![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
176 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Anatomical position |
The subject stands erect facing the observer , with the head level and the eyes facing forward . The feet are flat on the floor and direct forward , upper limbs area the side with the palms turned forward |
|
|
|
Prone |
Reclining body faced down |
|
|
|
Supine |
Reclining position faced up |
|
|
|
Superior |
Towards the head , or upper part of a structure the |
The heart is superior to the liver |
|
|
Inferior |
Away from the head , or the lower part of the structure |
The stomach is inferior to the Lungs |
|
|
Inferior |
Away from the head , or the lower part of the structure |
The stomach is inferior to the Lungs |
|
|
Anterior |
Nearer to or at the front of the body |
The sternum ( breastbone ) is anterior to the heart |
|
|
Inferior |
Away from the head , or the lower part of the structure |
The stomach is inferior to the Lungs |
|
|
Anterior |
Nearer to or at the front of the body |
The sternum ( breastbone ) is anterior to the heart |
|
|
Posterior |
Nearer to or at the back of the body |
The esophagus is posterior to the trachea ( wind pipe ) |
|
|
Inferior |
Away from the head , or the lower part of the structure |
The stomach is inferior to the Lungs |
|
|
Anterior |
Nearer to or at the front of the body |
The sternum ( breastbone ) is anterior to the heart |
|
|
Posterior |
Nearer to or at the back of the body |
The esophagus is posterior to the trachea ( wind pipe ) |
|
|
Medial |
Nearer to the midline |
The ulna is medial to the radius |
|
|
Lateral |
Farther from the midline |
The lungs are lateral to the heart |
|
|
Intermediate |
Between two structures |
The transverse colon is intermediate to the ascending and descending colons |
|
|
Ipsilateral |
On the same side of the body as another structure |
The gallbladder and ascending colon are ipsilateral |
|
|
What does the head consist of ? |
The skull and face |
|
|
|
Superficial |
Towards or on the surface of the body |
The ribs are superficial to the lungs |
|
|
Deep ( internal ) |
Away from the surface of the body |
The ribs are deep to the skin of the chest and back |
|
|
Planes |
Imaginary flat surfaces that pass through body parts |
|
|
|
Sagittal plane |
A vertical plane that divides the body or organ into right and left sides |
|
|
|
Midsagittal ( median ) plane |
A plane passes through the midline of the body or an organ and divides into equal right and let sides |
|
|
|
Parasagittal plane |
A sagittal plane does not pass through the midline but instead divides the body or a organ into unequal right and left sides |
|
|
|
Frontal ( coronal ) plane |
Divides the body or organ into anterior and posterior portions |
|
|
|
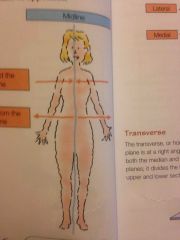
Transverse ( horizontal ) plane |
Divides the body or organ into superior and interior portions |
|
|
|
Oblique plane |
Passes through the body or an organ at an oblique angle (an angel other that 90 degrees angle ) |
|
|
|
Body cavities |
Protect and support internal organs and isolate them from one another |
|
|
|
What does the skull do ? |
Encloses and protects the brain |
|
|
|
What 3 things separate the various body cavities ? |
1. Bones 2. Muscles 3. Ligaments |
|
|
|
Cranial cavity |
Formed by the cranial bones and contains the brain |
|
|
|
Vertebral canal |
Formed by the bones of the vertebral column ( backbone ) which contains the spinal cord |
|
|
|
What are two major cavities of the trunk ? |
The thoracic and abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Thoracic cavity |
Chest cavity , is encircled by the ribs , the muscles of the chest , the sternum ( breastbone ) , and the thoracic portion of vertebral column |
|
|
|
Pericardial cavity |
Containing the heart and two pleural cavities |
|
|
|
Pleural cavities |
Two cavities containing each lung |
|
|
|
Mediastinum |
Located between the lungs and extends from the sternum to the vertebral column and from the first ribs to the diaphragm |
|
|
|
What does the mediastinum |
All thoracic organs except the lungs themselves , the heart , esophagus , trachea , thymus , and several large blood vessels that enter and exit the heart |
|
|
|
What is the face ? |
The front portion of the head that includes the eyes , nose , mouth , forehead , cheeks , and chin |
|
|
|
What does the neck do ? |
Supports the head and attaches it to the trunk |
|
|
|
What does the trunk consist of ? |
The cheat , abdomen , and pelvis |
|
|
|
Upper limbs |
Attached to the trunk and consist of the shoulder , armpit , arm , forearm , wrist and hand |
|
|
|
Lower limbs |
Attached to the trunk and consist of the buttocks , thigh , leg , ankle and foot |
|
|
|
Contralateral |
