids |
|
|
All hormones except those of the adrenal cortex and the sex glands fall into this category
|
Amino acid compound
|
|
|
these hormones are types of lipids derived from the steroid cholesterol
|
Steroids
|
|
|
Can be recognized by the ending -one, as in progesterone, testosterone
|
Steroids
|
|
|
Hormones produced by the adrenal cortex and the sex glands
|
Steroids
|
|
|
The method most commonly used to regulate hormone levels
|
Negative feedback
|
|
|
Hormone cycle of the adrenal cortex follow this pattern
|
24 hours
highest before getting up in morning lowest right before bed |
|
|
tissues other than the endocrine glands that produce hormones
|
Brain
Digestive organs Kidneys |
|
|
A small gland avout the size of a cherry; divided into two parts the anterior lobe and the posterior lobe
|
Pituitary
hypophysis |
|
|
Commonly used when refering to the pituitary gland because it releases hormones that affect the working of other glands
|
Master gland
|
|
|
Hormones produced in the anterior pituitary are not released until these chemical messengers arrive from the hypothalamus
|
Releasing hormones
|
|
|
Hormone that causes contraction of uterine muscle; causes ejection of milk from mamary glands
|
Oxytocin
|
|
|
Hormone that stimulates liver to release glucose, thereby increasing blood sugar levels
|
Glucagon
|
|
|
Two hormones of the posterior pituitary
|
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Oyxitocin |
|
|
Hormone that acts directly on most body tissues, promoting protein manufacture that is essential for growth
|
Growth Hormone (GH)
|
|
|
Hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce throid hormones
|
Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH)
|
|
|
Hormone that stimulates the production of hormones in the cortex of the adrenal glands
|
Adrenocorticotopic Hormone (ACTH)
|
|
|
Hormone that stimulates the production of milk in the breasts
|
Prolactin (PRL)
|
|
|
Hormone that stimulates the development of eggs in the ovaries and sperm cells in the testes
|
Follicle-stimulating Hormone (FSH)
|
|
|
Hormone that causes ovulation in females and sex hormone secretion in both males and females
|
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
|
|
|
Hormones that act on the gonads to regulate growth, development, and function of the reproductive systems in both males and females
|
Gonadotropins
|
|
|
Hormone that promotes the reabsorbtion of water from te kidney tubules and thus decrease water excretion
|
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
|
|
|
the largest of the endocrine glands; has two roughly oval lobes on either side of the larynx connected by a narrow band called an isthmus
|
Thyroid
|
|
|
The principle hormone produced by the thyroid; contains 4 iodine atom in each molecule; increase energy metabolism and protein metabolism
|
Thyroxine (T4)
|
|
|
Other hormone produced by the thyroid; contains 3 iodine atoms in each molecule; increases energy metabolism and protein metabolism
|
Triiodothyronine (T3)
|
|
|
Another hormone produced by the thyroid, active in calcium metabolism
|
Calcitonin
|
|
|
The uniform overgrowth of the thyroid gland
|
Simple goiter
|
|
|
An irregular-appearing goiter accompanied by tumor formation
|
Adenomatous or nodular goiter
|
|
|
Underactivity of the thyroid
|
hypothyroidism
|
|
|
A condition resulting from hypothyroidism in infants and children
|
Infantile hypothyroidism or cretinism
|
|
|
Disorder that results from thyroid atrophy in an adult
|
Myxedema
|
|
|
overactivity of the thyroid gland with excessive secretion of hormone
|
Hyperthyroidism
|
|
|
Common form of hyperthyroidism characterized by a goiter, a strained appearance of the face, intensive nervousness, weight loss, a rapid pulse, sweating, tremors, and an abnormally quick metabolism
|
Graves Disease
|
|
|
Protrusion of the eyes caused by swelling of the tissue behind the eyes
|
exophthalmos
|
|
|
