![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
144 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
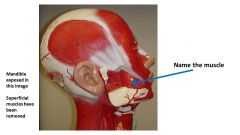
|
Buccinator
|
|
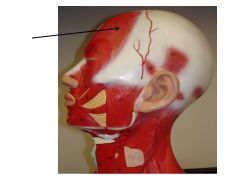
|
Frontalis
|
|
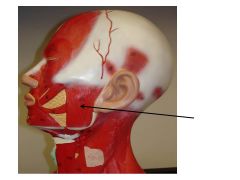
|
Masseter
|
|
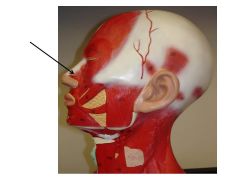
|
Nasalis
|
|
|
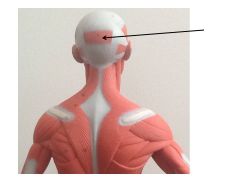
Occipitalis
|
|
|
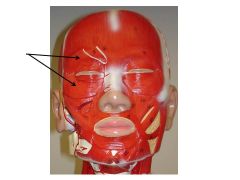
Orbicularis Oculi
|
|
|
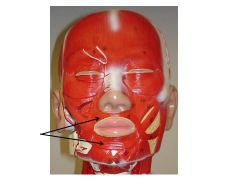
Orbicularis oris
|
|
|
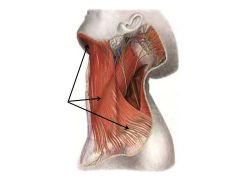
Platysma
|
|
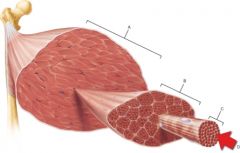
Letter B
|
Single fascicle
|
|
|
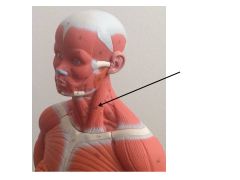
sterno cleido mastoid
|
|
|
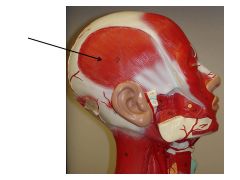
temporalis
|
|
|
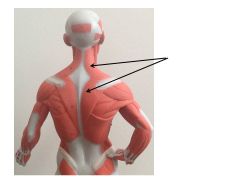
trapezius
|
|
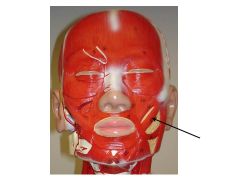
|
Zygomaticus Major
|
|
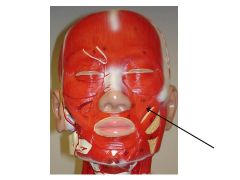
|
Zygomaticus Minor
|
|
|
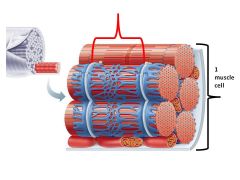
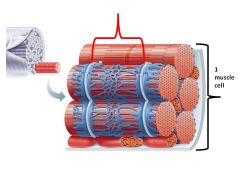
One single muscle cell is known as a
|
muscle fiber
|
|
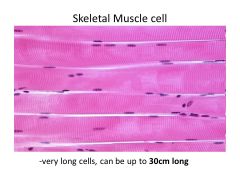
The faint stripes are known as
|
Striations
|
|
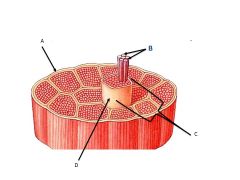
Letter B |
Muscle fibers
|
|
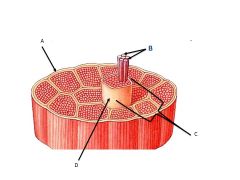
Letter c is pointing to a ______ made up of ______
|
fascicle made up of many muscle fibers
|
|
|
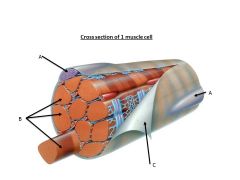
Which of the following surrounds the individual muscle cell?
|
Endomysium
|
|
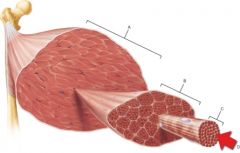
Letter A
|
Tendon
|
|
|
The connective tissue sheaths of skeletal muscle, in order from internal to external, are the _____
|
Endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium.