On the opposite side of the body from another structure |
The ascending and descending colons are Contralateral |
|
|
Proximal |
Nearer to the attachment of a limb to the trunk ; nearer to the origination of a structure |
The humerus is proximal to the radius |
|
|
Distal |
Farther from the attachment of a limb to the trunk : farther from the origination of a structure |
The phalanges are distal to the carpals |
|
|
Superficial |
Towards or on the surface of the body |
The ribs are superficial to the lungs |
|
|
Superficial |
Towards or on the surface of the body |
The ribs are superficial to the lungs |
|
|
Deep ( internal ) |
Away from the surface of the body |
The ribs are deep to the skin of the chest and back |
|
|
Superficial |
Towards or on the surface of the body |
The ribs are superficial to the lungs |
|
|
Deep ( internal ) |
Away from the surface of the body |
The ribs are deep to the skin of the chest and back |
|
|
Planes |
Imaginary flat surface that passes through body parts |
|
|
|
Sagittal plane |
A vertical plane that divides the body or organ into right and left sides |
|
|
|
Sagittal plane |
A vertical plane that divides the body or organ into right and left sides |
|
|
|
Midsagittal ( median ) plane |
A plane passes through the midline of the body or an organ and divides into equal right and left sides |
|
|
|
Sagittal plane |
A vertical plane that divides the body or organ into right and left sides |
|
|
|
Midsagittal ( median ) plane |
A plane passes through the midline of the body or an organ and divides into equal right and left sides |
|
|
|
Parasagittal plane |
Does not pass through the midline but instead divides the body or an organ into unequal right and left sides |
|
|
|
Sagittal plane |
A vertical plane that divides the body or organ into right and left sides |
|
|
|
Midsagittal ( median ) plane |
A plane passes through the midline of the body or an organ and divides into equal right and left sides |
|
|
|
Parasagittal plane |
Does not pass through the midline but instead divides the body or an organ into unequal right and left sides |
|
|
|
Frontal ( coronal ) plane |
Divides the body or organ into anterior and posterior portions |
|
|
|
Transverse ( horizontal ) plane |
Divides the body or organ into superior and inferior portions |
|
|
|
Transverse ( horizontal ) plane |
Divides the body or organ into superior and inferior portions |
|
|
|
Oblique plane |
Passes through the body or an organ at an oblique angle ( an angle other than 90 degrees angle ) |
|
|
|
Transverse ( horizontal ) plane |
Divides the body or organ into superior and inferior portions |
|
|
|
Oblique plane |
Passes through the body or an organ at an oblique angle ( an angle other than 90 degrees angle ) |
|
|
|
Body cavities |
Protects and supports internal organs and isolate them from another |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
A dome shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic cavity |
Subdivided into abdominal and pelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Abdominal cavity |
Contains stomach , spleen , liver , gallbladder , small intestines , and most of large intestines ; the serous membrane of the abdominal cavity is peritoneum |
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Contains urinary bladder , portions of large intestines and internal organs of reproduction |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
A dome shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic cavity |
Subdivided into abdominal and pelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Abdominal cavity |
Contains stomach , spleen , liver , gallbladder , small intestines , and most of large intestines ; the serous membrane of the abdominal cavity is peritoneum |
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Contains urinary bladder , portions of large intestines and internal organs of reproduction |
|
|
|
Viscera |
Organs inside the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
A dome shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic cavity |
Subdivided into abdominal and pelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Abdominal cavity |
Contains stomach , spleen , liver , gallbladder , small intestines , and most of large intestines ; the serous membrane of the abdominal cavity is peritoneum |
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Contains urinary bladder , portions of large intestines and internal organs of reproduction |
|
|
|
Viscera |
Organs inside the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Blood is typically drawn from the antecubital space. Where is this ? |
Front of elbow |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
A dome shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic cavity |
