![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Systemic Anatomy
|
Anatomy of the organ systems
|
|
|
Gross Anatomy
|
Study of the body without dissection or microscope
|
|
|
Histology
|
the study of tissues
|
|
|
Cytology
|
the study of cells
|
|
|
Pathological Anatomy
|
study of disease progression within the body
|
|
|
Palpitation
|
feeling organs or parts to determine size, shape, density, and conditions of parts
|
|
|
Auscultation
|
listening for the sounds of internal organs by ear or stethoscope
|
|
|
Percussion
|
tapping on the surface to determine condition of underlying structure. High sound = air, low sound = fluid
|
|
|
Levels of organization
|
molecule (biochem) => organelles & cells (cytology) => tissues (histology) => organs (anatomy)
|
|
|
Totipotent
|
The ability of a single cell to divide and produce all the differentiated cells in an organism, including extra-embryonic tissues
|
|
|
Pluripotent
|
A stem cell that has the potential to differentiate into any of the three germ layers:
=> Ectoderm => Endoderm => Mesoderm |
|
|
Multipotent
|
Multipotent "progenitor cells" have the potential to give rise to cells from multiple, but a limited number of lineages.
Ex: hematopoietic cell — a blood stem cell can develop into several types of blood cells, but can't develop into brain cells or other types of cells |
|
|
Three germ layers
|
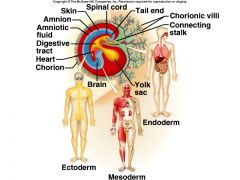
Ectoderm: skin, hair, nerves, spinal chord
Mesoderm: muscles, bones, heart, kidneys, blood, gonads Endoderm: throat to rectum and lungs |
|
|
Coelom
|
Any fluid filled cavity
|
|
|
Prokaryotes
|
Organism with no cell nucleus or membrane bound organelles. Has 4 components necessary for survival:
- DNA - Ribosomes - Cytoplasm - Plasma Membrane |
|
|
Eukaryotes
|
cell whose composed of complex structures enclosed in membranes
|
|
|
Nucleus
|
Holds DNA performs replication and transcription
|
|
|
Nucleolus
|
Ribosomal RNA synthesis and construction of ribosomes
|
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
Packaging of proteins
|
|
|
Golgi Apparatus
|
applies location signal to packaged proteins; production of carbs
|
|
|
Ribosome
|
translates mRNA into proteins - aka protein production
|
|
|
Mitochondria
|
Supplies energy for the cell, ATP produced in cristae
|
|
|
Lysosomes
|
Janitor of the cell, cleans everything up
|
|
|
Cell membrane
|
Phospholipid bilayer with hydrophilic heads on the outside and hydrophobic tails on the inside. Cholesterol helps to maintain integrity and control fluidity of the membrane.
|
|
|
Membrane proteins
|
Serve various functions: signaling receptors, anchors, channels and carriers
|
|
|
Glycocalyx
|
Slimy surrounding area of cellular membrane - aids in cell to cell communication, protection, attachment of cell to extracellular matrix, binding of antigens.
|
|
|
H & E stain
|
Haematoxylin-Eosin: stains bases - pink (cytoplasm & matrix) and acids - blue (nuclei)
|
|
|
Masons Tri-chrome
|
differentiates by staining collagen blue
|
|
|
GMS
|
Gomori-Methanamine silver forms metal deposits, used to identify fungus
|
|
|
Immunocytochemistry
|
secondary antigen that is labeled with flourophore, attaches to primary antigen which attaches to intended molecule of interest
- cheaper |
|
|
Electron Microscope
|
- Transmission - similar to light, image in 2D
- Scanning - image transferred to computer/screen much more detailed and in 3D - Fixation of sample (osmium tetroxide, resin, etc) allows for better handling without degradation |
|
|
Chromatin
|
a complex of DNA and proteins that fills the nucleus
|
|
|
Heterochromatin
|
Tightly packed DNA that is preparing for transcription, usually covers the inner layer of the nucleus
|
|
|
Euchromatin
|
Loosely packed chromatin that is scattered throughout the center of the nucleus
|