|
|
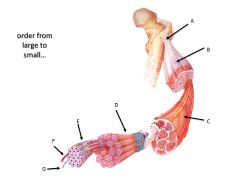
Letter D
|
1 muscle fiber
|
|
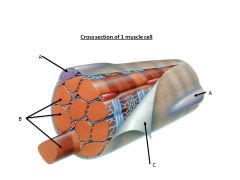
Arrow B
|
Myofibrils
|
|
Letter A, which is man made term for a repeating unit
|
sacromere
|
|
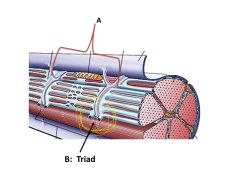
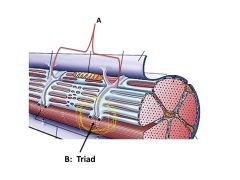
which of the following is NOT a part of the triad?
|
troponin
|
|
|
The major function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum is muscle contraction is to
|
regulate intracellular calcium concentration
|
|
Letter c
|
Sarcolemma
|
|
Area within the red brackets is known as 1
|
sarcomere
|
|
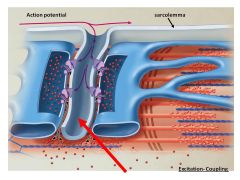
red arrow is pointing to the extension of the sarcolemma, the _______
|
transverse tubule
|
|
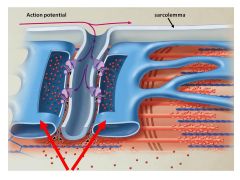
The central T tubule plus the 2 areas at the tip of the 2 red arrows is known as a
|
triad
|
|
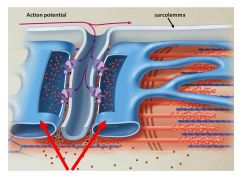
On either side of the T tubule is a ______ of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
|
terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
_______ is a chemical neurotransmitter that is released from the neuron, crosses the synaptic cleft and binds to a specific receptor on the ________
|
acetylcholine, binds to a specific receptor on the sarcolemma
|
|
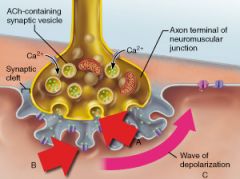
What cellular event is indicated by A?
|
exocytosis
|
|
|
in a neuromuscular junction, synaptic vesciles in the motor neuron contains which neurotransmitter?
|
acetylcholine
|
|
|
When an action potential arrives at the axon terminal of a motor neuron, which ion channels open?
|
voltage-gated calcium channels
|
|
|
What means of membrane transport is used to release the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft?
|
exocytosis
|
|
|
The binding of the neurotransmitter to receptors on the motor end plate causes what to occur?
|
binding of the neurotransmitter causes chemically gated sodium channels to open in the motor end plate and sodium enters the cell
|
|
|
How is acetylcholine removed from the synaptic cleft?
|
simple diffusion away from the synaptic cleft and acetylpholinesterase
|
|
|
The action potential on the muscle cell leads to contraction due to the release of calcium ions. Where are calcium ions store in the muscle cell?
|
terminal cisterns of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
|
|
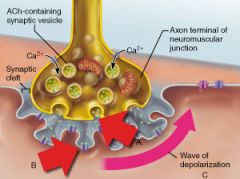
What specific neurotransmitter is released from the axonal terminus as shown in A?
|
Acetylcholine
|
|
|
Which is the next step that happens after the action potential is re-generated on the sarcolemma of the muscle cell?
|
Action potential moves through sarcolemma and then down the T Tubule
|
|
|
As the action potential moves along the T tubule, it causes proteins in the wall of the t tubule to change shape to release _____ from the terminal cisternae
|
Calcium
|
|
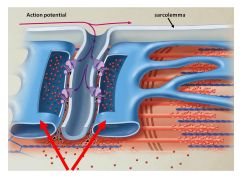
What is being released from these terminal cisternae at either side of the T tubule?
|
Calcium
|
|
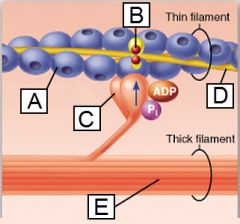
The protein actin is indicated by which letter?
|
A
|
|
|
When the myosin head binds to the actin myofilament, it forms the ____ ______.
|
myosin crossbridge
|
|
|
After calcium is released, which important step occurs next?
|
calcium binds to troponin and causes troponin to change shape
|
|
|
When troponin changes shape, it moves topomyosin and this_______.
|
uncovers the binding sites on actin, allowing myosin to bind to actin
|
|
|
Once the action potential causes calcium to be released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, the acual events that cause contraction occur in a cycle that will repeat over and over until either: Full contraction of the muscle or: stop signaling the muscle to contract. Which is the 1st of the 4 steps of the cross bridge cycle?
