![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the denticulate ligament |
Specializations of pia mater. Form longitudinal shelf separating the dorsal and ventral rootlets, suspending the spinal cord in the subarachnoid space. |
|
|
What does the conus medullaris give origin to |
Cauda equina. Conus medullarus is located at L2, most of cauda equina originate here. L2= solid spinal cord done, therefore L4 safe for spinal tap S2= end of dura and subarachnoid |
|
|
A neuron with a cell body in the dorsal root ganglia could convey what type of fibers? |
Sensory to skin overlying back. DRG carry somatic sensory neurons NOT motor. Motor neurons have cell bodies in the ventral horn of the spinal cord, leave through ventral root, join a spinal nerve, then divide into ventral and dorsal rami. |
|
|
Cranial Nerves that exit jugulr foramen |
IX, X, XI |
|
|
What is another name for the anterior condylar canal |
hypoglossal canal, lies just anterior to the occipital condyle |
|
|
What direction does the superior rectus pull the eyeball |
Upwards and inwards Need inferior oblique to pull upwards and outwards |
|
|
Why does a cut in the scalp bleed so profusely |
Vessels are held open by CT under the skin They bleed from both ends of vessel because of anastomosis |
|
|
What arteries supply the scalp |
External carotid: occipital, posterior auricular, superficial temporal Internal carotid: opthalmic (supra-orbital and supratrochlear) |
|
|
Muscles (plus innervation) that originate at the styloid process |
Styloglossus (XII) Stylopharyngeus (IX) Stylohyoid (VII) |
|
|
Pressure generally causes bone reabsorption, what is the exception |
Alveolar bone, mastication |
|
|
Constrictor muscle that is a complete sphincter, only opens during swallowing |
cricopharyngeus part of inferior constrictor Innervated by RLN (X) |
|
|
What supplies the frontal, parietal, and medial portions of the temporal lobes |
Middle Cerebral artery |
|
|
What supplies the medial and superior surfaces of the brain |
Anterior Cerebral artery |
|
|
What supplies the inferior surface of the brain and the occipital pole |
Posterior Cerebral artery |
|
|
What supplies the dura |
middle meningeal artery |
|
|
What drains the deep cerebrum, including the junction of the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli |
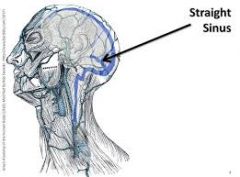
Straight sinus |
|
|
What nerve does sensory innervation to the skin of the ear, external auditory meatus, and TMJ |
Trigeminal V3, auriculotemporal branch |
|
|
Innervation of lower eyelid and upper lip |
Trigeminal V3, infraorbital branch |
|
|
What nerve travels through the parotid gland |
VII |
|
|
What muscle serves to dampen the vibrations of the tympanic membrane, quieting sounds |
Stapedius VII innervation |

