![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
151 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
inervates: second cervical spinal nerve
|
sensory to skin of neck, ear, and back of neck
|
|
|
|
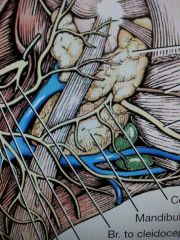
What forms external jugular vein
|
linguofacial and maxillary veins
|
|
|
|
mandibular salivary gland
|
between linguofacial and maxillary veins
|
|
|
|
mandibular lymph nodes
|
on either side of linguofacial vein ventral to salivary gland
|
|
|
|
superficial cervical lymph node
|
under omotransversarius
|
|
|
|
inervates: accessory or 11 cranial nerve
|
motor to trapezius, omotransversarius, cleidocephalicus, and sternocephalicus
|
|
|
|
vagosympathetic nerve trunk
|
with carotid artery
|
|
|
|
medial retropharyngeal lymph node
|
next to carotid sheath opposite larynx
|
|
|
|
location: dorsal intercostal arteries
|
inside body wall from aorta
|

|
|
|
supplies: dorsal intercostal arteries
|
intercostal muscles
|
|
|
|
ventral intercostal branches of internal thoracis artery
|
join with dorsal intercostal arteries on internal surface of body
|
|
|
|
intercostal nerves
|
ventral branch of t1-12 spinal nerves
|

|
|
|
action: lateral thoracic nerve
|
motor to cutaneous trunci
|
|
|
|
axillary lymph nodes
|
dorsal to deep pectoral in axilla
|
|
|
|
location: cranial epigastric artery
|
between costal arch and sternum deep to rectus abdominus. terminal end of internal thoracic artery
|
|
|
|
location: cranial superficial epigastric artery
|
branch of cranial epigastric artery that goes through rectus abdominus
|
|
|
|
supplies: cranial superficial epigastric artery
|
cranial abdominal mamma
|
|
|
|
supplies: cranial epigastric artery
|
rectus abdominus
|
|
|
|
transversus thoracis muscle
|
deep to internal thoracic muscle
|
|
|
|
pleura over lungs
|
pulmonary/visceral
|
|
|
|
pleura over ribs
|
costal parietal
|
|
|
|
pleura over diaphragm
|
diaphragmatic parietal pleura
|
|
|
|
mediastinal parietal pleura
|
middle of body
|

|
|
|
mediastinum
|
the two mediastinal pleura and the space between them
cranial, middle, dorsal, ventral, and caudal parts (relative to heart) |
|
|
|
pericardial mediastinal pleura
|
mediastinal pleura over heart
|
|
|
|
right caudal partial mediastinal pleura around caudal vena cava
|
plica venae cavae
|
|
|
|
pulmonary ligament
|
between left caudal lobe of lung and mediastinum
|
|
|
|
location: internal thoracic artery
|
from subclavian artery to sternum
|
|
|
|
supply: internal thoracic artery
|
phrenic nerve, thymus and mediastinum
|
|
|
|
musculophrenic artery
|
terminal end of internal thoracic artery with cranial epigastric artery
|
|
|
|
left lung lobes
|
cranial and caudal
|
|
|
|
right lung lobes
|
cranial middle caudal and accessory
|
|
|
|
cardiac notch
|
between cranial and middle right lung lobes
|
|
|
|
principal bronchi
|
where the trachea bifurcates with a carina between them and further bifurcates into lobar bronchi
|

