![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Maintain blood volume Body defense Transport fatty acids to liver Cleanup interstitial space |
4 rules of lymph |
|
|
Lymphatic capillaries are distributed among but not connected to the |
Blood capillaries |
|
|
Drains fluid from R side of head and neck into bracio symphatic vein |
Right lymphatic duct |
|
|
Drains fluid from the rest of the body |
Thoracic lymphatic duct |
|
|
Spleen |
Recycles old rbcs Stimulates wbcs |
|
|
Lymph moves |
Body movement Breathing Gravity Massage |
|
|
2 main functions for respiratory system |
Gas exchange Sound production |
|
|
Oral cavity |
Alternate route for breathing |
|
|
Nasal cavity |
Passageway for air |
|
|
Hoe many palates are their? |
2-hard and soft |
|
|
Hard palate |
Formed by the maxilla bone |
|
|
Soft palate |
Combo of soft tissue |
|
|
Pharynx |
Food air and water mix here can be dangerous. |
|
|
Larynx |
Where sound is produced |
|
|
What is inferior to the pharynx and superior to the trachea? |
Larynx |
|
|
Lungs |
Superior to the diaphragm |
|
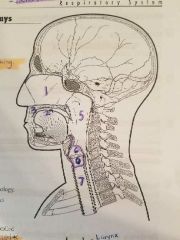
|
1- nasal cavity 2- oral cavity 3- hard palate 4- soft palate 5-pharynx 6-larynx 7- trachea |
|
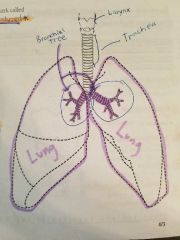
|
Larynx Trachea Bronchial tree Lungs |
|
|
Tunica mucosa |
Mucous coated epithelial layer |
|
|
Tela submucosa |
Vascular loose connective tissue layer |
|
|
Tunica media |
Larynx it has large cartilages amd skeletal muscles Bronchial tree cartilages are small and smooth |
|
|
Tunica adventitia |
Outer connective tissue coat that wraps around other layers |
|
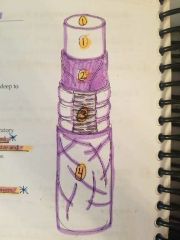
|
1- tunica mucosa 2-tela submucosa 3-tunica media 4- tunica adventitia |
|
|
First they form a strong wall that keeps the larynx from collapsing, Second, they stabilize and adjust the tension in the vocal tissues for sound production. Third, the epiglottis closes off the respiratory passageways so you dont choke when you swallow food or liquids. |
Cartilages of the larynx |
|
|
Elastic cartilage |
Protects airway from food, water, etc |
|
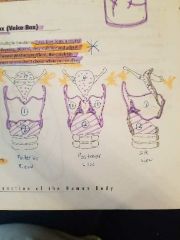
|
1- thyroid cartilage 2- cricoid cartilage 3- arytenoid cartilage 4- epiglottis 5- maxillary |
|
|
Move the cartilages of the larynx to produce varied degrees of tension on the vocal tissues |
Functions of skeletal muscles |
|
|
Trachea |
Anterior to esophagus Air only |
|
|
Brachial tree |
Carries air into lungs |
|
|
Trachia is lined with |
Psuedo stratified epithelium |
|
|
Blood returns to the heart to the |
Left atrium |
|
|
Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place in the |
Pulmonary cappilaries |

