![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the properties of the skin?
|
Cosmetic
REgulate temperature Protect from environment Vitamin D metabolism Sensation Immunologic origin |
|
|
Where on the body is the dermis the thickest
|
The back
|
|
|
What type of epithelium is the epidermis?
|
keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium
|
|
|
What are the cell types in the epidermis?*
|
Keratinocytes
Melanocytes Langerhans cells Merkel cells |
|
|
What is the layer of cells in the epidermis that divides?
|
Keratinocytes
|
|
|
What are the layers of the keratinocytes?
|
Base to top:
Basal Spinous: desmosomes Granular basopihlic, keratohyaline granules Cornified: no organelles |
|
|
What's the turnover time for the skin?
|
30 days
|
|
|
What is the effect of fixing on the epidermis?
|
The stratum cornium looks more fenestrated than it really is.
|
|
|
What is the origin of the melanocytes?
|
Neural crest
|
|
|
What is the function of the melanocytes?
|
Create melanin, which protects from UV
|
|
|
How is melanin distributed throughout thse skin? Where does it go?
|
Melanasomes
To the keratinocytes |
|
|
What type of a cell is the melanocyte?
|
Dendritic cell
|
|
|
What layer of cells stains with silver stain? Why? Why is this important
|
Basal cell layer
Lots of melanin You need to protect these guys from the sun! |
|
|
Why is darker skin darker?
|
Lighter skin: less aggregated MELANOSOMES
Darker skin: melanosomes are more active The number of melanocytes is the same! |
|
|
What enzyme is more active in darkly-skinned people to make their skin darker?
|
Tyrosinase
|
|
|
What is vitiligo?
|
When the melanocytes just die off.
|
|
|
What is the origin of the langerhans cell? What type?
|
Bone marrow
Dendritic cells |
|
|
Where are the langerhans cells found?
|
Inside the spinous layer
|
|
|
What is the function of the langerhans cells?
|
Skin immune response! - APC
Hypersensitivity reactions (poison ivy) |
|
|
How do you see langerhans cells inside the body?
|
You either do a special immunostain or look for the Birbeck granules (it looks like a tennis racket)
|
|
|
Where are the merkel cells found?
|
In the epidermis and dermis
|
|
|
What is the function of the merkell cells?
|
Tactile sensation/slow adapting touch
|
|
|
Where in the body are the merkel cells found?
|
Lower epidermis
Also, in the upper dermis |
|
|
What are the different layers of the basement membranes?
|
Laamina lucida
Lamina densa Sublamina densa |
|
|
What attaches the epidermis to the dermis and collagen?
|
The anchoring fibrils
|
|
|
What are the components of the pilosebaceous unit?
|
Hair follicle
Sebacious Arector pili |
|
|
What are the three parts of a hair follicle?
|
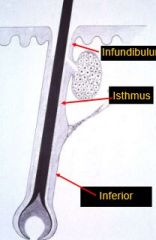
Infundibulum
Isthmus Inferior Also, note that the arrector pilli are on an angle. |
|
|
What are the layers of a hair follicle?
|
External (glycogenated) root sheath
Internal root sheath Hair itself |
|
|
What are the different cycles of hair growth?
|
Anagen (growth) - 3-4 years, 85-90%
Catagen (involutional) - 3 days, 1% Telogen (resting) - 3 months, 10-14% |
|
|
How can the hair cycle be disrupted?
|
You have a stressor, causing less of the hairs to be in the anagenic phase and more in the telogenic phase
More hair comes out! |
|
|
What kind of secretion happens with the sebaceous glands?
|
Holocrine secretion
There's so much lipid inside the cells that they explode! |
|
|
Where are sebaceous glands found?
|
Everywhere except the palms/soles
|
|
|
Where are the apocrine sweat glands found?
|
Axilla
Groin |
|
|
Other than the axilla and groin, where are apocrine glands found?
|
Eyelids
External auditory canal |
|
|
What type of secretion happens in the apocrine glands?
|
You have little blips of cytoplasm coming off and then going into the ducts
|
|
|
Where are the eccrine glands found?
|
Palms
SOles Axilla Forehead |
|
|
When you're "sweating" due to exertion, what sweat glands are active?
|
Eccrine sweat glands
|
|
|
What's the structural distance between eccrine and apocrine glands?
|
Eccrine connects directly to the surface (via straight duct)
|
|
|
What are the layers of the dermis?
|
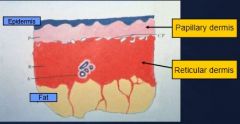
Papillary dermis
Reticular dermis |
|
|
What are the different components of the dermis?
|
Colagen
Elastic tissue Ground substance Fibroblasts, mast cells, dermal dendrocytes |
|
|
What cells synthesize collagen in the dermis?
|
Fibroblasts
|
|
|
What are the types of collagen found in the skin?
|
Type I: most abundant, coiled; reticular dermis
Type III: Fine, loosely arranged; papillary dermis Type IV, VII: BM (IV: basal lamina, VII: anchoring fibrils) |
|
|
What cells make elastic tissue?
|
Fibroblasts
|
|
|
What is the function of the elastic tissue?
|
Elasticity of the skin
|
|
|
What are the different proteins in the elastic tissue?
|
Elastin
|
|
|
What amino acids are unique to elastic tissue?
|
Desmosine
Isodesmosine |
|
|
What happens to the elastic tissue as you age?
|
They get damaged!!!
You get wrinkles! |
|
|
What cells make the ground substance?
|
Fibroblasts
|
|
|
What are the components of the ground substance?
|
Fibronectin
Glycosaminoglycans |
|
|
What do fibroblasts produce?
|
Collagen
Elastin Ground substance |
|
|
What part of the dermis are thicker?
|
Reticular
|
|
|
What type of collagen is in the reticular dermis?
|
Type I collagen
|
|
|
What are the types of nerves in the skin?
|
Free nerve endings
Meissner's corpuscle Merkel cell complex Pacinian corpuscle |
|
|
What are the functions of the free nerve endings?
|
Temperature
Pain PUritis |
|
|
What are the functions of the Meissner's corpuscle?
|
Fine touch
|
|
|
What are the functions of the Merkel cell complex?
|
Slow adapting touch
|
|
|
What are the functions of the Pacinian corpuscle?
|
Deep pressure
Vibration |
|
|
Where are Meissner's corpuscles located in high concentrations?
|
Fingertips, etc.
|
|
|
What do pacinian corpuscles look like?
|
ONIONS!
|

