![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 3 functions of joints and describe them?
|
Synarthroses = immovable
Ampharthroses= slighty movable Diarthroses = freely movable |
|
|
What are the 3 types joints and there characteristics?
|
1)Fibrous- fixed or limited movement
2)Cartilagenous- limited movement 3) Synovial- freely moveable, filled with fluid |
|
|
What are 3 types of Fibrous joints and examples of each?
|
1)Sutures- joints in skull
2)Gomphosis- teeth to maxillae or mandible 3)Syndemosis- fibrous joint connecting 2 bones(ex.radius/ulna) |
|
|
What are the 2 types of Cartilagenous joints and examples of each?
|
1)Synchrondoses- connected by hyaline cartilage(ex. epiphyses and diaphysis, rib and sternum)
2)Symphyses- connected by fibrous cartilage (ex. pubic bones, vertebral disks) |
|
|
What are the 4 types of synovial joints and there functions?
|
1)Uniaxial joints- permit movement in one plane
2)Biaxial joints- permit movement in two planes 3)Multiaxial joints- permit movement in 3 ore more planes 4)Nonaxial joints- do not move around an axis |
|
|
What are the 2 types of Uniaxial joints and examples?
|
1)Hinge joint - elbow
2)Pivot joint - axis/atlas |
|
|
What are the 2 types of Biaxial joints and examples?
|
1)Saddle joints - thumb
2)Condyloid joints - atlantoocipital |
|
|
What is a type of Multiaxial joints and example?
|
Ball and socket joints
Ex. hip and shoulder |
|
|
What is a type of Nonaxial joint and example?
|
Gliding joints
Ex. between anterior surfaces of vertebrae |
|
|
Flexion and Extensions?
|
Flexion - decreases angle between bones
Extension - increases angle between bones |
|
|
Adduction and Abduction?
|
Adduction - toward the median plane
Abduction - away from the median plane |
|
|
Inversion and Eversion?
|
Inversion - sole of foot inward
Eversion - sole of foot outward |
|
|
Protraction and Retraction?
|
Protraction - pushing a part outward
Retraction - moving a part back |
|
|
Rotation and Circumduction?
|
Rotation -pivoting on the axis of a bone
Circumduction - distal end moves in a circle (ex. pitchers wind up) |
|
|
Depression and Elevation?
|
Depression - moving a part downward
Elevation - moving a part up |
|
|
Tendons, Ligaments, and Aponeuroses?
|
Tendons - muscles to bone
Ligamants - bone to bone Aponeuroses - muscle to muscle (broad sheets) |
|
|
What are points of attachment in muscles and there functions?
|
Origin - doesnt move when the muscles contract (often proximal to the insertion)
Insertion - moves when the muscle contract |
|
|
What are the functions and characteristics of a muscle?
|
Functions - movement, maintenance of posture, and heat production
Characteristics - excitability, contractility, extensibility, and elasticity |
|
|
What causes movement of the muscle?
|
Contraction of the belly of the muscle, generally proximal to the moved part.
|
|
|
How does movement occur in the muscle?
|
Contraction of the sacromeres within the sacroplasm of the muscle cells.
|
|
|
What is a sacromere composed of?
|
myosin and actin fibers arranged in a formation
|
|
|
What is a sarcolemma?
|
A muscle cell membrane
|
|
|
What does myoglobin bind?
|
binds oxygen-protein present in myofibers
|
|
|
What is the sliding mechanism of a muscle contraction and its action?
|
Neuromuscular junction - acetyl choline released from the motor neuron axon onto muscle fibers = activation
(Neuron + fibers = motor unit) |
|
|
What is a threshold?
|
Smallest stimulus which can stimulate action potential (action potentials are all or none, not graded)
|
|
|
Increasing muscular contraction is due to what?
|
due to recruitment of motor units
|
|
|
What are the differences between red and white muscle fibers?
|
Red- more myoglobin(stores ATP), thinner, more mitocondria, more blood capillaries, slow twitch(Type1), slow fatique (neck postural)
White - less myoglobin, thicker, fewer mitochondria, fewer capillaries, fast twitch (type IIB), fast fatique(arm strength) |
|
|
Name the 4 muscle act and there functions?
|
Prime Mover- directly performs the function
Antagonists- opposes the action of the prime mover when contracting Synergists- facilitate the action of the prime mover Fixators- joint stabilizers |
|
|
How are muscles named?
|
location, function, shape, direction of the fibers, number of heads, points of attachment, and action
|
|
|
What are the names of the muscles with 2, 3, and 4 heads or bellies?
|
biceps, triceps, and quadriceps
|
|
|
What are the different directions of fibers?
|
transverse, rectus, oblique, and orbicularis
|
|
|
What are the different shapes of muscles?
|
deltoid (triangle) and trapezoid
|
|
|
What are attachments of muscles for facial expressions?
|
1 point of attachment is to deep layers of the skin
(doesn't have orgin and insertion, only ONE) |
|
|
What is the Origin/Insertion and action of Orbicularis Oculi?
|
Circular muscles attached to the skin around the eye
OI - skin around eye (occipital bone) A - opens and closes eye |
|
|
What is the Origin/Insertion and action of Orbicularis Oris?
|
OI - skin around lips
A - closes lips (kissing muscle) |
|
|
What is the Origin/Insertion and action of the Zygomatic major?