Subdivided into abdominal and pelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Abdominal cavity |
Contains stomach , spleen , liver , gallbladder , small intestines , and most of large intestines ; the serous membrane of the abdominal cavity is peritoneum |
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Contains urinary bladder , portions of large intestines and internal organs of reproduction |
|
|
|
Viscera |
Organs inside the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Blood is typically drawn from the antecubital space. Where is this ? |
Front of elbow |
|
|
|
Is the esophagus anterior or posterior to the trachea |
Posterior |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
A dome shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic cavity |
Subdivided into abdominal and pelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Abdominal cavity |
Contains stomach , spleen , liver , gallbladder , small intestines , and most of large intestines ; the serous membrane of the abdominal cavity is peritoneum |
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Contains urinary bladder , portions of large intestines and internal organs of reproduction |
|
|
|
Viscera |
Organs inside the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Blood is typically drawn from the antecubital space. Where is this ? |
Front of elbow |
|
|
|
Is the esophagus anterior or posterior to the trachea |
Posterior |
|
|
|
Is the urinary bladder medial or lateral to the ascending colon ? |
Medial |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
A dome shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic cavity |
Subdivided into abdominal and pelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Abdominal cavity |
Contains stomach , spleen , liver , gallbladder , small intestines , and most of large intestines ; the serous membrane of the abdominal cavity is peritoneum |
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Contains urinary bladder , portions of large intestines and internal organs of reproduction |
|
|
|
Viscera |
Organs inside the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities |
|
|
|
Blood is typically drawn from the antecubital space. Where is this ? |
Front of elbow |
|
|
|
Is the esophagus anterior or posterior to the trachea |
Posterior |
|
|
|
Is the urinary bladder medial or lateral to the ascending colon ? |
Medial |
|
|
|
Is the radius proximal or distal to the humerus ? |
Distal |
|
|
|
Are the ribs superficial or deep to the lungs ? |
Superficial |
|
|
|
Are the ribs superficial or deep to the lungs ? |
Superficial |
|
|
|
Which directional term can be used to specify the relationship between the elbow and the shoulder ? |
Proximal and distal |
|
|
|
Which directional term can be used to specify the relationship between the left and right shoulder ? |
Medial and lateral |
|
|
|
Which directional term can be used to specify the relationship between the left and right shoulder ? |
Medial and lateral |
|
|
|
Which directional term can be used to specify the relationship between the sternum and the humerus ? |
Medial and lateral |
|
|
|
Which directional term can be used to specify the relationship between the left and right shoulder ? |
Medial and lateral |
|
|
|
Which directional term can be used to specify the relationship between the sternum and the humerus ? |
Medial and lateral |
|
|
|
Which directional term ca. Be used to specify the relationship between the heart and diaphragm |
Superior and inferior |
|
|
|
What is the difference between a plane and a section ? |
Planes are imaginary flat surfaces that pass through various parts of the body ; a section is a cut through a structure along a plane |
|
|
|
The diaphragm separates what two cavities ? |
Thoracic and abdominopelvic |
|
|
|
The diaphragm separates what two cavities ? |
Thoracic and abdominopelvic |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the urinary bladder located ? |
Pelvic cavity |
|
|
|
The diaphragm separates what two cavities ? |
Thoracic and abdominopelvic |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the urinary bladder located ? |
Pelvic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the stomach located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
The diaphragm separates what two cavities ? |
Thoracic and abdominopelvic |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the urinary bladder located ? |
Pelvic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the stomach located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the heart located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
The diaphragm separates what two cavities ? |