|
myosin crossbridge formation
|
|
during a contraction, the sarcomere (in the bracket):
|
shortens in length
|
|
|
The energy molecule, ATP, is responsible for 3 important steps of the sliding filament theory. What are the 3?
|
Energizes the head of the myosin myofilament to allow the "power stroke", is needed to transport calcium back to the terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmis reticulum after contraction, and is required to disconnect myosin from actin.
|
|
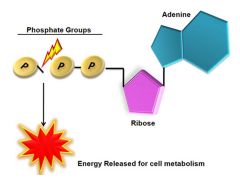
During muscle contraction, TP transfers energy to the myosin head, 1 phosphate group is broken off, leaving:
|
adenosine diphosphate
|
|
|
when a muscle fiber contracts, the first energy source that will be used is:
|
ATP within that muscle fiber
|
|
|
Which of the following is the only carbohydrate that will enter the muscle cell?
|
Glucose
|
|
|
Glycogen is an energy storage molecule found in skeletal muscle, composed of branched chains of
|
glucoswe
|
|
|
here in the human body do we store glycogen?
|
skeletal muscle and the liver
|
|
|
Glycolysis is the breakdwon of glucose which occurs in the _____ of the muscle cell.
|
sarcoplasm
|
|
|
How does a muscle cell produce the majority of ATP?
|
majority of cellular ATP is produced in the organelle, the mitochondria
|
|
|
Which pathway for regenerating ATP provides the majority of the energy used for muscle activity during 30 minutes of light to moderate exercise?
|
aerobic respiration
|
|
|
Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by
|
storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP.
|
|
|
When muscle cells break down glucose to generate ATP under oxygen deficient conditions, they will form _________.
|
Lactic acid
|
|
|
During vigorous exercise, there may be insufficient oxygen available to completely break down pyruvic acid for energy. As a result, the pyruvic avid is converted to ________.
|
lactic acid
|
|
|
Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by ______.
|
storing energy that wil be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP
|
|
|
The 100 meter dash is a quick short run. On completeion of the dash the runners will continue to breathe hard for several seconds to minutes even though they are no longer running. Why?
|
the runners' use of stored oxygen, glucose and creatine phosphate is being replenished and this requires a prolonged increase of oxygen intake.
|
|
|
The oxygen-binding protein found in muscle cells is ______.
|
myoglobin.
|
|
|
After a muscle cell uses all ATP in the cell, it will recreate ATP from ADP by using
|
breakdown of creatine phosphate
|
|
|
What happens during long periods of muscle contraction, when the body cannot supply enough oxygen fast enough? How do the muscle cells produce ATP?
|
anaerobic respiration
|
|
|
Which method or methods of energy production do NOT require oxygen to produce ATP?
|
both glycolysis and creatine phosophate breakdown do not require oxygen
|
|
|
WHat is the purpose or function of myoglobin, a protein found in muscle fibers?
|
storage of extra oxygen
|
|
|
____________________ stores oxygen in the muscle cell
|
Myoglobin
|
|
|
What color is myoglobin?
|
red
|
|
|
Rigor mortis occurs because ___________
|
no ATP is available to release attached actin and myosin molecules.
|
|
|
Muscle tone is ____________
|
a state of sustained partial contraction
|
|
|
botox is used cosmetically to reduce wrinkles on the face and forehead. Regarding muscle contraction, botox will cause ____
|
hypotonia
|
|
|
The force of a muscle contraction is NOT affected by _________.
|
the amount of atp stored in the muscle cell.
|
|
|
In an isotonic contraction, the muscle _______
|
changes in length and moves the "load"
|
|
|
A contraction in which the muscle does not shorten but its tension increases is called
|
isometric contraction
|
|
|
Which of the following statements is most accurate?
|
muscle tension remains relatively constant during isotonic contraction.
|
|
|
during _________, the energy used appears as movement.
|
isometric contractions
|
|
|
In which type of contraction will tension reach maximum, but the muscle does not shorten or lengthen?
|
isometric
|
|
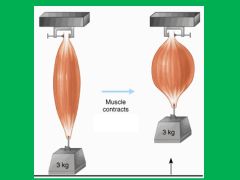
which type of muscle is seen in this image?
|
concentric muscle contraction
|
|
|
During concentric muscle contraction, ___________
|
muscle tension will increase, load will remain constant.
|
|
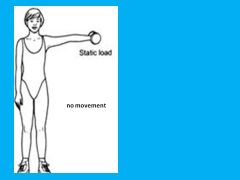
Which type of contraction is seen in the image below?
