![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Anterior (ventral) |
Toward the front |
|
|
|
Posterior (dorsal) |
Toward the back |
|
|
|
Superior |
Toward the head |
|
|
|
Inferior |
Away from the head |
|
|
|
Medial |
Toward the midline of the body |
|
|
|
Lateral |
Away from the midline of the body |
|
|
|
Proximal |
Toward the attached end of the limb, origin of the structure, or midline of the body |
|
|
|
Distal |
Away from the attached end of the limb, origin of the structure, or midline of the body |
|
|
|
Superficial |
External; located close to or on the body structure |
|
|
|
Deep |
Internal; located further from beneath the body surface than the superficial structures |
|
|
|
Cervical |
Regional term referring to the neck |
|
|
|
Thoracic |
Regional term referring to the portion of the body between the neck and the abdomen; also known as the chest (thorax) |
|
|
|
Lumbar |
Regional term referring to the portion of the back between the abdomen and the pelvis |
|
|
|
Plantar |
The sole or bottom of the feet |
|
|
|
Dorsal |
Top surface of the feet and hands |
|
|
|
Plamar |
Anterior or ventral surface of the of the hands |
|
|
|
Sagittal plane |
A longitudinal line that divides the body or any of its parts into right and left sections |
|
|
|
Frontal plane |
A longitudinal section that divides the body into anterior and posterior parts; lies at right angle to the sagittal plane |
|
|
|
Transverse plane |
Also known as the horizontal plane; an imaginary line that divides the body or any of its parts into superior and inferior sections |
|
|
|
Arthro- |
Joint |
Arthritis: inflammation in a joint |
|
|
Bi- |
Two |
Biceps: 2-headed muscle |
|
|
Brachium |
Arm |
Brachialis: muscle of the arm |
|
|
Cardio |
Heart |
Cardiology: study of the heart |
|
|
Cephalo |
Head |
Cephalic: pertaining to the head |
|
|
Chondro |
Cartilage |
Chondroectomy: excision of a cartilage |
|
|
Costo |
Rib |
Costochondral: pertaining to a rib and it's cartilage |
|
|
Dermo |
Skin |
Dermatitis: inflammation of the skin |
|
|
Hemo, hemat |
Blood |
Hemorrhage: internal or external bleeding |
|
|
Ilio |
Ilium |
Ilium: the wide, upper part of the pelvic bone |
|
|
Myo- |
Muscle |
Myositis: inflammation of a muscle |
|
|
Os, osteo |
Bone |
Osteomalacia: softening of the bone |
|
|
Pulmo |
Lung |
Pulmonary artery: vessel that brings blood to the lungs |
|
|
Thoraco |
Chest |
Thorax: chest |
|
|
Tri |
Three |
Triceps: 3 headed muscle |
|
|
4 structural levels |
System --> organ --> tissue --> cells |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular system |
Made up of blood, blood vessels, and the heart
Heart, arteries, capillaries, veins, back to the heart |
|
|
|
Purpose of CV system |
Together with the respiratory system, the heart and blood vessels deliver oxygen and nutrients to the bodys tissues while removing waste, like CO2 and metabolic by-products |
|
|
|
Arteries and aterioles |
Carry oxygen rich blood away from the heart |
|
|
|
Veins and venules |
Return oxygen poor blood to the heart |
|
|
|
Capillaries |
Provide sites for gas, nutrients, and waste exchange between the blood and tissue |
|
|
|
Major arteries of the body |
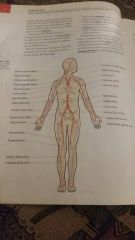
Anterior view |
|
|
|
Major veins of the body: |
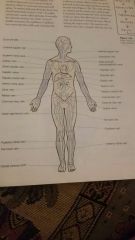
Anterior view |
|
|
|
How does blood flow through the body: |
Heart Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins |
|
|
|
Heart |
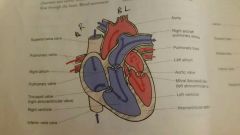
4 chambers and 2 pumps Right 2 chambers are responsible for pulmonary circulation Left 2 chambers are responsible for systemic circulation Separated by the interventricular septum Atria (receiving chambers) to the ventricles (propulsion chambers) to the arteries. Backwards movement of blood is prevented by 4 one way valves |
|
|
|
Pulmonary circuit |
Right side of the heart receives blood that is partially depleted of its oxygen content and contains an elevated level of CO2 after having passed through the cells. Blood is then pushed into the lungs, where it releases it's CO2 in exchange for oxygen |
|
|
|
Systemic circuit |
Left side of the heart receives newly oxygenated blood from the lungs and pump it to various tissues of the body |
|
|
|
Flow of blood through the heart: |
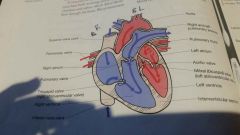
Veins Right atrium Tricuspid valve Right ventricle Pulmonary valve Pulmonary arteries Lungs Pulmonary veins Left atrium Mitral valve Left ventricle Aortic valve Aorta |
|
|
|
Cardiac cycle: |
Period from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next |
|
|
|
Systole |
Contraction phase of the cardiac cycle, during which blood leaves the ventricles |
|
|
|
Diastole |
Relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle, where blood fills the ventricles |
|

