![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Endochondral bone |
"cartiliage-replacement" bone - |
|
|
Endochondral vs. intramembranous bone |
Chondroblasts, chondrocytes (endochondral) Mesenchymal cells ( intramembranous) Osteoblasts and clasts are in each |
|
|
Chondroblast- chondrocyte become what |
cartilage |
|
|
osteoblast, osteocyte become what |
bone |
|
|
Epiphysis and Diaphysis and medullary cavity
bone structure |
Epiphysis- ends Diaphysis- middle
medullary cavity - inside the diaphysis with the vascular supply
|
|
|
Bone Growth (formation) |
Cartilage model grows , cartilage is calcified, osteoblasts invade and secrete osteiod, osteoid is mineralized into bone, remodeled over and over by osteoblast and osteoclasts |
|
|
Compact Bone |
dense, solid white color |
|
|
cancellous bone (spongy) |
speckled, and porous in the middle of the epiphysis |
|
|
Osteon (osteoid) |
functional unit of bone, type 1 collagen |
|
|
intramembranous bones: |
dont need cartilage to form (stem cells are needed instead) |
|
|
Cartilage - avascular or vasclular? Bone? |
Cartilage - avascular bone - vascular |
|
|
What controls bone growth? |
Endocrine - hormones Growth hormone, and IGF-1 |
|
|
Calcium Homeostasis |
Calcium in the blood in transferred to the bones and then circulated back into the blood. The Parathyroid gland secretes PTH and the thyroid then secretes calcitonin, the intestine absorbs calcium from food and activated Vitamin D increasing Ca absorption. Kidney reabsorb calcium from Urine and the bones get and store the calcium |
|
|
Vitamin D |
Synthesized by the sun and modified in the liver , its activated by the kidneys and promotes more calcium reabsorption |
|
|
Joint Types |
Fibrous- immovable Synovial - highly movable Cartilagenous- slightly movable |
|
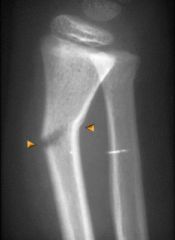
|
Greenstick Fracture |
|
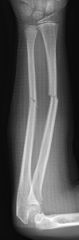
|
Transverse Fracture |
|
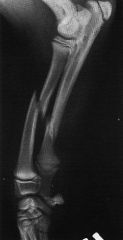
|
Oblique Fracture |
|
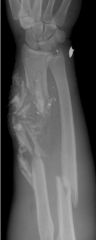
|
Comminuted Fracture |
|
|
How are bones repaired? |
Hematoma forms around the fracture, and then new blood vessels form into the bone and an internal and external callus form bringins osteoblasts to form new bone |
|
|
Muscle Types |
Smooth Cardiac Skeletal |
|
|
Smooth Muscle |
involuntary movement - found in digestive tract, respiratory, urogenital, and cardiovascular lacks striations , usually arranged in sheets, slow and sustained contractions |
|
|
Cardiac Muscle |
involuntary movement, operated heart pump, found in cardiovascular contractions propagated across tissue via the intercalated discs, rapid contractions |
|
|
Skeletal muscle |
voluntary movement moves skeleton eyes face lips - controls swallowing inspiration, expiration
multiple nuclei per cell, each cell stimulated by a nerve branch |
|
|
How does skeletal muscle form? |
Develop from Progenitor cells ( myoblasts) , cells elongate and fuse to form syncitium which is why they have multiple nuclei. and each new muscle cell gets cytoskeletal proteins that allow them to contract. |
|
|
Hierarchical structural org. of skeletal muscle |
muscle cell bound by endomysium are bound again in bundles called fascicles wrapped by epimysium and multiple fascicles are wrapped by perimysium to create a muscle tissue |
|
|
myofiber |
muscle cell |
|
|
myofibril |
makeup the myofiber, contain the sarcomeres
|
|
|
sarcomere |
the unit of contraction in a muscle cell |
|
|
myofilaments |
actin and myosin, inside the sarcomeres - actually do the contraction |
|
|
Triad? |
Three molecules important for muscle contraction -
Sodium Potassium Calcium |
|
|
T Tubule |
Membrane connecting events at the cell membrane to the sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
sarcoplasmic reticulum |
empty area between the cell membrane and the connecting tissue |