|
Isometric
|
|
|
_____________ are important contractions that allow humans to hold their posture over time.
|
Isometric contractions
|
|
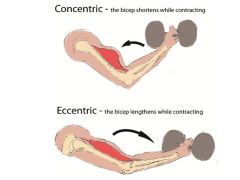
Both contraction types shown in the image below are:
|
isotonic
|
|
|
in a _______________ type contraction, the muscle shortens as it contracts
|
isotonic - concentric
|
|
|
What is the primary purpose of an eccentric contraction?
|
to stabilize the joint and to provide controlled resisistance to gravity during an extension
|
|
|
A muscle that is lengthening while it produces tension is performing a _____________ contraction
|
eccentric
|
|
|
Slow oxidative muscle fibers are best suited for ___________
|
running a marathon
|
|
|
Slow or fast: Depends on oxygen delivery and aerobic mechanisms
|
slow
|
|
|
Slow or fast: have very fast-acting myosin ATPases and depend upon anaerobic metabolism during contraction |
fast
|
|
|
slow or fast: red fiberes, the smallest of the fiber types
|
slow
|
|
|
slow or fast: contains abundant amounts of glycogen
|
fast
|
|
|
slow or fast: abundant in muscles used to maintain psoture
|
slow
|
|
|
slow or fast: a relatively high percentage are found in successful marathon runners
|
slow
|
|
|
The occipitalis muscle was named due to
|
location
|
|
|
a muscle that was named due to its action
|
the adductors or pronator teres
|
|
|
The transversalis was named due to direction of fibers that run
|
side to side
|
|
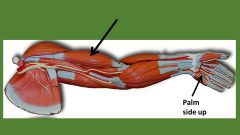
|
biceps bracchii
|
|
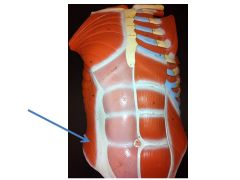
|
external oblique muscles. named after direction of fibers.
|
|
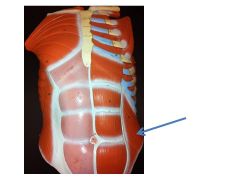
|
internal oblique
|
|
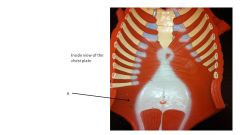
|
transversalis muscle
|
|
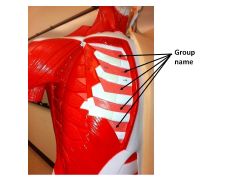
|
intercostals
|
|
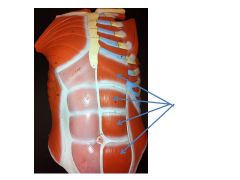
|
rectus abdominis
|
|
|
The ________ of the right and left external oblique connects the 2 muscles at the center and will fuse with the linea alba.
|
aponeurosis
|
|
|
Which abdominal muscle is most superficial?
|
external oblique
|
|
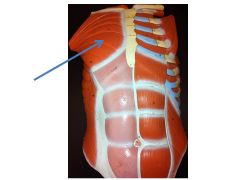
|
pectoralis major
|
|
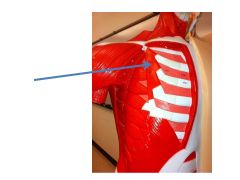
|
pectoralis minor
|
|
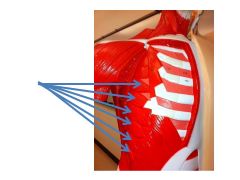
|
serratus anterior
|
|
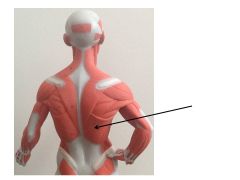
|
latissimus dorsi
|
|
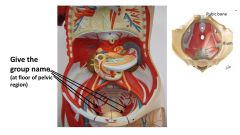
|
levator ani
|
|
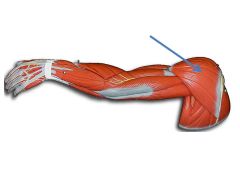
|
Deltoid
|
|
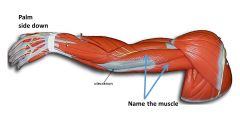
|
triceps brachii |
|
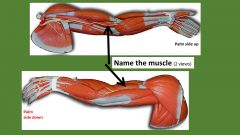
|
Brachialis
|
|
|
which arm muscle flips the hand over?
