![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
what is the axial skeleton
|
the skull,vertebral column, and bony thorax
-80 bones -form long axis |
what does it include. how many bones.
|
|
|
what are the three categories of bone markings
|
-projections for muscles and ligament attachment
-projections forming joints - depressions/opening gor the passage of vessel, nerves pr muscles |
p p d
|
|
|
the function of skull
|
protection, have foramina for passages for nerves / vessels
|
|
|
|
what joins skull bones
|
joined by sutures- fibrous joint
|
|
|
|
what are the 8 large cranium bones
|
-frontal
- parietal (2) -temporal (2hours) -occipital -sphenoid - ethmoid |
|
|
|
skull bones two division
|
cranium and facial bones
|
|
|
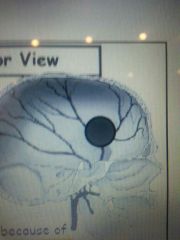
what is this area called?
|
pterion- sensitive arw a that has an underlying middle menial artery - ruptured can cause epidural hematoma
|
|
|
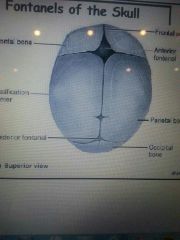
what are the sutures ?
|
frontal suture, anterior fontenel, posterior fontenel
|
|
|
|
role of the skeleton
|
-framework to support body and provides site for muscle attachment (movement)
-protection of organs -contain bone marrow to produce cells -acts as storage ot buffer for minerals |
|
|
|
what are the plans of reference
|
coronal-frontal-cutting body into posterior and anterior
sagittal-longitudinal- cutting body into left and right transverse-horizontal- cutting body into the superior and interior areas of body at waist |
|
|
|
levels of organization
|
chemical :atoms and molecules
cellular: basic cell structures tissue: a group of similar cells working toward a common function organ level: system level: organism: |
|
|
|
define the body cavities
|
cranial, vertebral ,thoracic, abdominal , pelvic
|
|
|
|
characteristics of the epithelial tissue
|
very little extracellular material, cells are close, form the surface lining of almost everything, are avascular, are polarized, have high regeneration capacity,
|
|
|
|
what are the shapes of cells
|
spaumous-can act as barriers because it is quickly regenerates- not many functions for it is small
cuboidal- larger and can fit more and has more functions columnar-can create tough cell tissue , does not regenerate as fast, it is tall and can perform more functions |
|
|
|
which cell shape lines the vessels
|
spaumous
|
|
|
|
which epithelial cell shapes are on the glands
|
cuboidal
|
|
|
|
which epithelial cells shape are used for absorption and secretion
|
columnar
|
|
|
|
function of the connective tissue
|
support and binding, provides protection, defense against infections, insulating, storing fluid-matrix, transports substances, movement
|
|
|
|
characteristics of connective tissue
|
1.has a large extracellular matrix 2. contains fibers like collagen, reticulum and elastic) 3. contains ground substances,defense cells and adipose cells 4. made up of loose,regular and dense. 5. made up of cartilage, bone, and blood
|
|
|
|
what are some specialized connective tissue
|
cartilage, bone, blood
|
|
|
|
what are the three types of cartilage
|
1. hyaline- supports and reinforces
- resilient cushioning -resists compressive stress 2. elastic -more elastic for its made of elastic fibers - flexible buy maintains shape 3. fibrocartilage- greater tensile strength -absorbs compressive shock - less firm then hyaline |
|
|
|
describe collagen
|
strongest and most abundant
also resists tension and contributes to strength of connective tissue |
|
|
|
what are the types of fibers in the matrix of connective tissue
|
collagen, reticular, elastic
|
|
|
|
describe elastic fibers
|
form a branching framework, stretch and recoil, made up of elastin
|
|
|
|
describe reticular fibers in connective tissue
|
short, finer, sponge like networks. creates a network that covers and supports the structures bordering the connective tissue
|
|
|
|
what are the types of muscle tissue
|
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
|
|
|
|
what does muscle tissue do?
|
helps with body movement, by containing muscle fibers that elongate and contract forcefully
|
|
|
|
what does the epithelia tissue do?
|
protects, contains nerves endings, helps with diffusion, secretion, absorption, filters fluid
|
|
|
|
what are the three layers of the skib
|
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis
|
|