Thoracic and abdominopelvic |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the urinary bladder located ? |
Pelvic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the stomach located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the heart located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the lungs located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
The diaphragm separates what two cavities ? |
Thoracic and abdominopelvic |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the urinary bladder located ? |
Pelvic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the stomach located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the heart located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the lungs located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the small intestines located ? |
Abdominal cavity |
|
|
|
The diaphragm separates what two cavities ? |
Thoracic and abdominopelvic |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the urinary bladder located ? |
Pelvic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the stomach located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the heart located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the lungs located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the small intestines located ? |
Abdominal cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the thymus located ? |
Thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the liver located ? |
Abdominal cavity |
|
|
|
In which cavity is the liver located ? |
Abdominal cavity |
|
|
|
What is the name of the cavity that surrounds the heart ? |
Pericardial |
|
|
|
What is the name of the cavity that surrounds the lungs ? |
Pleural |
|
|
|
What organ lies distinctly in both the abdominal and pelvic cavities ? |
Large intestines |
|
|
|
Serous membrane |
The thoracic and abdominal cavity walls and viscera are covered with a thin , slippery "serous membrane" |
|
|
|
Serous membrane |
The thoracic and abdominal cavity walls and viscera are covered with a thin , slippery "serous membrane" |
|
|
|
Right and left hypochondriac region contains ? |
Contains the diaphragm , portions of the kidneys , the right side of the liver , the spleen , and part of the pancreas |
|
|
|
Serous membrane |
The thoracic and abdominal cavity walls and viscera are covered with a thin , slippery "serous membrane" |
|
|
|
Right and left hypochondriac region contains ? |
Contains the diaphragm , portions of the kidneys , the right side of the liver , the spleen , and part of the pancreas |
|
|
|
Epigastric region contains ? |
Most of the pancreas and portions of the stomach , liver , inferior vena cava , abdominal aorta and duodenum |
|
|
|
Right and left lumbar ( lateral ) region contains ? |
Includes portions of the small and large intestines and portions of the kidneys |
|
|
|
Umbilical region contains ? |
Sections of the small and large intestines , inferior vena cava and abdominal aorta |
|
|
|
Right and left lumbar ( lateral ) region contains ? |
Includes portions of the small and large intestines and portions of the kidneys |
|
|
|
Umbilical region contains ? |
Sections of the small and large intestines , inferior vena cava and abdominal aorta |
|
|
|
Right and left iliac ( inquinal ) region contains ? |
Includes portions of the small and large intestines |
|
|
|
Right and left lumbar ( lateral ) region contains ? |
Includes portions of the small and large intestines and portions of the kidneys |
|
|
|
Umbilical region contains ? |
Sections of the small and large intestines , inferior vena cava and abdominal aorta |
|
|
|
Right and left iliac ( inquinal ) region contains ? |
Includes portions of the small and large intestines |
|
|
|
Hypogastric ( pubic ) region contains ? |
Portion of the sigmoid colon , urinary bladder and ureters and portion of the small intestines |
|
|
|
In which abdominopelvic region is most of the liver found ? |
Epigastric |
|
|
|
In which abdominopelvic region is most of the liver found ? |
Epigastric |
|
|
|
In which abdominopelvic region is the transverse colon found |
Umbilical |
|
|
|
In which abdominopelvic region is most of the liver found ? |
Epigastric |
|
|
|
In which abdominopelvic region is the transverse colon found |
Umbilical |
|
|
|
In which abdominopelvic region is the urinary bladder found ? |
Hypogastric |
|
|
|
In which abdominopelvic region is most of the liver found ? |
Epigastric |
|
|
|
In which abdominopelvic region is the transverse colon found |
Umbilical |
|
|
|
In which abdominopelvic region is the urinary bladder found ? |
Hypogastric |
|
|
|
In which abdominopelvic region is the spleen found ? |
Left lumbar |
|
|
|
Dorsal cavity |
Subdivided into the cranial cavity and the vertebral cavity |
|