|
pronator teres
|
|
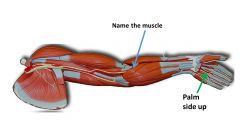
|
pronator teres
|
|
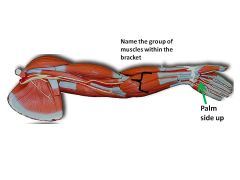
|
flexor carpi
|
|
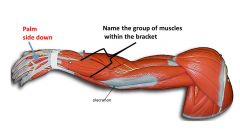
|
extensor carpi
|
|
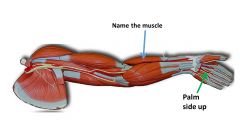
|
brachioradialis
|
|
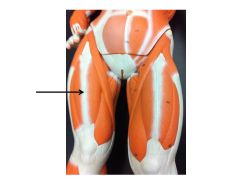
|
rectus femoris
|
|
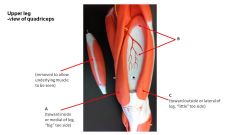
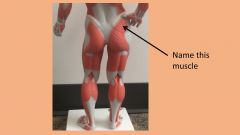
name letter b
|
vastus intermedius
|
|
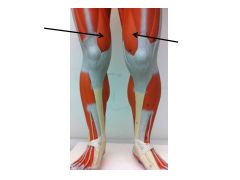
|
vastus medialis
|
|
|
which thigh muscle would be found on the inner side of the anterior thigh?
|
vastus medialis
|
|
|
Which thigh muscle would be found on the outer edge of the anterior thigh?
|
vastus lateralis
|
|
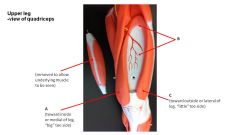
name C
|
Vastus Lateralis
|
|
|
tensus fasciae latae
|
|
|
sartorius
|
|
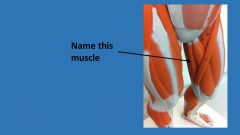
|
gracilis
|
|
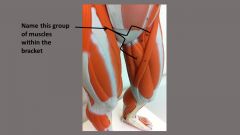
|
adductors
|
|
|
gluteus maximus
|
|
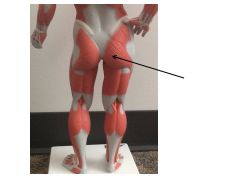
|
gluteus medius
|
|
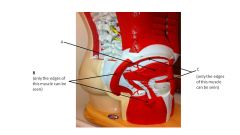
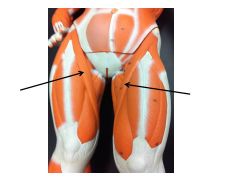
name C
|
gluteus medius
|
|
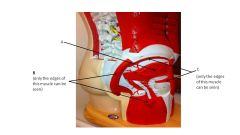
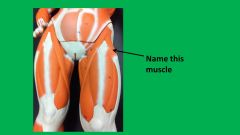
Name A
|
gluteus minimus
|
|
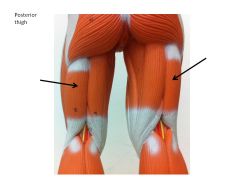
|
biceps femoris
|
|
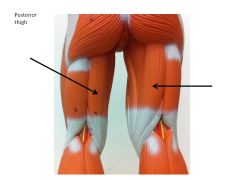
|
semi tendinosus
|
|
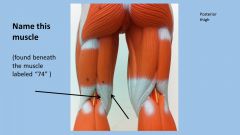
|
semi membranosus
|
|
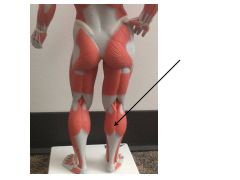
|
gastrocnemius
|
|
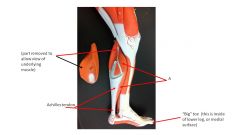
|
soleus
|
|
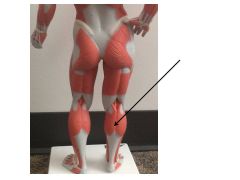
|
gastrocnemius
|
|
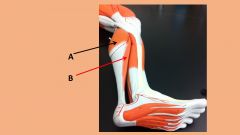
Letter B
|
Soleus
|
|
|
Which 2 muscles insert into the Calcaneus bone via the Achilles tendon?
|
Gastrocnemius and soleus
|
|
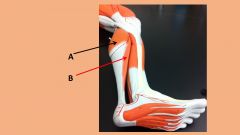
Which muscle is an antagonist to the 2 muscles shown below?
|
Tibialis Anterior
|
|
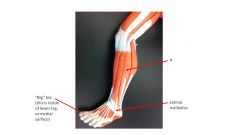
Letter A
|
Fibularis Longus
|
|
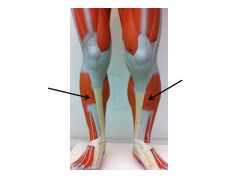
|
Tibialis Anterior
|
|
|
|
|