An exaggerated form of hyperthyroidism with a sudden onset
|
Thyroid storm
|
|
|
Hormone that promotes calcium release from bone tissue, thus increasing the amount of calcium circulating in the bloodstream
|
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
|
|
|
The active form of vitamin D used along with PTH and calcitonin to regulate calcium balance
|
Calcitriol
|
|
|
Series of muscle contractions involving the face and hands due to a low concentration of blood calcium
|
Tetany
|
|
|
Two small glands located atop the kidneys
|
Adrenal glands
|
|
|
Inner area of the adrenal gland
|
Medulla
|
|
|
Outer portion of the adrenal gland
|
Cortex
|
|
|
Effects of fight-or-flight hormones
|
Stimulation of the involuntary muscle in the walls of the arterioles
Conversion of glycogen stored in the liver into glucose Increase in the heart rate Increase in the metabolic rate of body cells Dilation of the bronchioles |
|
|
Maintain the carbohydrate reserve if the body by stimulating the liver to convert amino acids into glucose instead of protein
|
Glucocorticoids
|
|
|
Hormones produced by the adrenal cortex
|
Glucocorticoids
Mineralocorticoids Sex Hormones |
|
|
Major hormone in the glucocorticoid group
|
Cortisol
|
|
|
Important in the regulation of electrolyte balance
|
Mineralocorticoid
|
|
|
Major hormone in the mineralocorticoid group
|
Aldosterone
|
|
|
Disease characterized chiefly by muscle atrophy, weakness, skin pigmentation, and disturbances in salt and water balance
|
Addison disease
|
|
|
Hypersecretion of cortisol; symptoms include obesity, with a round face, thin skin that bruses easily, muscle weakness, bone loss, and elevated blood sugar
|
Cushing syndrome
|
|
|
Cells that make up the endocrine portion of the pancreas
|
Islets
|
|
|
The most important hormone secreted by the islets; lowers blood sugar levels
|
Insulin
|
|
|
Active in the transport of glucose across plasma membranes, increasing cellular glucose uptake
|
Insulin
|
|
|
Hormone produced by islets that works with insulin to regulate blood sugar levels; increases blood sugar levels
|
Glucagon
|
|
|
Mass of lymphoid tissue that lies in the upper part of the chest superior to the heart; important in the development of immunity
|
Thymus gland
|
|
|
Hormone secreted by the thymus gland; assists in the maturation of certain white blood cells (T cells)
|
Thymosin
|
|
|
A small, flattened, coneshaped structure located posterior to the midbrain and connected to the roof of the third ventricle
|
Pineal gland
|
|
|
Hormone produced by the pineal gland; influences the regulation of sleep-wake cycles
|
Melatonin
|
|
|
A group of local hormones made by most body tissues
|
Prostagalndins
|
|
|
Hormone used for the treatment of children with a deficiency of this hormone
|
Growth hormone
|
|
|
Hormone used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus
|
Insulin
|
|
|
Hormones used for the relief of inflammation in such diseases as rheumatoid arthritis
|
Adrenal steroids
|
|
|
Hormone used for stimulation of the heart muscle when rapid response is required
|
Epinephrine
|
|
|
Hormones used in the treatment of hypothyroid conditions
|
Thyroid hormones
|
|
|
Hormone used in severe chronic illness to aid tissue building and promote healing
|
Androgens
|
|
|
Hormones uses as oral contraceptives and as treatment for menopause
|
Estrogen
Progestrogen |
|
|
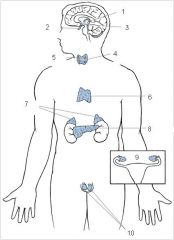
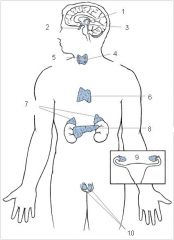
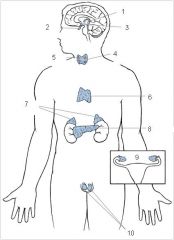
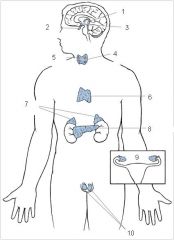
Pineal
|
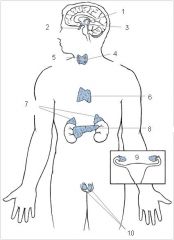
1
|
|
|
Pituitary
|
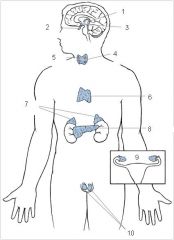
2
|
|
|
Hypothalamus
|
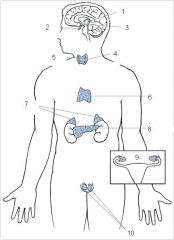
3
|
|
|
Thyroid
|
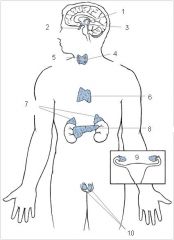
4
|
|
|
Parathyroid
|
5
|
|
|
Thymus
|
6
|
|
|
Adrenal glands
|
7
|
|
|
Pancreas
|
8
|
|
|
Ovaries
|
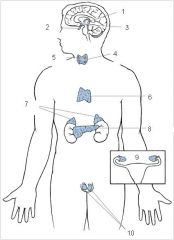
9
|
|
|
Testes
|
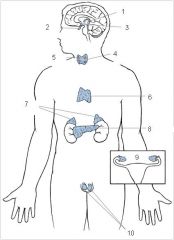
10
|