|
|
|
lymph nodes at bifurcation of trachea
|
tracheobronchial lymph nodes
|
|
|
|
aortic impression
|
on left lung where aorta sits
|
|
|
|
thoracic duct
|
lymph system after diaphragm along spinal area
from cisterna chyli in abdomen and right/left tracheal trunk from head |
|
|
|
parts of aorta
|
aortic arch, ascending and descending aorta (thoracic and abdominal)
|
|
|
|
branches off the aorta
|
1st: brachiocephalic trunk
2nd: left subclavian |
|
|
|
branches of the brachiocephalic trunk
|
left/right common carotid and right subclavian
|
|
|
|
branches of the subclavian arteries
|
vertebral: towards head
costocervical trunk: straight down/back superficial cervical: to neck internal thoracic: to sternum |
|
|
|
supply: vertebral arteries
|
cervical muscles and nerves
|
|
|
|
supply: costocervical trunk
|
base of neck, 1-3 intercostal spaces
|
|
|
|
supply: superficial cervical
|
base of neck and scapula region
|
|
|
|
location: bronchoesophageal artery
|
leaves right 5th costal area abd cruises to left into esophagus and then continues into bronchi
|
|
|
|
somatic efferent neurons
|
striated muscle
|
|
|
|
visceral efferent neurons
|
smooth muscle, glands, viscera
|
|
|
|
sympathetic autonomic nervous system
|
preganglionic neurons T1-L5 (thorocolumbar) and releases norephinephtine
|
|
|
|
parasympathetic autonomic nervous system
|
cranial nerves 3,7,9,10
and sacral nerves (craniosacral) and releases acetylcholine |
|
|
|
spinal nerve
|
joined ventral and dorsal root from spine
|
|
|
|
ventral branch of spinal nerve
|
ramus communicans with joins sympathetic trunk made of sympathetic trunk ganglion
|
|
|
|
sympathetic ganglion in neck
|
cranial cervical ganglion
|
|
|
|
first large cranial ganglion in sympathetic trunk
|
cervicothoracic ganglion
|
|
|
|
branch of cervicothoracic ganglion that flows with vertebral artery
|
vertebral nerve
|
|
|
|
branch between cervicothoracic ganglion and next large ganglion
|
ansa subclavia
|
|
|
|
large ganglion after cervicothoracic ganglion
|
middle cervical ganglion
|
|
|
|
branches of middle cervical ganglion that go to heart
|
cardiac nerves
|
|
|
|
recurrent laryngeal nerves
|
left: around arch of aorta up neck
right: around right subclavian and up neck terminate as caudal laryngeal nerves |
|
|
|
branching of vagus nerve
|
ventral/dorsal vagal trunk
|

|
|
|
layers of pericardium (out to in)
|
pericardial mediastinal pleura, fibrous pericardium, parietal serous pericardium
|

to yellow
|
|
|
fibrous pericardium to sternum
|
phrenicopericardial ligament
|
|
|
|
layers of serous pericardium (out to in)
|
parietal serous pericardium, pericardial cavity, visceral serous pericardium
|
|
|
|
surfaces of heart
|
auricular surface (left with auricles)
atrial surface (right with atrium) |
|
|
|
sulcus between atrium and ventricles
|
coronary sulcus
|
|
|
|
sulcus between ventricles
|
paraconal interventricular sulcus (under left auricle)
subsinuosal interventricular sulcus (caudal surface) |
|
|
|
parts of the right atrium
|
sinus venarum and right auricle
|
|
|
|
opening next to caudal vena cava
|
coronary sinus
|
|
|
|
parts of right atrium
|
interatrial septum, intervenous tubercle, fossa ovalis, pectinate muscle (auricle), and crista terminalis (between atrium and auricle)
|

|
|
|
valve between right/left atrium and ventricle
|
right/left atrioventricular valve
parietal and septal cusps attached to papillary muscles via chordae tendineae |
|
|
|
muscle strands of ventricle
|
trabeculae carneae and trabecular septomatginalis (have purkinje fibers)
|
|
|
|
funnel shape of ventricle before pulmonary valve
|
conus arteriosus
|
|
|
|
parts of pulmonary/aortic valve
|
three semilunar cusps with nodules in middle
|
|
|
|
features of left atrium and auricle
|
pectinate muscles and valve of foramen ovale
|
|
|
|
remnants of the ductus arteriosus
|
ligamentum arteriosum
|
|
|
|
expansion of aorta after valve
|
sinus of the aorta
|
|
|
|
arteries supplying heart
|
right coronary artery (in coronary groove)
left coronary artery circumflex branch towards right side paraconal interventricular branch spiral branch (goes in) |
|
|
|
vein that carries blood into coronary sinus
|
great cardiac vein in paraconal interventricular sulcus
|
|
|
|
branches of axillary artery
|
external thoracic, lateral thoracic, subscapular (thoracodorsal and caudal circumflex humeral), cranial circumflex humeral arteries
|

|
|
|
supplies: external thoracic artery
|
superficial pectoral
|
|
|
|
supplies: lateral thoracic artery
|
latissimus dorsi, deep pectoral, cutaneous trunci
|
|
|
|
supplies: subscapular artery
|
scapula
|
|
|
|
supplies: thoracodorsal artery
|
teres major and skin
|
|
|
|
supplies: caudal circumflex humeral artery
|
triceps, deltoideus, coracobrachialis, and infraspinatus and shoulder joint
|
|
|
|
supplies: cranial circumflex humeral artery
|
biceps brachii and joint
|
|
|
|
branches of brachial artery
|
collateral ulnar, superficial brachial (cranial superficial antebrachial) and transverse cubital arteries
|