|
OI - Corners of mouth
A - smiling |
|
|
What is the Origin/Insertion and action of Occipitofrontalis?
|
OI - skin over frontal bone
A - raises eyebrows |
|
|
What are the 2 muscles that close the jaw? Name there origin, insertion, and action?
|
Masster:
O - Maxillae I - Mandible A - closes jaw Temporalis: O - Parietal bone I - Mandible A - closes jaw |
|
|
Name the muscle that moves the head and its origin, insertion, and action?
|
Sternocleidomastoid:
O - sternum and clavicle I - mastoid process A - flex head |
|
|
Name the 3 muscles of breathing (Thorax) and there Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
External intercoastal muscles:
O - Rib I - Rib below A - Voluntary Inspiration (elevates ribs) Internal intercoastal muscle: O - Rib I - Rib above A - Voluntary Expiration (depresses ribs) Diaphragm: A - Involuntary respiration and inspiration |
|
|
What is the only muscle nescessary for life?
|
Diaphragm
|
|
|
Name the 4 muscle of the abdominal wall and there Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
External Oblique:
O - Ribs I - Oscoxae Internal Oblique: O - Oscoxae I - Ribs Rectus Abdominus: (Antagonist of diaphragm) O - Oscoxae I - Ribs Tranverse Abdominus: O - Oscoxae I - Ribs All have the same Action - straining, flex trunk, rotate trunk |
|
|
Name the muscle of the pelvic floor and its Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
Levator ani:
O - Pubic bone and Ischium I - Sacrum and Coccyx A - Support |
|
|
Name the muscles of the back and there Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
Trapezius:
O - occipital bone and Vertabrae I - scapula and clavicle A - either extends head or raises shoulders (shrugs) Latissimus Dorsi: O - Oscoxae and Lower Vertebrae I - Humerus A - Adduct arms posteriorly |
|
|
Name the Muscles of the Lower Leg and there Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
Tibialia Anterior:
O - Tibia I - Tarsal A - dorsiflex foot (Posterior) Gastrocnemius: o - Tibia I - Tarsal bones A - Flex foot (Posterior) Soleus: O - Fibula I - Tarsal bones A - Flex foot **last 2 are important for walking and jumping |
|
|
Name the 2 muscles of the chest and there Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
Pectoralis Major:
O - sternum, clavicle, ribs I - ribs A - adducts arms anteriorly Serratus Anterior: O - Ribs I - Scapula A - pulls scapula forward and rotates the shoulder as in punching |
|
|
Name the muscle of the shoulder and its Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
Deltoid: (Triangular shape)
O - Scapula and Clavicle I - Humerus A - Abduct/raise arm and shoulder |
|
|
Name the 3 muscles of the upper arm and there Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
Triceps brachii:
O - Scapula and Humerous I - Ulna A - Extends arms Biceps Brachii: O - Scapula I - Radius A - Flex and supinate Brachialis: O - Humerous I - Ulna A - flex and pronate |
|
|
Name the 2 muscles of the forearm and there Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
Flexor carpi:
O - humerus or ulna I - carpals or metacarpals A - flexes hand Extensor carpi: O - humerus or ulna I - carpals or metacarpals A - extends hand (or digitorum?) |
|
|
Name the 4 muscles of the buttock region and there Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
Gluteus minimus:
O - posterior ilium I - femur Gluteus medius: O - Posterior ilium I - femur Gluteus maximus: O - sacrum, coccyx, ilium I - femur **All above have same ACTION - extends thigh and rotates thigh outward Tensor faseia latae: O - ilium I - tibia A - abducts leg |
|
|
Name the 4 muscles of the anterior leg (thigh) and there Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
Main muscle is Quadriceps femoris, divided into 4 muscles.
1. rectus femoris 2. vastus medialis 3. vastus lateralis 4. vastus intermedius **All have same origin, insertion, and action. O - femur/oscoxae I - Tibia A - extends knee and flexes hip |
|
|
Name the 3 muscles of the posterior leg (thigh) and there Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
"Hanstring Group"
1. Semitendinosis 2. Semimembranous 3. Biceps femoris **All have the same origin, insertion, and action. O - ischium and femur I - tibia or fibula A - flex knee/ extend thigh |
|
|
Name the muscles of the medial leg (thigh) and there Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
Gracilis:
O - pubic I - tibia A - adduct leg |
|
|
Name the 3 muscles of the adductor group (thigh) and there Origin, Insertion, and Action?
|
1. Brevis
2. Longus 3. Magnus **all have same origin, insertion, and action O - pubic bone I - medial femur A - adducts thigh |
|
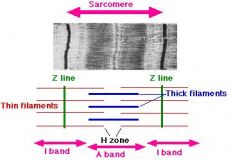
Label the Diagram
|
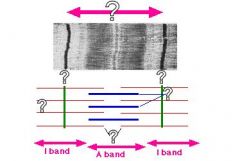
Answers on picture
|
|
|
What are articulations?
|
joints - the point of contact between 2 bones
|
|
|
What are fontanels?
|
"soft spots" where ossification is incomplete at birth (membrane filled spaces between bones of the skull)
|
|
|
What are the layers of Muscle connective tissue?
|
1. Epimysium
2. Perimysium tendon 3. Endomysium |
|
|
What is sacroplasmic reticulum?
|
a network of tubules that contain T-tubules
(perpendicular - running to outside) |

