![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which part of the oral cavity is the vestibule? |
The area bounded by the lips, cheeks and teeth |
|
|
What part of the oral cavity is the oral cavity proper? |
The area inside the mouth behind the teeth |
|
|
What are the fauces? |
The arches/folds near the back of the mouth that lead to the pharynx. eg. The palatoglossal fold and the palatopharyngeal fold (posterior fauces) |
|
|
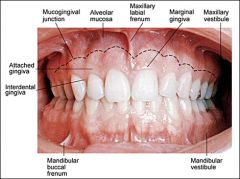
Where is the free gingiva? |
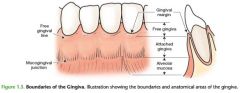
The gingiva that lies unattached at the neck of the tooth. |
|
|
Where is the attached gingiva? |
The gingiva that is bound to underlying cementum and the alveolar bone (bone which surrounds the roots of the teeth) |
|
|
What is the mucogingival junction? |
This junction/line separates the attached gingiva from the alveolar mucosa |
|
|
What are interdental papilla? |
It is the part of the gingiva which fills the spaces inbetween adjacent teeth |
|
|
What is the labial frenulum? |
It is the vertical band of oral mucosa that attaches the lips to the alveolar mucosa on both the maxilla and the mandible arch. |
|
|
What is the pterygomandibular raphe? |
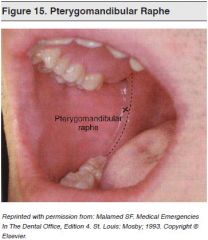
It is the ridge that extends from the upper to lower alveolus (between back molars) |
|
|
What is the palatoglossal fold? |
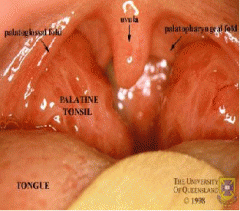
It is the anterior pillar of fauces that covers the palatoglossus and palatopharyngeus muscles. |
|
|
What is the palatopharyngeal fold? |
The posterior pillar of the fauces which also covers the palatoglossus and palatopharyngeus muscles. |
|
|
What is the uvula? |
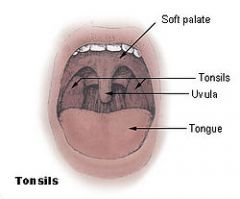
A soft tissue projection |
|
|
Where is the palatine tonsil? |
It sits inbetween the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal folds. |
|
|
Where and what is the Parotid Papilla? |
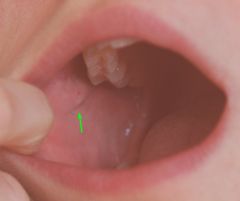
It is by the 2nd molar. The papilla is the raised area and the parotid duct is the dot/small hole. |
|
|
What are the Fordyce spots?~ |
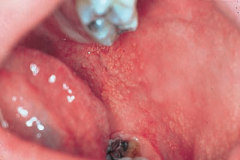
Tiny white spots (sebacious glands) on the inside of the cheeks and lips. |
|
|
What is the incisive papilla? |
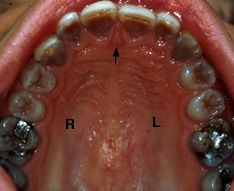
It is a slight bulge/projection on the hard palate near the incisors inbetween the rugae. |
|
|
What is the palatal rugae? |
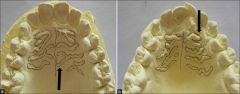
The rough ridges on the side of the palate. |
|
|
What is the palatal raphe? |
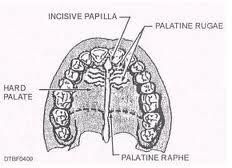
The midline of the hard palate |
|
|
What is the palatal torus?~ |
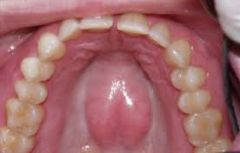
The big lump/raised area in the midline |
|
|
What is the lingual frenulum? |
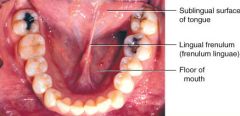
The vertical band of oral mucosa that attaches lips to the alveolar mucosa of the mandibular arch |
|
|
What is the sublingual papillae? |
They are openings on the sublingual glands under the tongue, either side of the lingual frenulum |
|
|
What are the sublingual folds? |
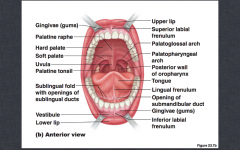
The entire part of the gland that secretes saliva |
|
|
What are the genial tubercles? |
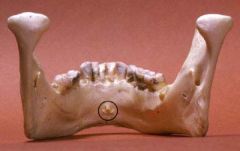
The raised area on the inner surface of the mandible body, muscles attach here. |
|
|
What is the lingual tori? ~ |
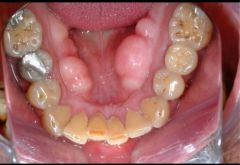
This is the projected bone on the dental arch |
|
|
What are the filiform papillae responsible for and what is their appearance like? |
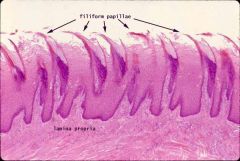
They increase the friction between food and the tongue and are paler dots. NBB// They are not involved in taste. |
|
|
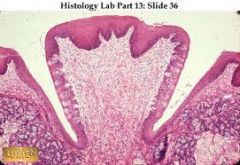
What are the fungiform papillae responsible for and what is their appearance like? |
They are involved in taste and appear as red dots |
|
|
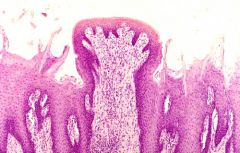
What are the circumvallate papillae responsible for and what is their appearance like? |
They are involved in taste and appear as bigger, raised, red spots on the back of the tongue. |
|
|
What are the foliate papillae responsible for and what is their appearance like? |
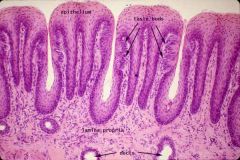
They are involved in taste and are the ridges on the side of the tongue. |
|
|
What and where is the lingual tonsil? |
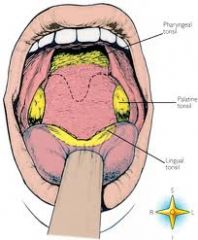
Tonsils stimulate immune response and the lingual tonsil lies on the back of the tongue. |
|
|
What and where are the lingual varicositites? |
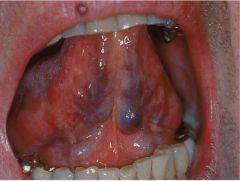
This is where the veins are more dialated, hence look blue underneath the tongue. |
|
|
What is the TMJ? |
The tempromandibular junction/joint
|
|
|
Where is the ascending mandibular ramus? |
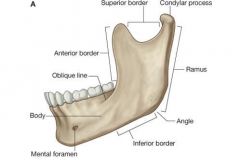
Between the mandible and the TMJ. |