|
|
|
supplies: collateral ulnar artery
|
triceps and ulnar nerve and elbow
|
|
|
|
supplies: superficial brachial artery
|
dorsum of forepaw
|
|
|
|
supplies: transverse cubital artery
|
elbow and adjacent muscles
|
|
|
|
location/inervation: cranial pectoral nerve
|
into superficial pectoral
|
|
|
|
location: suprascapular nerve
|
between supraspinatus and subscapularis
|
|
|
|
inervation: suprascapular nerve
|
supraspinatus and infraspinatus
|
|
|
|
location/inervation: subscapular nerve
|
subscapularis
|
|
|
|
inervation: musculocutaneous nerve
|
coracobrachialis, biceps and brachialis and skin sensory
|
|
|
|
inervation: axillary nerve
|
teres major, teres minor, deltoideus, and some subscapularis
|
|
|
|
inervation: thoracodorsal nerve
|
latissimus dorsi
|
|
|
|
inervation: radial nerve
|
triceps, tensor fascia antebrachii, and anconeus
deep branch extensor carpi radialis, common/lateral digital extensor, supinator, ulnaris lateralis superficial branch |
|
|
|
inervation: caudal pectoral nerves
|
deep pectoral
|
|
|
|
branches of brachial/median artery
|
common interosseous artery
ulnar artery cranial and caudal interosseous deep antebrachial artery radial artery |
|
|
|
supplies: ulnar artery
|
deep digital flexor and flexor carpi ulnaris
|
|
|
|
supplies: common interosseous and median artery
|
brachii and paw
|
|
|
|
supplies: deep antebrachial artery
|
flexor carpi radialis, deep digital flexor, flexor carpi ulnaris, superficial digital flexor
|
|
|
|
supplies: radial artery
|
deep vessels of forepaw
|
|
|
|
inervation: median nerve
|
pronator teres/quadratus, flexor carpi radialis, superficial/deep digital flexor
|
|
|
|
inervates: ulnar nerve
|
flexor carpi ulnaris and deep digital flexor
dorsal and palmer branch |
|
|
|
cutaneous area
|
area of sensory inervation by nerve
|
|
|
|
autonomous zone
|
area only that nerve supplies with sensory inervation
|
|
|
|
superficial artery branches of paw
|
dorsal or Palmer common digital
|
|
|
|
deep branches of arteries of paw
|
dorsal or Palmer metacarpal
|
|
|
|
external pudendal artery
|
branches to become caudal superficial epigastric artery
|
|
|
|
supply: caudal superficial epigastric artery
|
abdominal mamma, prepuce
|
|
|
|
lymph node in groin area
|
superficial inguinal lymph node
|
|
|
|
supplies: cranial abdominal artery
|
abdominal musculature
|
|
|
|
inervates: L1-4 nerves
|
abdominal wall
|
|
|
|
nerve that runs with external pudendal artery
|
genitofemoral nerve
|
|
|
|
Inervates: genitofemoral nerve
|
cremaster muscle, skin of inner thigh and prepuce
|
|
|
|
spermatic fascia
|
fascia over spermatic cord and continuation of transversalis fascia
|
|
|
|
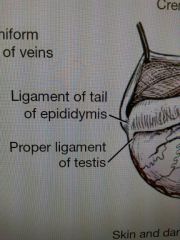
male anatomy terms
|
parietal/visceral vaginal tunic, mesorchium, mesoductus deferens, spermatic cord, ductus deferens, deferent artery and vein, testicular artery and vein (pampiniform plexus), testis, epididymis (ligament of the tail of epididymis and proper ligament of the testis), prostate, urethral crest, colliculus seminalis, penis (root, body, glands), corpus cavernosum, tunica albuginea, ischiocavernosus m., retractor penis m., bulbospongiosus m. (bulb of penis), corpus spongiosum, ischiourethralis m., bulbus glandis, pars longa glandis, os penis (urethral groove)
|
|
|
|
parts of abdominal cavity
|
peritoneal cavity (parietal/visceral peritoneum, connecting peritoneum)
|
|
|
|
falciform ligament
|
round ligament of liver (umbilical vein) and median ligament of the bladder
|
|
|
|
location: caudal epigastric artery
|
inside body wall near bladder coming of femoral artery with external pudendal artery
|
|
|
|
greater omentum
|
superficial and deep leaf (omental bursa between), gastrosplenic ligament, epiploic foreman
|
|
|
|
female reproductive anatomy
|
uterus, cervix, uterine horns, ovary (ovarian bursa), infundibulum (abdominal ostium), mesovarium, mesometrium, mesosalphinx (broad ligaments), round ligament of the uterus, suspensory ligament, proper ligament, vestibule (vestibular bulbs, urethral tubercle), clitoris (glans clitoridis, fossa clitoridis, retractor clitoridis m.), vulva (labia)
|
|
|
|
diaphragm
|
tendinous center, lumber part (crura), sternal part, costal part, cupula (extend into thorax), aortic hiatus, esophageal hiatus, caval foreman
|
|
|
|
liver
|
right lateral, right medial, quadrate, left medial, left lateral, caudate (caudate process w/renal impression, papillary process), hepatic duct
|
|
|
|
gallbladder
|
cystic duct
|
|
|
|
combining of cystic and hepatic duct
|
bile duct
|
|
|
|
path from esophagus to rectum
|
stomach (cardiac, fundus, body, pyloric w/antrum, canal, pylorus), cranial duodenal flexure, descending duodenum, caudal duodenal flexure, ascending duodenum, duodenojejunal flexure, jejunum, ileum, iliocolic orifice, cecum (cecocolic orifice), ascending colon, right colic flexure, transverse colon, left colic flexure, descending colon
|
|
|
|
lymph nodes in mesentery
|
mesenteric lymph nodes
|
|
|
|
pancreas
|
right and left lobe, pancreatic duct (major duodenal papilla) and accessory pancreatic duct (minor duodenal papilla)
|
|
|
|
kidneys
|
hilus, right kidney (more cranial), ureter, renal pelvis, renal sinus, renal cortex, medulla, arcuate branches (renal vessels) renal crest. renal pyramids, pelvis recesses
|
|
|
|
lesser omentum
|
hepatoduodenal ligament
|
|
|
|
mesentery of intestines
|
mesoduodenum, duodenocolic folds (between ascending duodenum and descending colon), mesentery (root of mesentery), mesocolon (w/each part)
|
|
|
|
ligaments between crura and lateral liver lobe
|
right/left triangular ligament between is coronary ligament
|
|
|
|
caudal sympathetic trunk nerves
|
major splanchnic nerve (T12-13), minor splanchnic nerve (T13-L1), lumbar splanchnic nerves (L2-5)
|
|
|
|
abdominal sympathetic ganglion
|
celiacomesenteric plexus (celiac ganglion, cranial mesenteric ganglion), caudal mesenteric ganglion (hypogastric nerves)
|
|
|
|
supply: lumbar artery
|
epaxial muscles, dorsal skin, and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
branches of celiac artery
|
hepatic
hepatic branches (liver) cystic (gall bladder) right gastric(lesser curve stomach) gastroduodenal (pylorus) right gastroepiploic (stomach and omentum) cranial pancreaticoduodenal (right pancreas and duodenum) left gastric (lesser curve stomach) splenic (spleen, stomach, pancreas) short gastric left gastroepiploic |
|
|
|
cranial mesenteric artery
|
middle colic artery(descending colon)
right colic artery (transverse colon) ileocolic artery colic branch (ascending colon) cecal artery (cecum) antimesenteric ileal artery mesenteric ileal branch (ileum) caudal pancreaticoduodenal artery (d. duodenum and right pancreas) jejunal arteries (jejunum) ileal arteries (ileum) |
|
|
|
common trunk
|
caudal phrenic artery (diaphragm)
cranial abdominal (body wall) |
|
|
|
artery to kidney
|
renal artery
|
|
|
|
artery to ovary or testicle
|
ovarian/testicular artery
|
|
|
|
branches of caudal mesenteric artery
|
left colic artery (descending colon)
cranial rectal artery (rectum) |
|
|
|
deep circumference iliac artery
|
caudodorsal abdominal musculature and skin over it
|
|
|
|
portal vein drains
|
intestines, stomach, pancreas, spleen
|
|
|
|
muscles that make the pelvic diaphragm
|
levator ani and coccygeus
|
|
|
|
nerves near prostatic or vaginal artery (inervates)
|
pelvic plexus (sympathetic and parasympathetic)
pelvic nerve (parasympathetic) inervates: urogenital and rectum/descending colon |
|
|

What are 1,2,3,4. (3 not in males)
|
1. pararectal fossa
2. rectogenital pouch 3. vesicogenital pouch 4. pubovesical pouch |
|
|
|
iliac arteries
|
external and internal
|
|
|
|
internal iliac artery branches
|
umbilical artery (fetus)
cranial vesical artery or round ligament of bladder (bladder) caudal gluteal internal pudendal vaginal(prostatic) uterine artery(artery of ductus deferens) caudal vesical artery (bladder) middle rectal (rectum, vagina/ prostate) ventral perineal artery caudal rectal artery (anus, vulva/ scrotum) artery of the penis (clitoris) |
|
|
|
parts of bladder
|
median and lateral (round) ligament, urethral muscle, trigone of the bladder
|
|
|
|
parts of rectum
|
anal canal, paranal sinus (entry into cutaneous zone), external/internal sphincter muscles, rectococcygeus muscle
|
|

